Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on May 15, 2025
Overview
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can arise from prolonged high blood sugar levels. We understand that this diagnosis can be concerning, as it leads to damage in the retinal blood vessels and may result in vision loss. Early detection is crucial, and regular eye exams can provide peace of mind.
There are various treatment options available to help manage this disease effectively. Monitoring your condition, undergoing laser treatment, or receiving injections are all possibilities that can help preserve your vision. It’s common to feel overwhelmed by these choices, but remember that you are not alone in this journey.
We are here to help you through this process, ensuring that you receive the care and support you need. Taking action now by scheduling regular eye exams can make a significant difference in your health. Together, we can work towards maintaining your vision and overall well-being.
Introduction
Diabetic retinopathy, a serious complication of diabetes, poses a significant risk to vision and quality of life for millions around the world. We understand that facing such a condition can be daunting. Approximately 28.5% of adults with diabetes are affected, making it essential to understand this condition for prevention and effective management.
As the disease progresses through various stages, early detection becomes critical. It’s common to feel overwhelmed, which emphasizes the need for regular eye examinations and a keen awareness of symptoms.
This article delves into the intricacies of diabetic retinopathy, exploring its:
- Causes
- Risk factors
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic procedures
- Treatment options
We are here to help you take charge of your eye health and mitigate the risk of severe visual impairment.
Define Diabetic Retinopathy and Its Importance
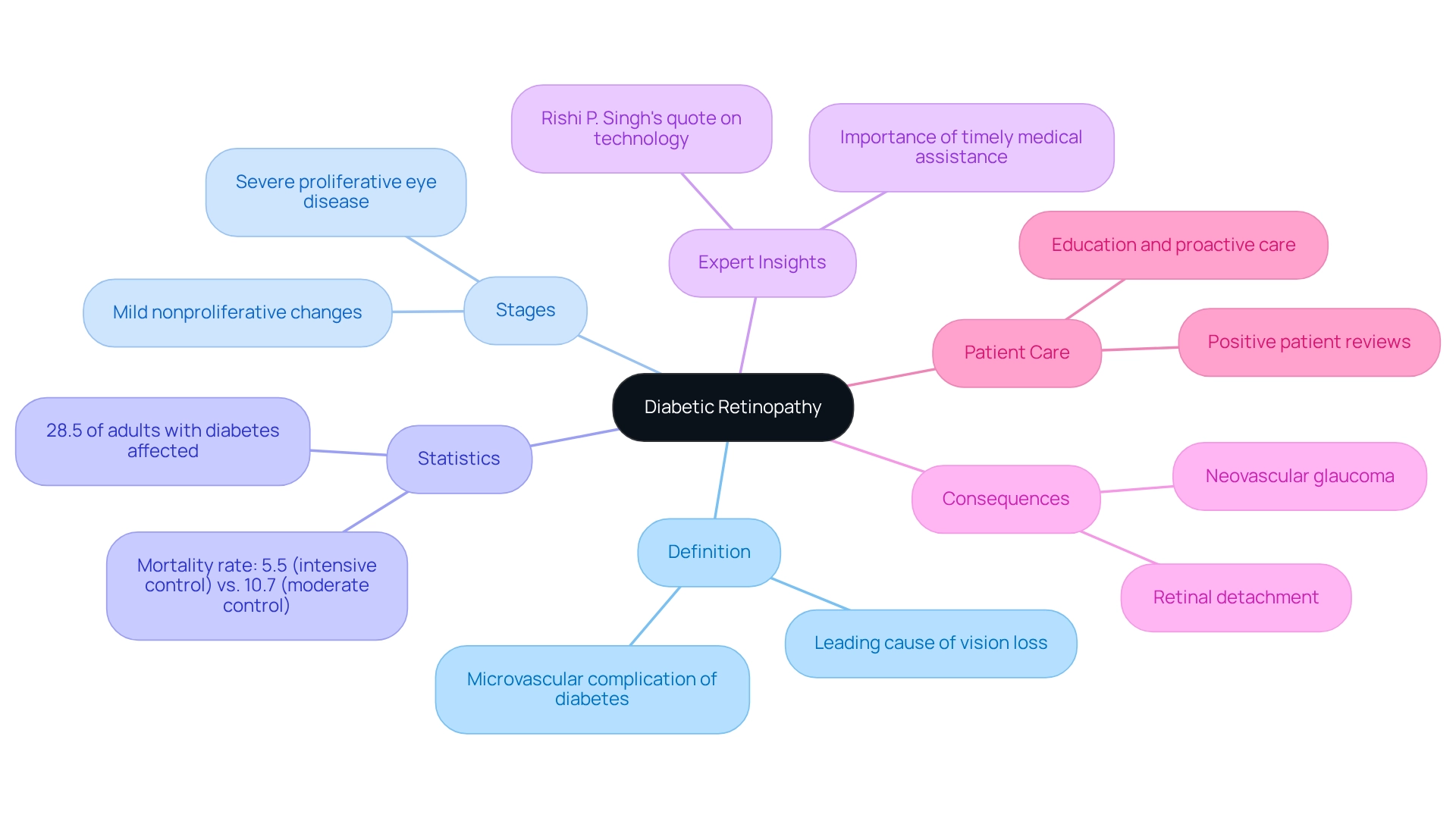
Diabetic retinopathy is a microvascular complication of high blood sugar that causes damage to the retinal blood vessels. It stands as a leading cause of vision loss among adults, particularly for those experiencing prolonged high blood sugar levels, and this condition is known as diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy typically progresses through specific stages, beginning with mild nonproliferative changes and advancing to severe proliferative eye disease, which can lead to significant visual impairment or even blindness. We understand that comprehending related to diabetes is essential for those affected. Early identification and prompt action can prevent serious consequences and help maintain eyesight.
Statistics indicate that approximately 28.5% of adults with diabetes are impacted by eye disease, underscoring the importance of regular eye check-ups. Recent studies reveal that intensive therapy can notably reduce the incidence of severe complications, showing a mortality rate of 5.5% in intensive control compared to 10.7% in moderate control.
Experts emphasize the necessity of understanding diabetic retinopathy, a diabetes-related eye disease. Rishi P. Singh, Vice President and Chief Medical Officer at Cleveland Clinic Martin Hospitals, observes that “technological advancements such as retinal photography with remote interpretation can lessen the load of screening for diabetes-related eye disease.” This insight highlights the importance of understanding the condition, enabling individuals to seek timely medical assistance, which is crucial for effective management. For instance, patients experiencing worsening symptoms after rapid decreases in HbA1c levels should be promptly evaluated by an ophthalmologist to determine appropriate management strategies, which may include monitoring, medication adjustments, or surgical interventions based on the severity of the condition.
The consequences of unmanaged diabetes-related eye disease, such as diabetic retinopathy, can be severe, potentially leading to complications like neovascular glaucoma and retinal detachment. Therefore, recognizing the [signs and symptoms early](https://nweyeclinic.com/9-key-signs-of-glaucoma-every-parent-should-recognize/) is vital. Key facts about diabetic retinopathy reveal that it not only affects vision but also significantly impacts quality of life. This makes education and proactive care critical components in managing this condition. Positive patient reviews reflect the clinic’s reputation for excellence and personalized solutions for individual needs, reinforcing the importance of patient-centered care.
Explore Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy
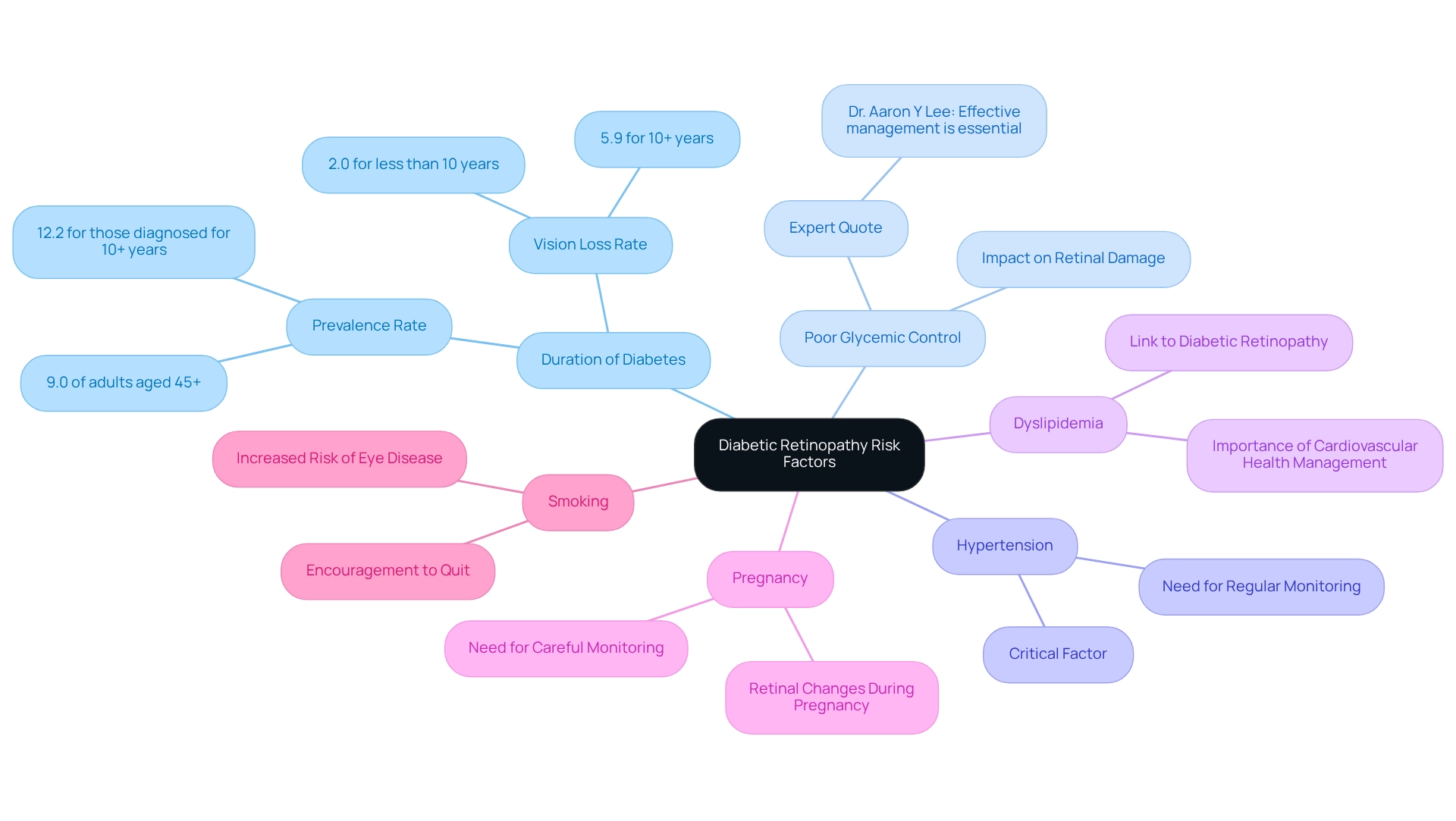
Diabetic retinopathy primarily arises from prolonged high blood sugar levels, which cause damage to the small blood vessels in the retina. We understand that facing this condition can be daunting, but recognizing the key risk factors can empower you to take control of your health.
- Duration of Diabetes: The risk of DR escalates with the length of time a person has diabetes. A study revealed that nearly 9.0% of adults aged 45 and over with diagnosed blood sugar issues showed signs of eye complications, with the occurrence increasing to 12.2% among those diagnosed for 10 years or more. Furthermore, the occurrence rate of vision-threatening complications associated with sugar intolerance has a 95% uncertainty interval of 3.90% to 6.57%, emphasizing the seriousness of this condition.
- Poor Glycemic Control: It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the need for consistent blood glucose management. However, maintaining optimal glycemic control is crucial, as elevated blood glucose levels can significantly exacerbate retinal damage. As Dr. Aaron Y Lee, MD, highlights, “Effective management of blood sugar levels is essential in preventing the advancement of diabetic retinopathy.”
- Hypertension: High blood pressure is another critical factor that can worsen the condition. Regular monitoring is essential for those at risk, and we are here to help you navigate this.
- Dyslipidemia: Dyslipidemia, which involves abnormal lipid levels, has been linked to an increased risk of diabetic retinopathy, highlighting the need for comprehensive management of cardiovascular health. Taking steps to manage your overall health can make a difference.
- Pregnancy: If you are a woman with diabetes, you may experience retinal changes during pregnancy. This period necessitates careful monitoring, and we want you to know that support is available.
- Smoking: Tobacco consumption is recognized to increase the likelihood of developing diabetes-related eye disease. Quitting smoking can significantly benefit your health, and we encourage you to seek support in this journey.
Comprehending these risk factors enables individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health and reducing the likelihood of vision loss related to diabetic retinopathy. indicate that tailored solutions can significantly enhance the quality of care and management strategies for those at risk. The case study titled ‘Diabetes-Related Eye Disease in Long-Term Diabetic Adults’ illustrates the connection between diabetes duration and the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, reinforcing the significance of early intervention and ongoing care. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Identify Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
In the early stages, symptoms of diabetic retinopathy often go unnoticed, highlighting the importance of awareness for timely intervention. As the condition progresses, you may experience several visual disturbances, including:
- Blurred Vision: It can become increasingly difficult to focus, especially as fluid accumulates in the retina. Blurred vision may also indicate other underlying conditions, such as cataracts, dry eyes, or uncorrected refractive errors, which are common among those affected. We encourage you to consult with a Northwest Eye doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. If you are experiencing blurred vision, please schedule an appointment to discuss your symptoms.
- Floaters: The appearance of small dark spots or strings in your visual field can indicate bleeding within the eye, a common symptom that requires immediate attention.
- Fluctuating Vision: Many individuals report changes in clarity throughout the day, which can be disconcerting and may signal underlying retinal changes.
- Impaired Color Vision: Difficulty in distinguishing colors may develop, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
- Vision Loss: In the most advanced stages, may occur, underscoring the importance of regular eye examinations.
It is essential for you to promptly report any of these symptoms to your eye care provider. Early detection and intervention can significantly alter the course of diabetic retinopathy, potentially preserving your vision and improving outcomes. Recent discoveries highlight that identifying these symptoms promptly can lead to more effective management approaches for diabetic retinopathy, including the use of nutraceuticals that enhance traditional therapies aimed at reducing the risk or severity of diabetes-related eye conditions. As Jiarui Wu points out, “Identifying the early signs of diabetes-related eye disease is essential for efficient management and treatment.” A case study of a 47-year-old woman with Type 1 diabetes illustrates this point; she presented with sudden left-sided hemiparesis and had a history of multiple complications related to her condition, including proliferative eye disease. This highlights the complex interplay between diabetes complications and vision health, reinforcing the need for vigilance in monitoring symptoms. We are here to help you through this process.
Understand Diagnostic Procedures for Diabetic Retinopathy
A series of essential procedures are involved in diagnosing diabetic retinopathy (DR) to ensure accurate detection and management of this condition. We understand that navigating health concerns can be daunting, and we are here to guide you through the process.
- Comprehensive Dilated Eye Exam: This is the cornerstone of DR detection. During the exam, eye drops are administered to dilate your pupils, enabling the ophthalmologist to conduct a thorough examination of your retina. This technique is acknowledged as the gold standard for detecting early indicators of diabetes-related eye disease.
- Fundus Photography: This technique captures high-resolution images of the retina, allowing for detailed documentation of any changes over time. It plays a crucial role in monitoring the progression of the disease, providing you with valuable insights into .
- Fluorescein Angiography: In this procedure, a dye is injected into your bloodstream, and photographs are taken to visualize blood flow in the retina. This assists in recognizing any leaking blood vessels, which are signs of diabetes-related eye disease, helping to ensure you receive the care you need.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): OCT provides cross-sectional images of the retina, facilitating the assessment of retinal thickness and fluid accumulation. This imaging test is vital for evaluating the severity of your condition and guiding treatment decisions.
Regular screenings using these diagnostic procedures are essential for the early detection and effective management of diabetic retinopathy. Statistics indicate that timely comprehensive dilated eye exams can significantly enhance outcomes for individuals, reducing the risk of vision loss. For instance, a recent program included 11 cases of type 2 diabetes and 1 case of type 1 diabetes, highlighting the varied demographics impacted by this condition. We believe that ongoing education and support are essential in enhancing self-management and engagement in your healthcare journey.
At Northwest Eye, we understand that financial concerns can be a barrier to accessing necessary eye care services. That’s why we offer a variety of financing programs and payment plans to make the cost of care easy and manageable. As one individual expressed, “Having not been able to afford an eye exam, I am so grateful to EyeCare America,” underscoring the importance of accessible eye care services. Additionally, a case study titled “Gratitude for ” illustrates the positive impact of accessible eye care, reinforcing the necessity of regular screenings. By understanding these diagnostic procedures, you can take proactive steps in safeguarding your eye health.
Review Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy is customized based on the severity of the condition and may involve multiple approaches. We understand that navigating this journey can feel overwhelming, but we are here to help you through this process.
- Monitoring: In the early stages, regular monitoring can be sufficient to track the progression of the disease. Current protocols are being designed to gain a deeper insight into the behavior of proliferative eye disease (PDR) and macular edema (DME) for effective treatment plans.
- Laser Treatment: Laser photocoagulation remains a cornerstone in managing diabetes-related eye disease. This technique effectively seals leaking blood vessels and reduces retinal swelling. Studies show its efficacy for over 40 years since (DRS) established its benefits.
- Anti-VEGF Injections: Medications such as ranibizumab and aflibercept are administered via injection into the eye. These treatments target fluid leakage and inhibit the growth of abnormal blood vessels, demonstrating superior visual acuity outcomes compared to traditional methods.
- Steroid Injections: Corticosteroids can be utilized to alleviate inflammation and swelling in the retina, providing relief in certain cases.
- Vitrectomy: For advanced diabetes-related eye disease, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove blood and scar tissue from the vitreous gel of the eye. Early intervention is crucial to prevent significant vision loss.
Recent advancements in laser technology, such as the PASCAL photocoagulator, have improved treatment precision and safety, resulting in enhanced comfort and reduced tissue damage. Additionally, Photobiomodulation Therapy (PBT) utilizes near-infrared light to enhance mitochondrial function and reduce inflammation, primarily as an adjunct treatment for DME, although its efficacy remains unconfirmed due to small sample sizes in studies.
As the landscape of treatment for diabetes-related eye conditions evolves, personalized care strategies that take into account each individual’s distinct situation are essential for attaining successful results. As noted by Stela Vujosevic, it’s crucial to consider both the physician and patient perspectives in shaping the clinical landscape of diabetic retinopathy. Continuous monitoring and exploration of novel therapeutic options will further enhance the management of diabetic retinopathy, a prevalent condition that affects over 422 million people globally.
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a significant concern for individuals living with diabetes, impacting a considerable percentage of this population. We understand that navigating this condition can be overwhelming. Therefore, it is essential to comprehend its causes, risk factors, symptoms, and the available diagnostic and treatment options for effective management and prevention of vision loss. Early detection through comprehensive eye exams, along with awareness of symptoms such as blurred vision, floaters, and fluctuating vision, can make a substantial difference in outcomes.
Managing blood sugar levels, monitoring blood pressure, and addressing lifestyle factors like smoking are crucial steps that can mitigate the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Moreover, advancements in diagnostic procedures and treatment options, including laser therapy and anti-VEGF injections, offer hope for preserving vision and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Ultimately, proactive engagement in eye health care, including regular screenings and timely interventions, empowers individuals to take charge of their vision. We emphasize that education and patient-centered care can lead to better outcomes, ensuring that those at risk of diabetic retinopathy are informed and equipped to manage their condition effectively. By prioritizing eye health, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of severe complications and maintain their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a microvascular complication of high blood sugar that damages the retinal blood vessels, leading to vision loss among adults, especially those with prolonged high blood sugar levels.
How does diabetic retinopathy progress?
Diabetic retinopathy progresses through specific stages, starting with mild nonproliferative changes and advancing to severe proliferative eye disease, which can result in significant visual impairment or blindness.
What are the statistics related to diabetic retinopathy?
Approximately 28.5% of adults with diabetes experience eye disease. Intensive therapy can reduce the incidence of severe complications, with a mortality rate of 5.5% in intensive control compared to 10.7% in moderate control.
Why is early identification important in diabetic retinopathy?
Early identification and prompt action can prevent serious consequences and help maintain eyesight, making it crucial for individuals to understand the condition.
What are the key risk factors for developing diabetic retinopathy?
Key risk factors include the duration of diabetes, poor glycemic control, hypertension, dyslipidemia, pregnancy, and smoking.
How does the duration of diabetes affect the risk of diabetic retinopathy?
The risk of diabetic retinopathy increases with the length of time a person has diabetes. For example, nearly 9.0% of adults aged 45 and over with diagnosed blood sugar issues showed signs of eye complications, which increased to 12.2% among those diagnosed for 10 years or more.
What role does glycemic control play in diabetic retinopathy?
Maintaining optimal glycemic control is crucial, as elevated blood glucose levels can significantly worsen retinal damage.
How does hypertension affect diabetic retinopathy?
High blood pressure can exacerbate diabetic retinopathy, making regular monitoring essential for those at risk.
What impact does dyslipidemia have on diabetic retinopathy?
Dyslipidemia, or abnormal lipid levels, has been linked to an increased risk of diabetic retinopathy, highlighting the need for comprehensive cardiovascular health management.
What should women with diabetes be aware of regarding pregnancy?
Women with diabetes may experience retinal changes during pregnancy, necessitating careful monitoring.
How does smoking influence the risk of diabetic retinopathy?
Tobacco consumption increases the likelihood of developing diabetes-related eye disease, and quitting smoking can significantly benefit overall health.
What are the potential consequences of unmanaged diabetic retinopathy?
Unmanaged diabetic retinopathy can lead to severe complications such as neovascular glaucoma and retinal detachment, which underscores the importance of recognizing signs and symptoms early.






