Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on August 12, 2025
Overview
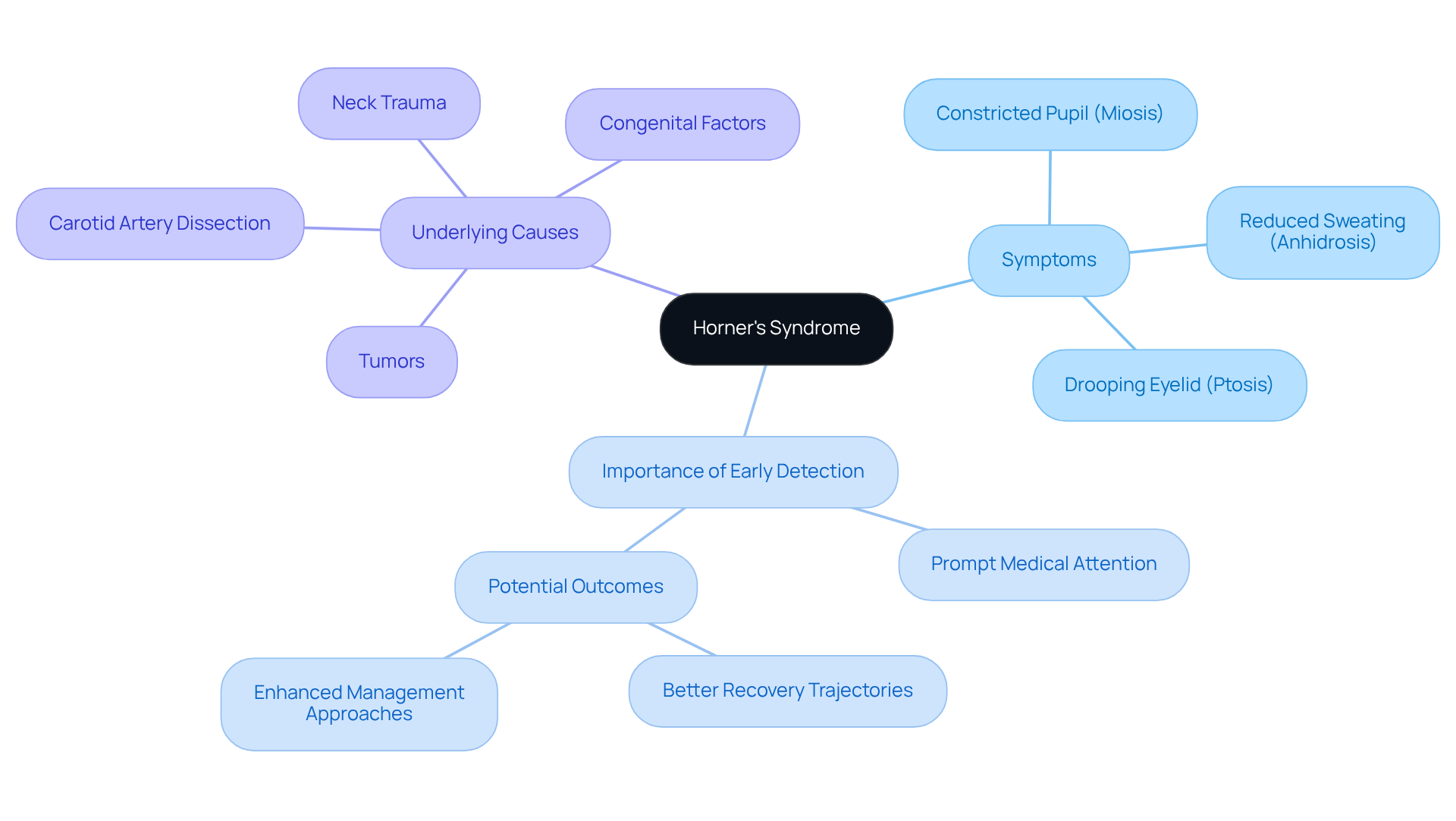
Horner’s Syndrome can be concerning, and it’s important to recognize its key symptoms:
- Drooping eyelids (ptosis)
- Unequal pupil sizes (miosis)
- Decreased sweating on one side of the face (anhidrosis)
These signs typically indicate underlying nerve damage, and we understand that noticing these changes can be unsettling.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention. They can signal more serious health issues, which makes prompt medical evaluation essential for effective treatment. We are here to help you through this process and provide the support you need.
Introduction
Recognizing the symptoms of Horner’s Syndrome is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. However, we understand that many individuals may remain unaware of the key indicators that can signal this rare condition. From drooping eyelids to constricted pupils and unusual facial flushing, these signs might seem innocuous but can point to serious underlying health issues. It’s common to feel uncertain about differentiating between benign symptoms and those that warrant immediate medical attention.
This article delves into the ten critical symptoms of Horner’s Syndrome, empowering you to identify potential warning signs and seek the necessary care. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you feel supported and informed every step of the way.
Northwest Eye: Expert Diagnosis of Horner’s Syndrome Symptoms
At Northwest Eye, we understand that navigating a diagnosis of Horner’s Syndrome can be concerning. This rare condition affects the . With over 50 years of experience in eye care, our specialists are here to help you. We utilize , including imaging tests like MRIs and CT scans, to accurately identify signs and underlying causes.
Common consist of:
- (ptosis)
- Unequal pupil sizes
- Decreased sweating on one side of the face
It’s important to note that Horner’s Syndrome symptoms usually affect just one side, which can lead to noticeable asymmetry. We recognize that these , especially since drooping eyelids may also be associated with other like . This highlights the importance of seeking expert assistance if you notice any troubling indicators.
While Horner’s Syndrome itself typically does not lead to major health or vision problems, it can signal more . Therefore, to determine the appropriate treatment. Our commitment to using the latest advancements in diagnostic methods means that you will receive a , enhancing your overall care experience.
If you are showing signs of Horner’s condition, we encourage you to consult a healthcare professional promptly for assessment. We are here to support you through this process and ensure you receive the care you need.
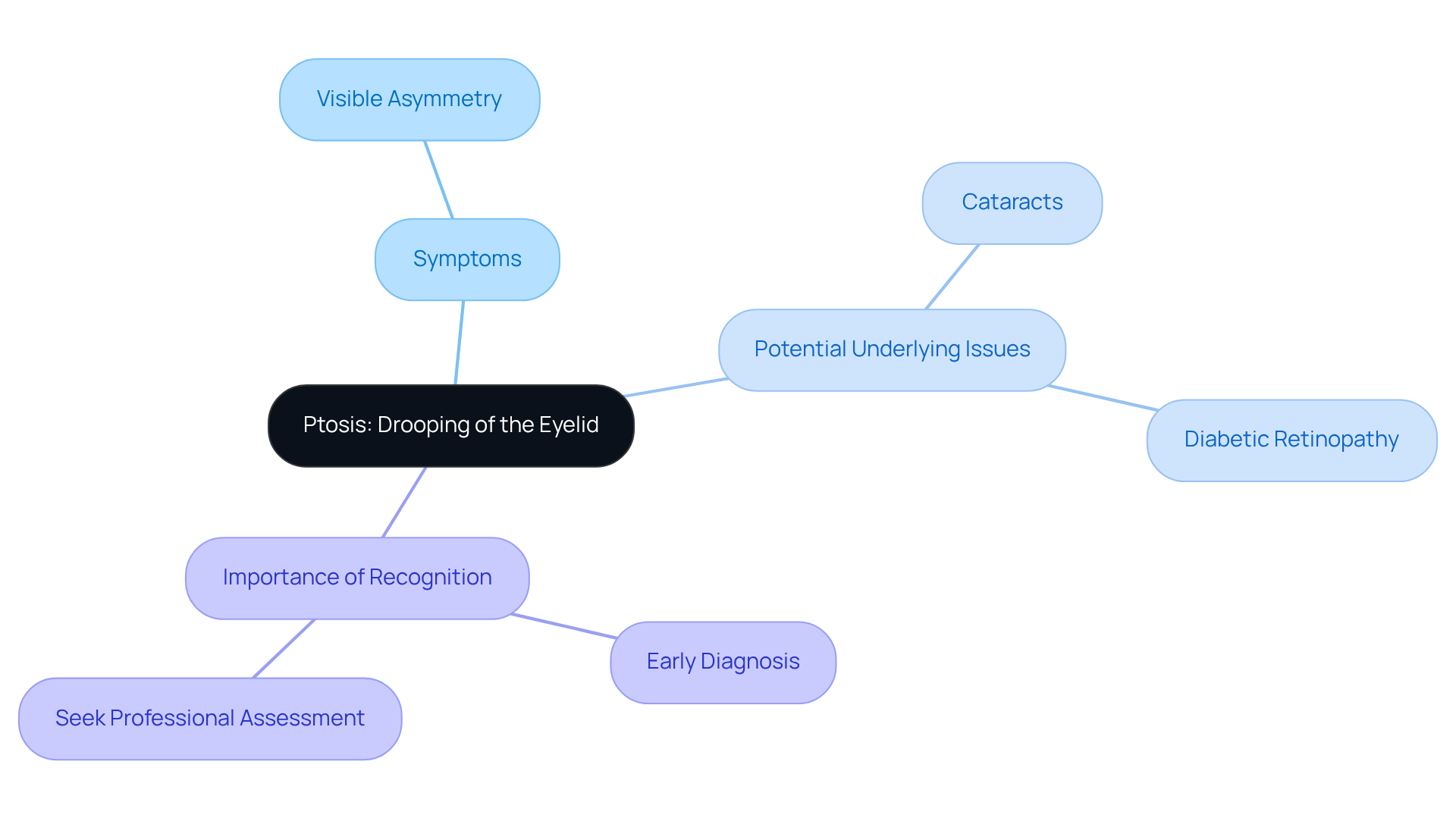
Ptosis: Drooping of the Eyelid as a Key Indicator
refers to the drooping of the upper eyelid, and it’s important to understand that this can be a significant indicator of . We recognize that noticing one eyelid appearing lower than the other can be concerning, often leading to . It’s common to feel anxious about these changes, and we want to reassure you that is crucial for .
This condition may signal underlying issues such as or , which is why understanding these indicators is so vital. We encourage you to pursue a from a physician or eye care expert. They can provide the appropriate treatment and care you need. Remember, we are here to help you through this process and ensure you receive the support you deserve.
Miosis: Constricted Pupil Signaling Potential Issues
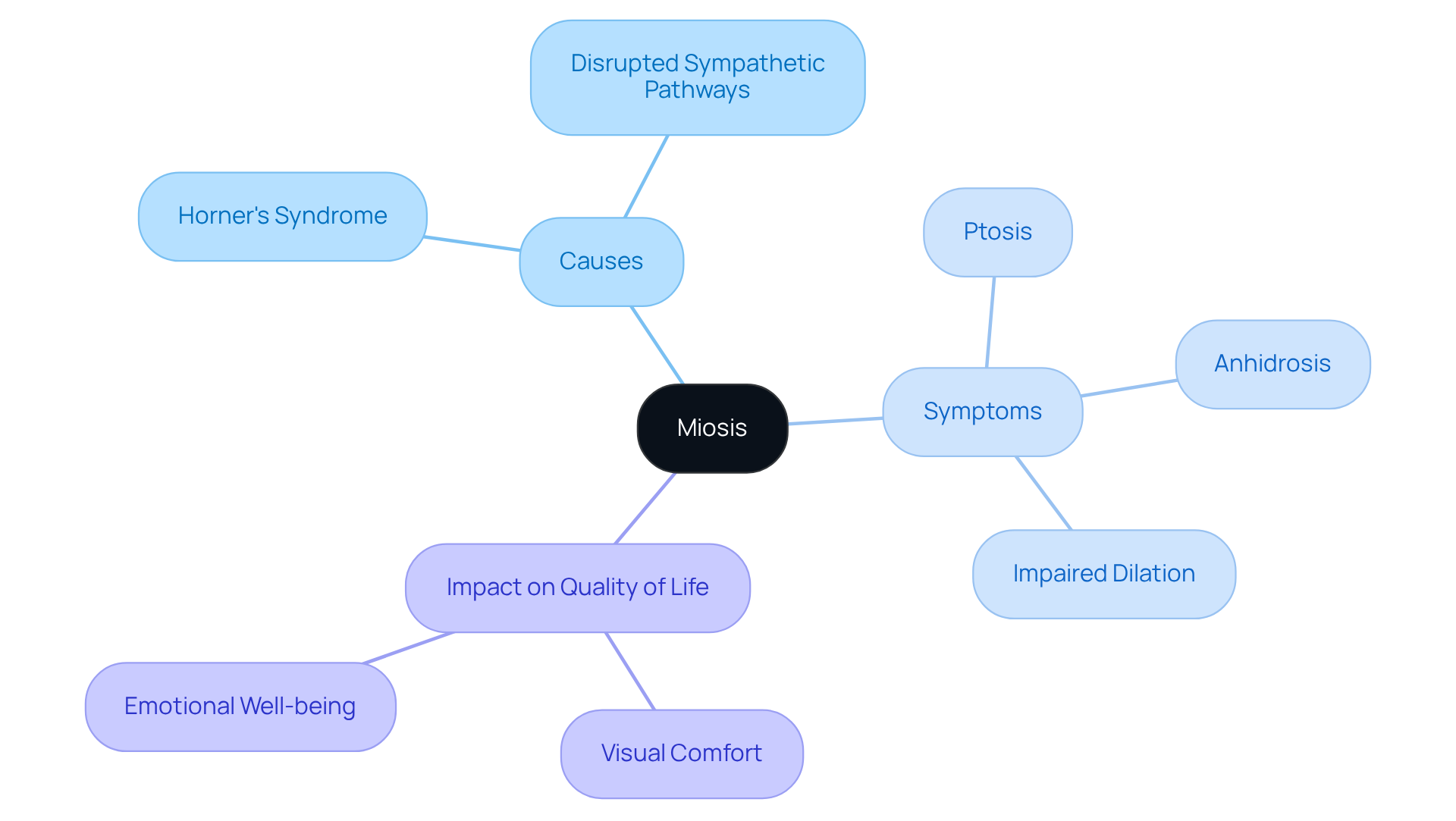
Miosis, characterized by an unusually narrowed pupil, is often a sign of . We understand that this can be concerning, as it results from , leading to an imbalance in pupil size. Patients may notice that the affected pupil does not dilate properly in dim lighting, which can be an .
Miosis frequently occurs alongside other signs, such as ptosis (drooping eyelid) and anhidrosis (lack of sweating), which together form the . Recognizing these signs is vital, as they may indicate , making prompt medical evaluation essential.
The impact of miosis on your quality of life can be significant. It can affect not just visual comfort, but also emotional well-being, as individuals may feel self-conscious about the noticeable difference in pupil size. We are here to help you navigate these feelings and understand the nuances of your condition, which is crucial for effective management and timely intervention.
As with any concerning eye indication, it’s important to for a precise diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Anhidrosis: Absence of Sweating on One Side of the Face
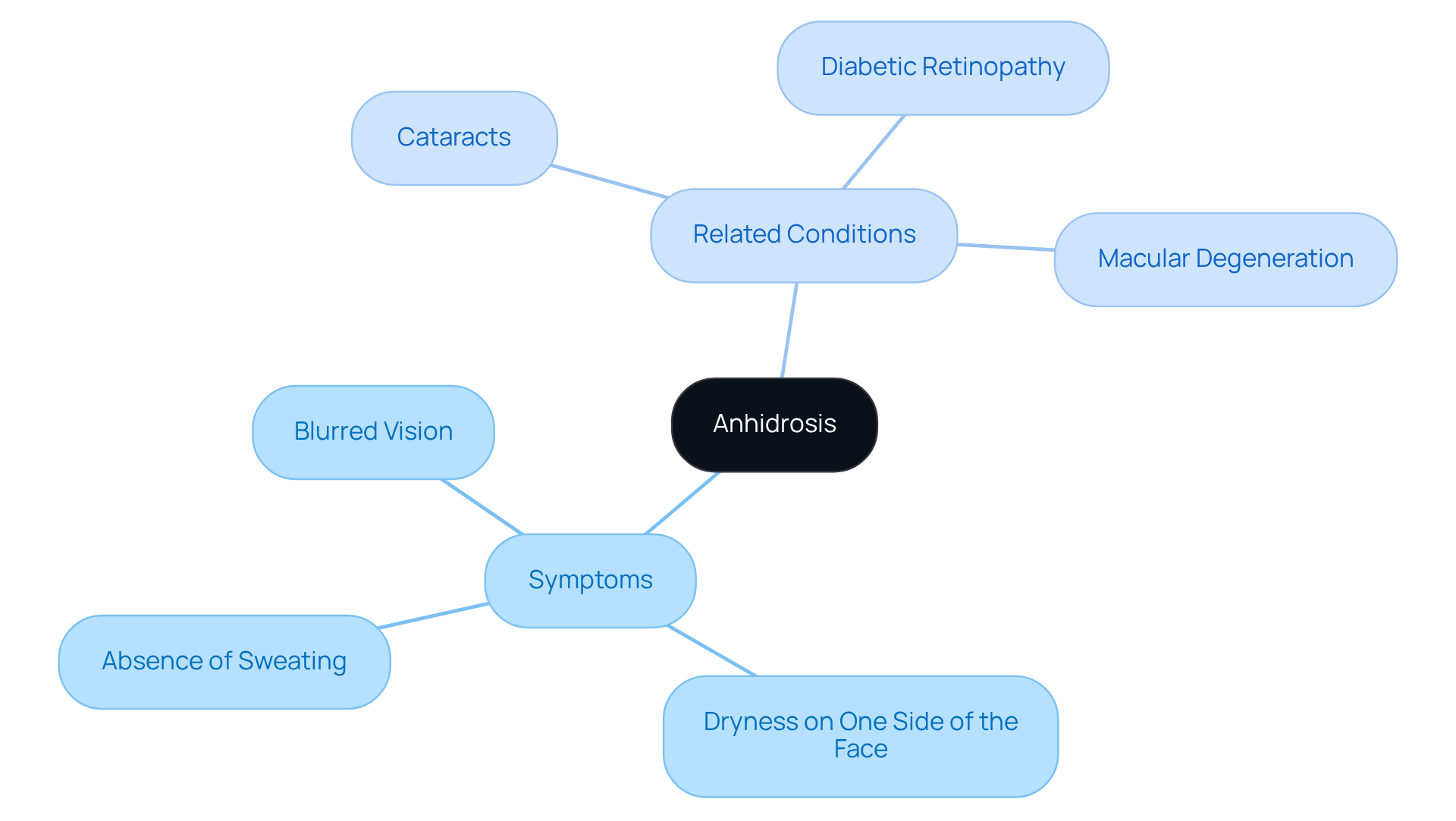
Anhidrosis, characterized by the absence of perspiration on one side of the face, can be a significant indicator of . We understand that noticing such a change can be concerning. This condition arises from a disruption of the sympathetic nerves that regulate sweat glands, resulting in a noticeable difference in moisture levels between the two sides of the face. Many patients report that one side feels significantly drier, which can serve as a .
It’s common to feel discomfort or self-consciousness due to the uneven appearance of your skin. Research shows that this condition can in various ways. Additionally, symptoms like may also occur, indicating potential underlying eye issues such as:
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Macular degeneration
These conditions necessitate professional assessment, and we are here to help you through this process.
Experts emphasize the importance of , including anhidrosis, as it can provide valuable insights into . Understanding these signs is vital for . If you are experiencing these symptoms, we encourage you to arrange a . Our team is dedicated to providing , ensuring you receive the compassionate care you deserve.
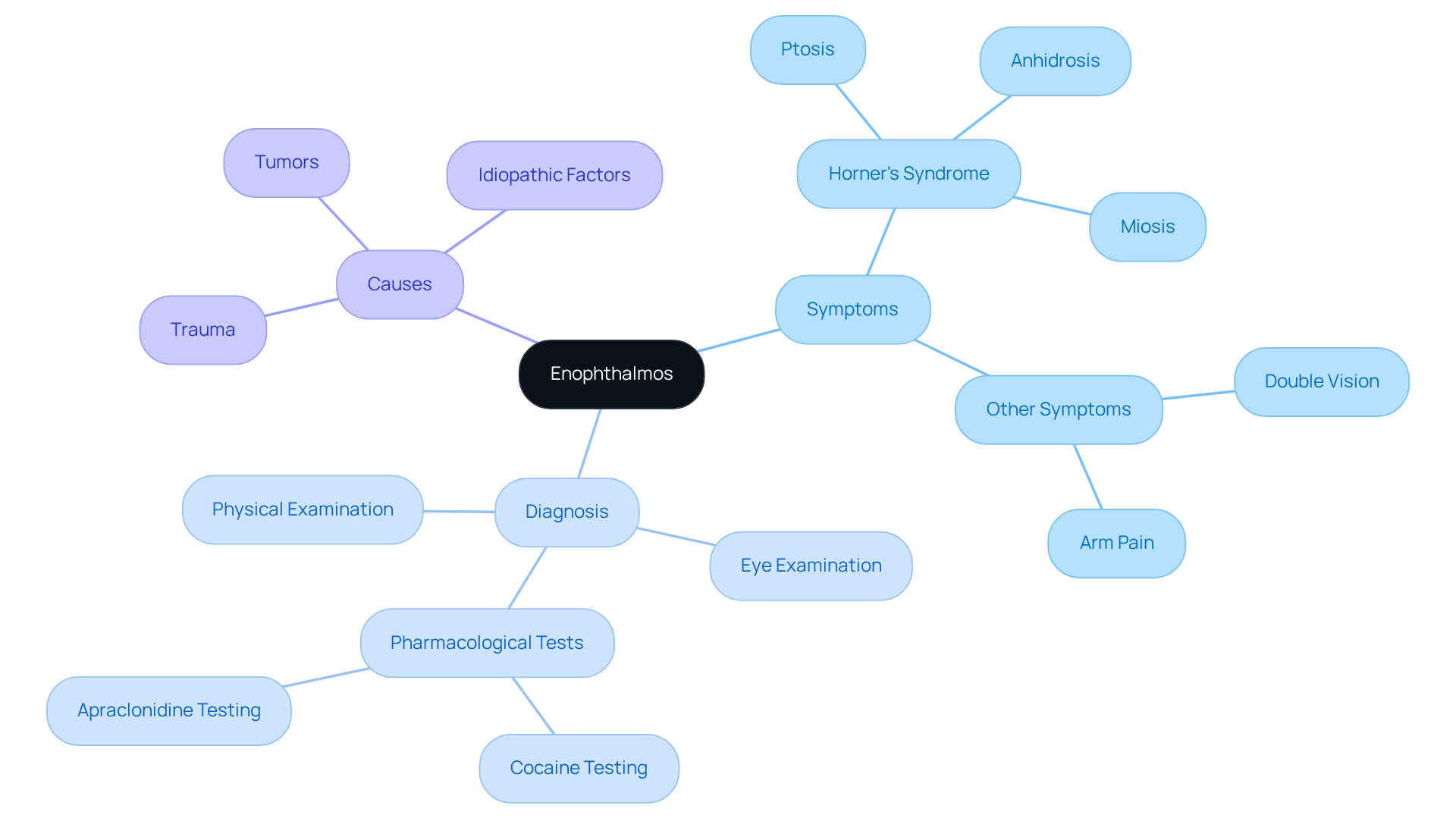
Enophthalmos: Sinking of the Eyeball as a Symptom
Enophthalmos, which refers to the sinking of the eyeball into the orbit, can be a significant indicator of symptoms. We understand that this condition may not be immediately noticeable, but it can be identified during a thorough by an ophthalmologist. The presence of enophthalmos often indicates , making it essential for healthcare providers to evaluate this symptom with care and attention.
Recent research highlights that enophthalmos typically measures between 1-2 mm and is frequently associated with Horner’s syndrome symptoms, such as . In clinical settings, diagnosing enophthalmos involves a combination of physical examination and specific tests, including pharmacological evaluations that can confirm the presence of Horner’s syndrome symptoms. It’s common to feel concerned about untreated symptoms, as they can lead to , which underscores the importance of .
Real-world examples show that enophthalmos can result from various causes, including trauma, tumors, or idiopathic factors. This diversity underscores the need for to identify the underlying cause and guide appropriate management. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you receive the .
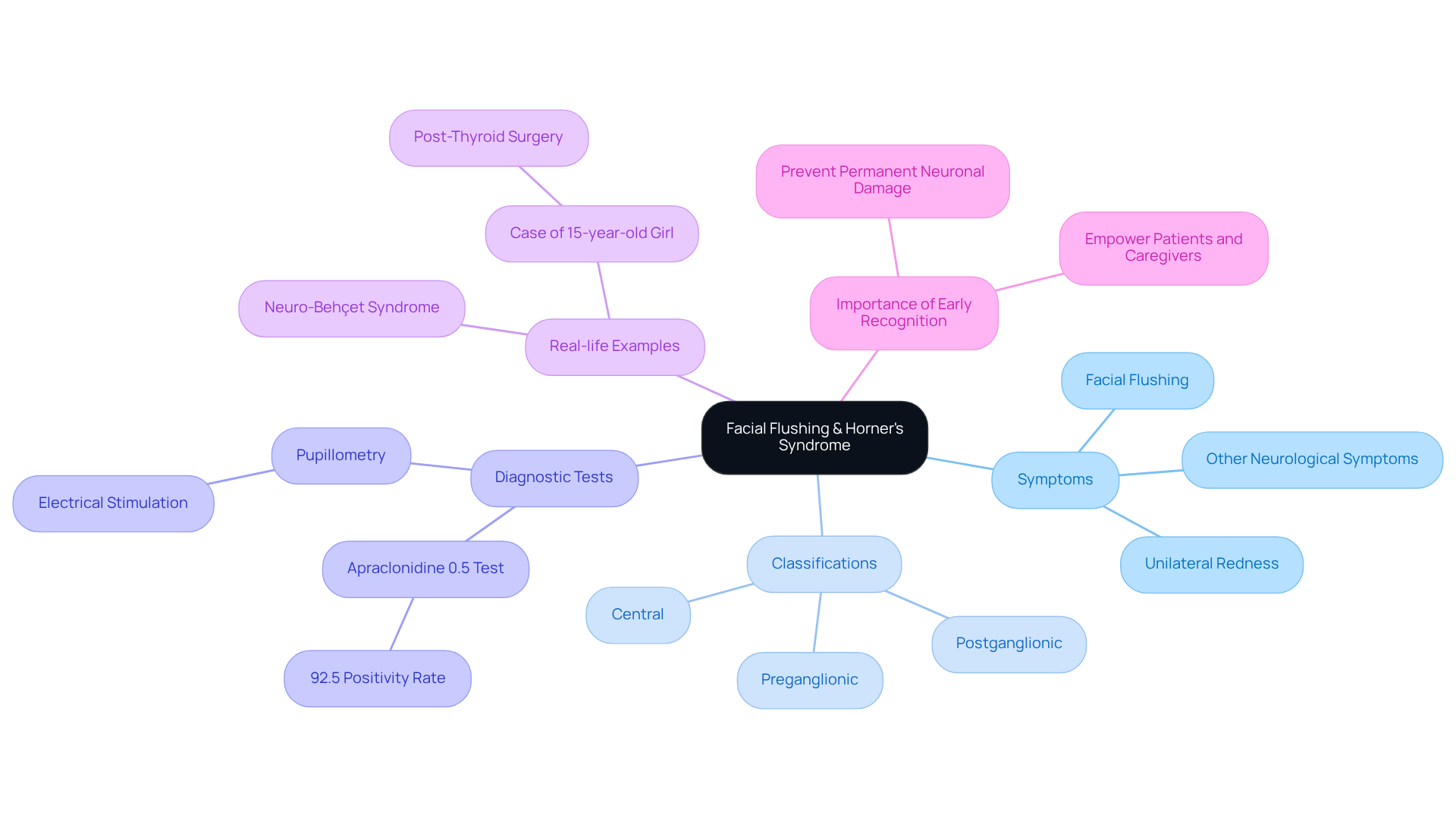
Facial Flushing: Unusual Redness Linked to Horner’s Syndrome
, characterized by unusual redness on one side of the face, is an important indicator of in patients. We understand that noticing such changes can be concerning, and this phenomenon arises from disruptions in , altering blood flow and leading to noticeable differences in facial coloration. Research shows that Horner’s syndrome symptoms can be a critical indicator of the syndrome, with studies revealing that 42% of are congenital. This underscores the importance of and intervention.
In clinical observations, patients often express that one side of their face appears more flushed than the other, which can understandably be alarming and may indicate Horner’s syndrome symptoms. A recent study found that the apraclonidine 0.5% test yielded a 92.5% positivity rate for , highlighting the effectiveness of in distinguishing it from pseudo-condition.
The condition can be categorized based on the underlying pathology:
- Central
- Preganglionic
- Postganglionic
Understanding this classification is essential for healthcare providers to determine the best diagnostic and treatment pathways, ensuring that you receive the most appropriate care.
Real-life examples can further illustrate the relevance of this condition. For instance, consider the case of a 15-year-old girl who developed a specific neurological condition after thyroid surgery, displaying considerable facial flushing along with other symptoms. This emphasizes the need for to prevent potential complications, including permanent neuronal damage.
Moreover, the occurrence of facial flushing in patients with Horner’s syndrome symptoms has been documented, with experts emphasizing its significance as a diagnostic characteristic. Isaac Lazar notes that understanding the epidemiology and clinical practice related to this condition is crucial for . Identifying signs such as facial flushing can empower patients and caregivers to seek timely medical attention, ultimately enhancing outcomes and quality of care. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you feel supported every step of the way.
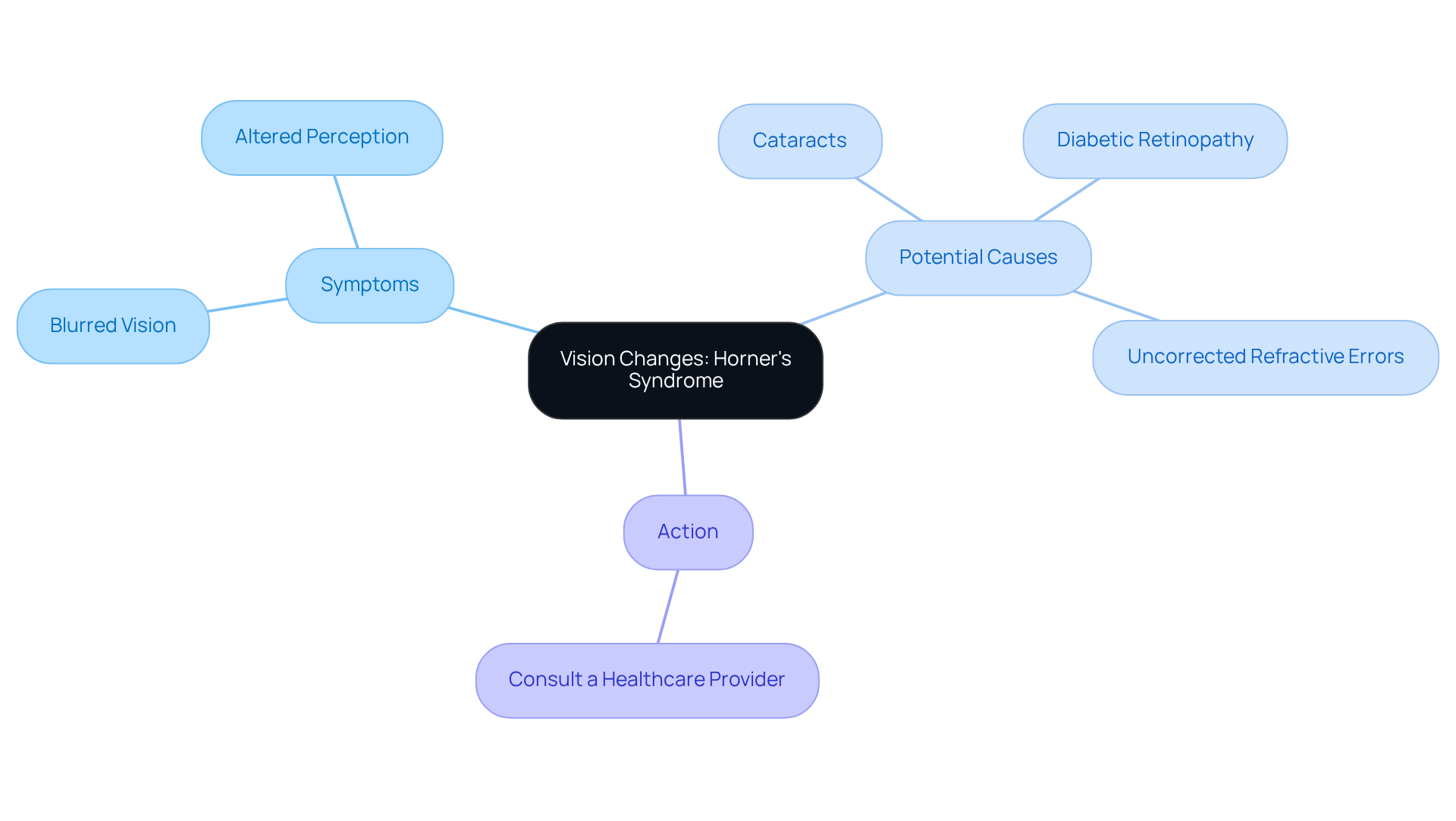
Vision Changes: Altered Perception as a Warning Sign
often include vision changes that can manifest as or altered perception in patients. We understand that Horner’s syndrome symptoms, while sometimes subtle, can be of potential nerve damage. Individuals may notice a distortion in their , where objects appear misaligned or colors seem less vibrant. Such alterations can significantly impact daily activities, from reading to driving.
Recognizing these changes is essential. If you observe any shifts in your vision, we encourage you to seek prompt consultation with a healthcare provider for . [Blurred vision](https://aao.org/interview/population-based-incidence-of-horner-syndrome) can arise from various conditions, including:
- Cataracts
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Uncorrected refractive errors
At Northwest Eye, we are here to help you through this process. We specialize in comprehensive eye care, including like such as the Light Adjustable Lens (LAL). The LAL allows for personalized adjustments post-surgery, enhancing the potential for optimal vision correction tailored to your lifestyle. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we are committed to supporting you every step of the way.
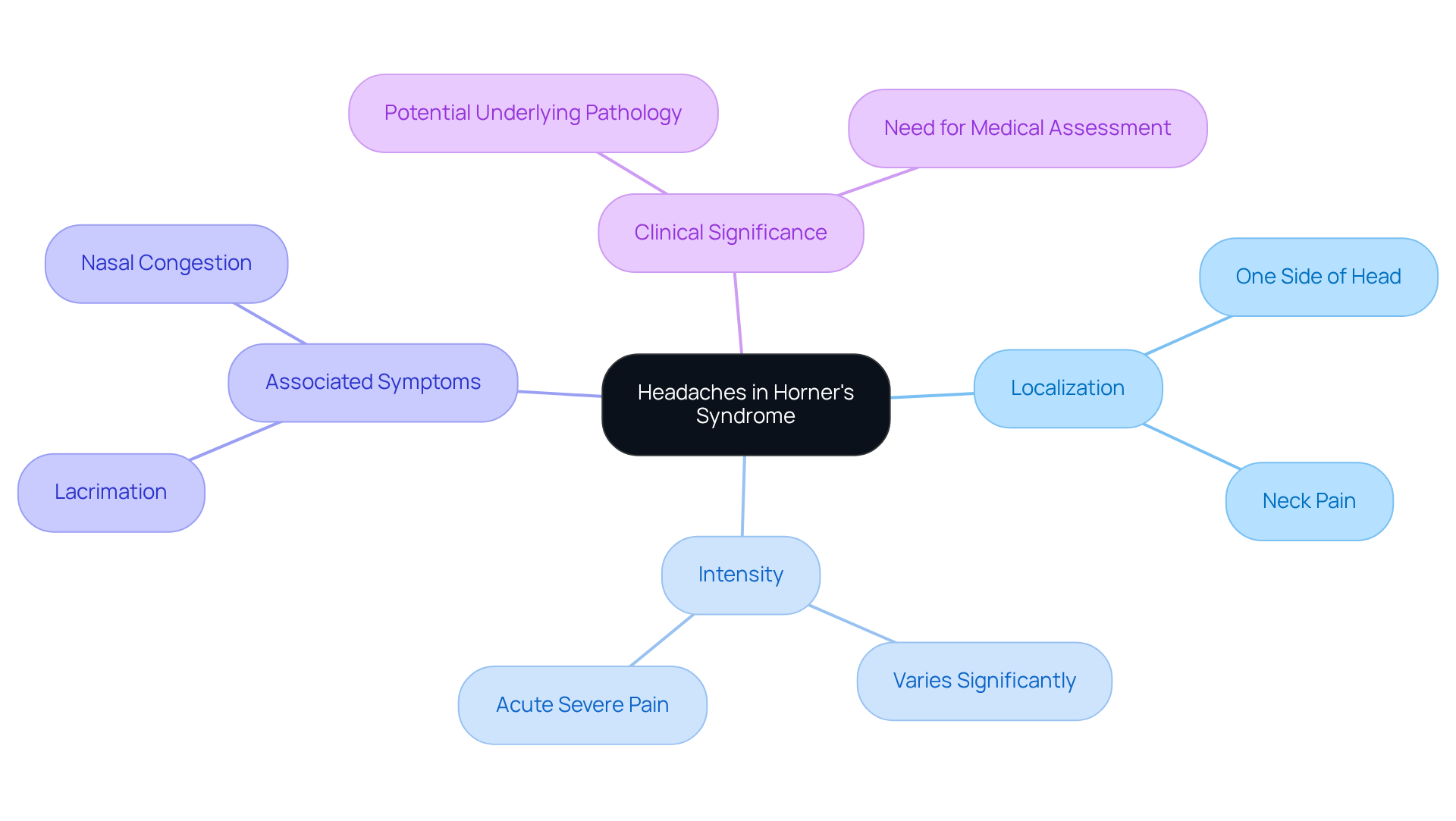
Headaches: Common Complaints Associated with Horner’s Syndrome
We understand that experiencing can be quite concerning. Patients with this condition often report headaches that may be of the head or neck, and the intensity can vary significantly. is crucial, as it may suggest an that necessitates . We are here to help you and encourage you to .
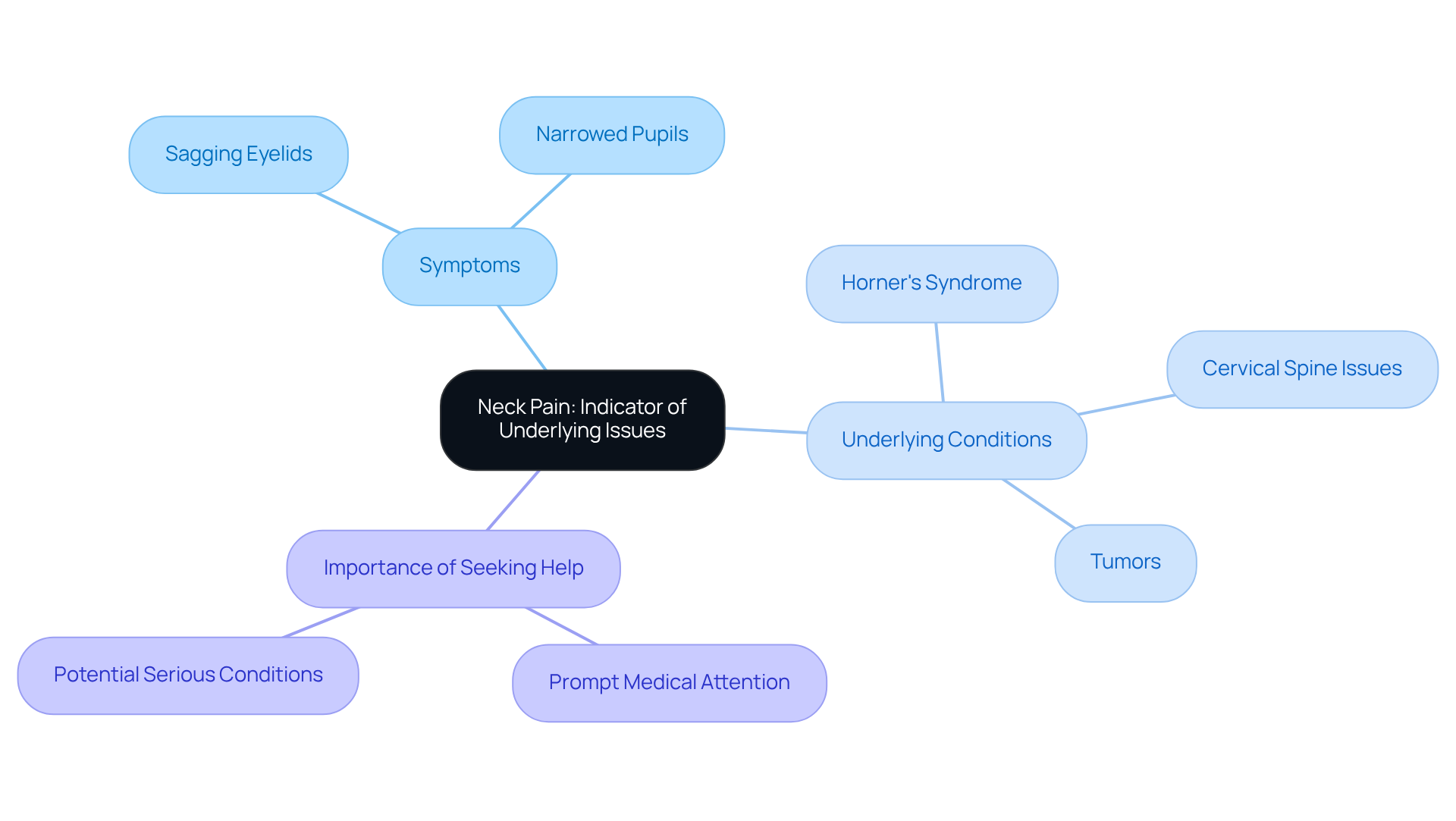
Neck Pain: A Possible Indicator of Underlying Issues
can be a significant indication of , especially when linked to cervical spine issues. We understand that experiencing discomfort or pain in the neck can be concerning, as it often signals . This syndrome affects approximately 1 in 6,000 individuals, making it essential to as a potential sign. If you notice neck discomfort alongside other Horner’s syndrome symptoms, such as sagging eyelids or narrowed pupils, it’s important to promptly.
It’s common to feel anxious about these symptoms, and we want to reassure you that acting quickly is crucial. , such as tumors or carotid artery dissection, may be involved. For instance, a case study highlighted a patient whose neck pain was linked to , which ultimately led to the identification of a . Therefore, being attentive to neck discomfort and can significantly influence the management of this condition.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We are here to help you through this process, and seeking guidance can provide you with the support you need.
Seek Medical Attention: Importance of Addressing Symptoms Promptly
Identifying the signs of and seeking is crucial. We understand that noticing , such as a , constricted pupil, and , can be concerning. These signs can indicate underlying nerve damage, which may be linked to serious conditions like tumors or carotid artery dissection. It’s common to feel anxious about Horner’s syndrome symptoms, particularly if they are accompanied by , as this may indicate other eye diseases.
Horner’s Syndrome affects roughly 1 in 6,000 individuals, making . Research shows that prompt intervention can greatly improve management approaches and enhance patient results. For instance, patients who received timely care often experienced . Case studies reveal that addressing issues without delay can lead to more favorable outcomes.
As Dr. William C Lloyd III, MD, emphasizes, “Anyone who notices indications and signs of Horner’s syndrome should consult their physician to ascertain the cause.” At , we are here to help you through this process. Our dedicated team is committed to providing for those experiencing these symptoms, ensuring that each patient receives the attention they need for effective treatment and management.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of Horner’s Syndrome is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This rare condition affects the sympathetic nerves that control eye and facial functions, presenting key indicators such as:
- Drooping eyelids (ptosis)
- Unequal pupil sizes (miosis)
- Decreased sweating on one side of the face (anhidrosis)
We understand that noticing these signs can be concerning, but understanding them aids in early detection and addresses potential underlying health issues that may require immediate medical attention.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted various symptoms, including:
- Enophthalmos (sinking of the eyeball)
- Facial flushing
- Vision changes
- Headaches
- Neck pain
Each of these symptoms can signal significant nerve damage or other serious conditions, such as tumors or cervical spine issues. It’s common to feel overwhelmed when faced with such indicators, but consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Early intervention can lead to better management and improved patient outcomes.
Ultimately, awareness and prompt action are vital regarding Horner’s Syndrome. If you or someone you know is experiencing any of the outlined symptoms, we encourage you to seek medical evaluation without delay. By taking this step, you can ensure that you receive the appropriate care and support needed to navigate this complex condition effectively. Remember, recognizing these signs empowers you and your caregivers, paving the way for enhanced health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Horner’s Syndrome?
Horner’s Syndrome is a rare condition that affects the sympathetic nerves controlling eye and facial functions. It can lead to symptoms such as drooping eyelids, unequal pupil sizes, and decreased sweating on one side of the face.
What are the common symptoms of Horner’s Syndrome?
Common symptoms include drooping eyelids (ptosis), unequal pupil sizes, and decreased sweating on one side of the face. These symptoms typically affect only one side of the face, leading to noticeable asymmetry.
How is Horner’s Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Horner’s Syndrome involves advanced diagnostic methods, including imaging tests like MRIs and CT scans, to accurately identify signs and underlying causes.
What should I do if I notice symptoms of Horner’s Syndrome?
If you notice signs of Horner’s Syndrome, it is important to consult a healthcare professional promptly for assessment and diagnosis.
Does Horner’s Syndrome lead to major health or vision problems?
While Horner’s Syndrome itself typically does not lead to major health or vision problems, it can signal more serious underlying issues, making prompt evaluation essential.
What is ptosis and how is it related to Horner’s Syndrome?
Ptosis is the drooping of the upper eyelid and is a significant indicator of Horner’s Syndrome. Noticing one eyelid appearing lower than the other can be concerning and may signal underlying issues like cataracts.
What is miosis and how does it relate to Horner’s Syndrome?
Miosis is characterized by an unusually narrowed pupil and is often a sign of Horner’s Syndrome. It results from disrupted sympathetic nerve pathways and can lead to an imbalance in pupil size.
Why is it important to recognize the signs of Horner’s Syndrome?
Recognizing the signs of Horner’s Syndrome is vital because they may indicate serious underlying conditions, such as stroke or tumors, necessitating prompt medical evaluation and intervention.






