Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on September 16, 2025
Overview
Fuchs corneal dystrophy is a progressive eye condition that can be distressing, particularly for those over 50. It is characterized by the deterioration of endothelial cells in the cornea, leading to fluid accumulation, swelling, and vision impairment. We understand that experiencing blurred vision and glare can be concerning, and it’s important to recognize these common symptoms.
Diagnostic methods, such as slit-lamp examinations, are crucial for identifying this condition. We want you to feel reassured that there are treatment options available, ranging from eye drops to surgical procedures. Early detection and tailored management are vital for preserving your vision, and we are here to help you through this process.
It’s common to feel overwhelmed when facing such challenges, but remember that support is available. Seeking care early can make a significant difference in your journey, and we encourage you to reach out for assistance. Together, we can navigate this condition and work towards maintaining your vision.
Introduction
Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy is a progressive eye disorder that can significantly challenge vision, especially for individuals over 50. We understand that facing such a condition can be daunting.
With approximately 590,000 adults in the U.S. affected, it is crucial to comprehend its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options to maintain a good quality of life. As the prevalence of this condition continues to rise, many may wonder how to effectively manage its impact and what advancements in treatment can provide hope.
This article delves into the intricacies of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy, empowering you with the knowledge needed to navigate this complex condition. We are here to help you through this process.
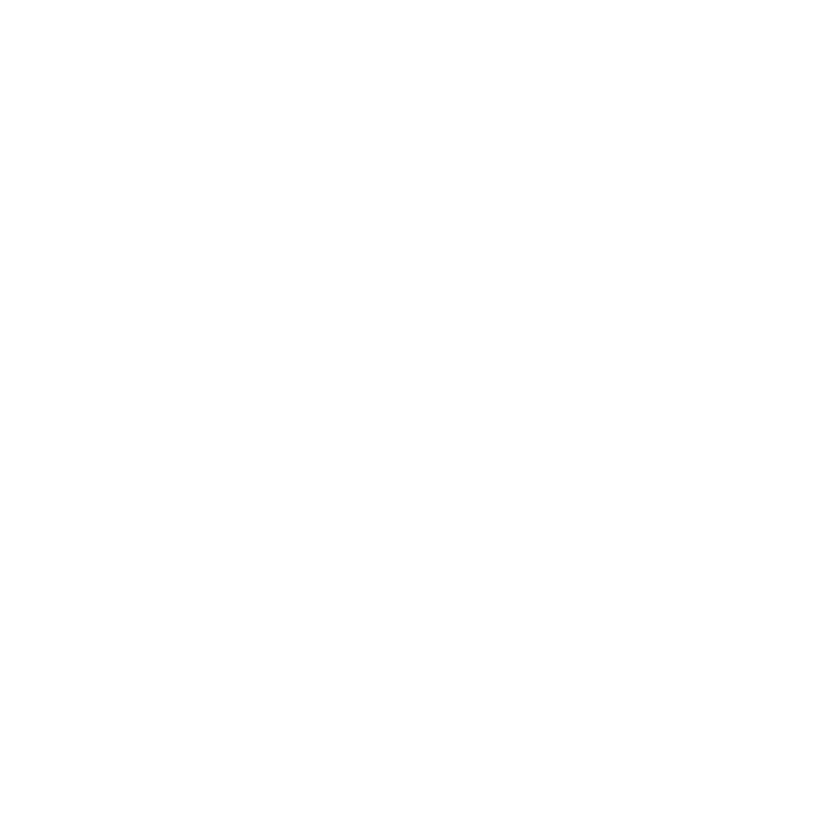
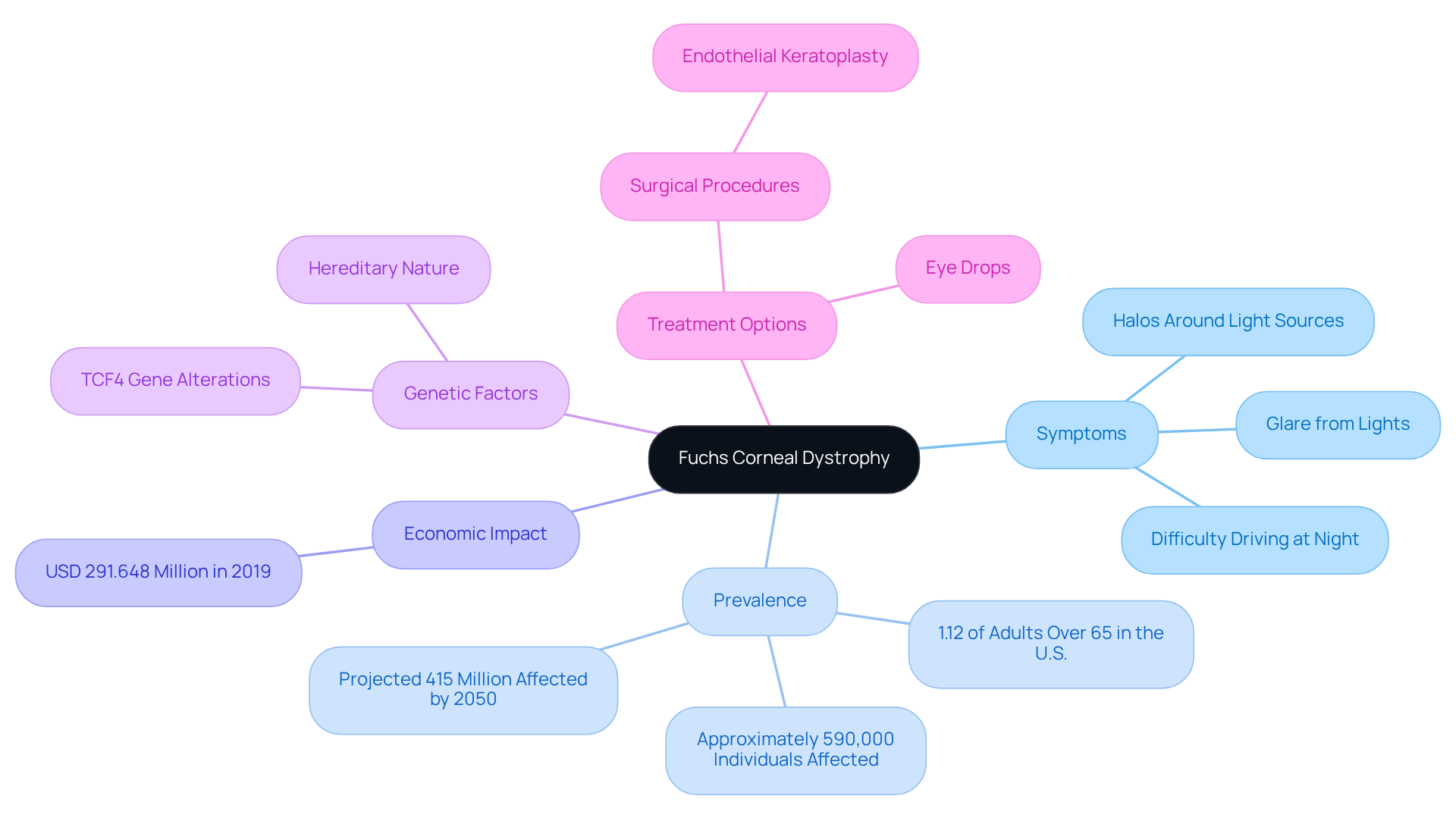
Define Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy
(FCD) is a progressive eye condition that primarily affects the cornea, particularly the endothelial cells that cover its inner surface. These cells are vital for maintaining corneal clarity by pumping excess fluid out. In , the gradual deterioration of endothelial cells leads to fluid accumulation, resulting in corneal swelling and, ultimately, .
We understand that this disorder can be concerning, especially since it is often hereditary and typically manifests in individuals over the age of 50. In the U.S., approximately 1.12% of adults in this age group are affected, which translates to around 590,000 individuals. Symptoms can vary widely among patients, but the disease is characterized by the presence of guttae—small, drop-like deposits on the cornea indicating endothelial cell dysfunction. Common symptoms include:
- Glare from lights
- Halos around light sources
- Difficulty driving at night, particularly in low-light conditions
These challenges can significantly impact daily activities, highlighting the importance of seeking .
It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the prospect of the condition worsening. Recent research indicates that the number of individuals affected by FCD is expected to rise significantly, with projections estimating that by 2050, over 415 million people will be impacted globally. In 2019, the was estimated at USD 291.648 million, highlighting the importance of .
Fortunately, effective treatment options are available, ranging from eye drops to surgical procedures such as endothelial keratoplasty, which can improve sight in more severe cases. Understanding the , such as alterations in the TCF4 gene, is crucial, as family background elevates the risk of developing this disorder. are essential for early detection and management, allowing for timely intervention to preserve vision.
At Northwest Eye, we are here to help you through this process. We offer an extensive to assist patients in comprehending and managing a broad spectrum of eye disorders, including Corneal Dystrophy. You are not alone in this journey; we are committed to supporting you every step of the way.
Identify Symptoms of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy
Symptoms of fuchs corneal dystrophy can manifest in various ways, often leading to significant visual impairment if not addressed promptly. We understand that experiencing these symptoms can be concerning, and it’s important to recognize them early. Common symptoms include:
- Blurred or Hazy Vision: Many patients frequently experience , particularly in the morning due to fluid accumulation in the cornea overnight. This symptom may improve as the day progresses, offering some relief.
- : It’s common for individuals to report increased discomfort in bright environments, making outdoor activities or bright indoor settings challenging.
- Glare and Halos: Difficulty seeing at night or in low-light conditions is often accompanied by halos around lights, which can be particularly distressing.
- : Discomfort may arise from fluid-filled blisters (bullae) on the cornea, leading to significant irritation and pain.
- : You may notice changes in visual clarity throughout the day, complicating daily tasks.
- : A constant sensation of sand or grit in your eyes can be bothersome, contributing to overall discomfort.
Identifying these signs of fuchs corneal dystrophy early is essential for prompt diagnosis and intervention, which can greatly help in maintaining your eyesight. With [blurred vision](https://nweyeclinic.com/9-key-dry-eye-symptoms-to-recognize-and-address) reported in approximately 68.5% of affected eyes, understanding these signs can empower you to seek . Regular eye exams are crucial, especially for those over 50, as early detection can lead to better management outcomes. We are here to help you through this process and ensure you receive the support you need.
![]()
Explain Diagnosis of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy
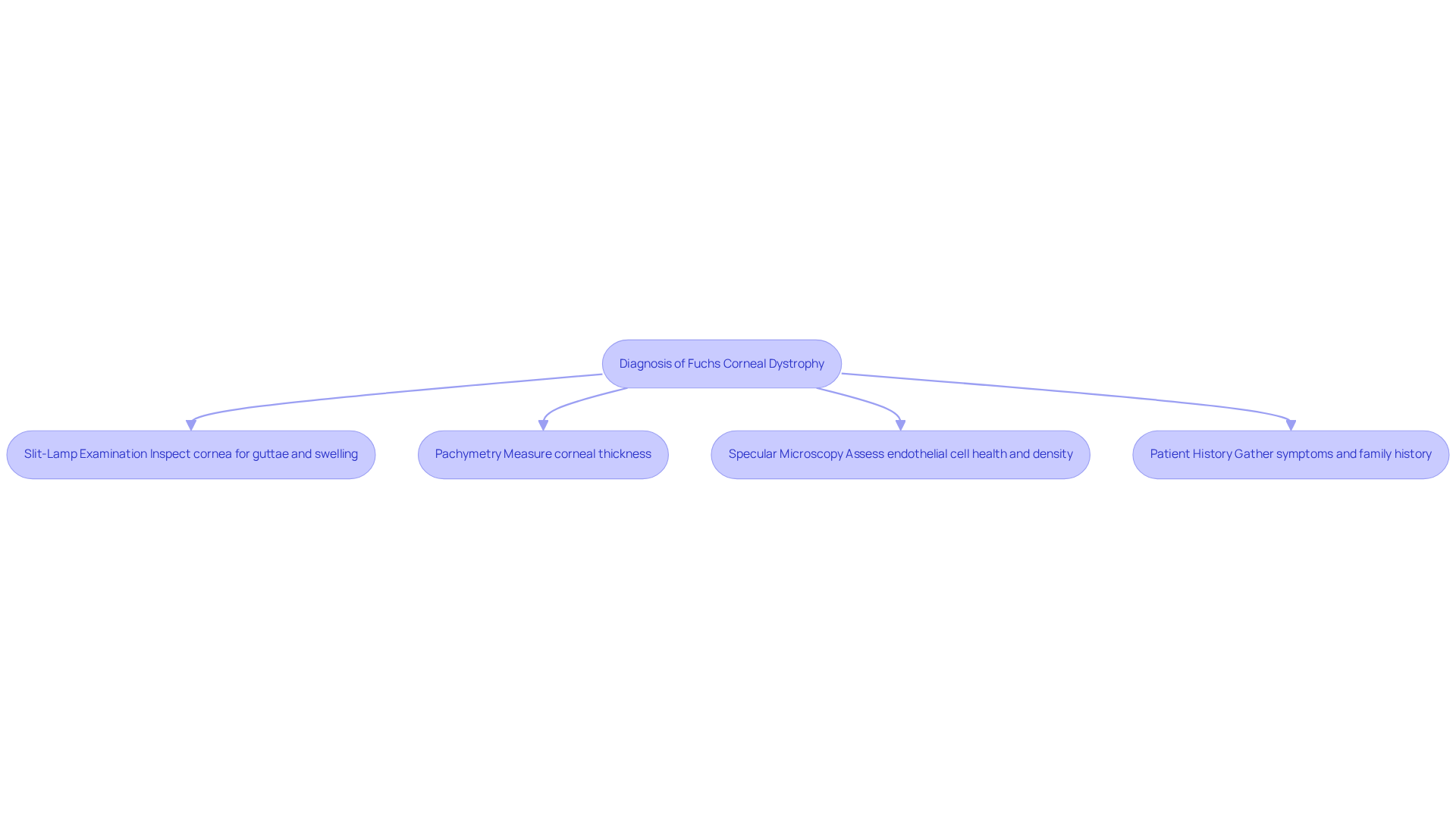
Diagnosing (FECD) involves a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist, utilizing several key diagnostic methods that prioritize your comfort and understanding:
- : We understand that this step can feel daunting, but it is essential. This critical examination allows the ophthalmologist to closely inspect your cornea for the presence of guttae and any signs of . Studies indicate that approximately 90% of diagnoses for Fuchs corneal dystrophy are made using this method, highlighting its effectiveness and reliability.
- Pachymetry: This painless test measures your , providing insight into the extent of edema. A central corneal thickness of 640 μm or less is particularly significant, as it suggests a higher likelihood of requiring surgical intervention. Knowing this can help you prepare for what may come next.
- : This advanced imaging technique assesses the health and density of endothelial cells, which are crucial for maintaining corneal clarity. It can reveal changes in cell morphology that are characteristic of fuchs corneal dystrophy, providing you with valuable information about your condition.
- : Gathering information about your symptoms and family history is vital. We recognize that fuchs corneal dystrophy (FECD) often has a , and discussing these factors can help contextualize the clinical findings regarding fuchs corneal dystrophy, making you feel more informed and involved in your care.
These diagnostic tools together verify the existence of Corneal Dystrophy while excluding other possible eye issues. It’s common to feel anxious about these procedures, but and artificial intelligence are also enhancing , paving the way for more effective management of this issue. Remember, we are here to help you through this process, providing support every step of the way.
Explore Treatment Options for Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy
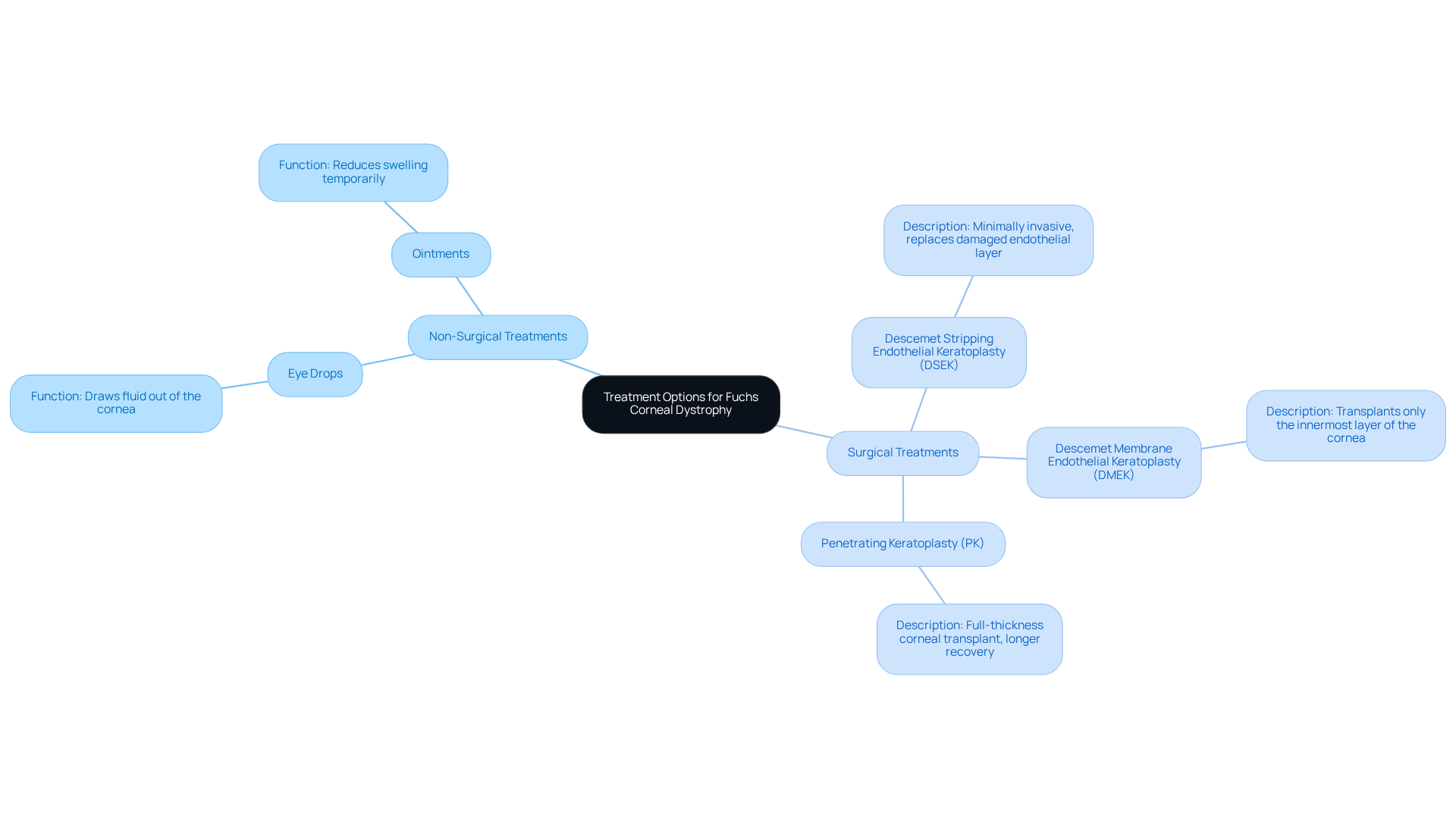
When it comes to , are thoughtfully tailored to match the severity of your condition. We understand that navigating this journey can be challenging, and we are here to help you through it. Treatment approaches encompass both non-surgical and , depending on your specific needs.
For those experiencing mild symptoms, such as eye drops or ointments can effectively draw fluid out of the cornea. These solutions may provide temporary relief, easing discomfort and enhancing vision. However, they do not address the underlying issue, which may necessitate further intervention as symptoms progress.
In cases where fuchs corneal dystrophy is more advanced, surgical options become essential. Here are a few procedures that may be recommended:
- Descemet Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK): This minimally invasive procedure replaces the damaged endothelial layer with healthy donor tissue, allowing for a quicker recovery compared to traditional methods.
- (DMEK): A refined technique, DMEK involves transplanting only the innermost layer of the cornea. This method significantly reduces recovery time and complications, making it a preferred choice for many.
- (PK): In severe instances, a full-thickness corneal transplant may be necessary. While PK can ensure better graft survival in some cases, it typically requires a longer recovery period.
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for and adjusting treatment as needed. We encourage you to engage in open discussions with your ophthalmologist to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored just for you. With , many patients report , often achieving 20/20 vision shortly after surgery. Remember, you are not alone in this process; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Fuchs corneal dystrophy is a progressive condition that primarily affects the cornea, leading to vision impairment due to the deterioration of endothelial cells. We understand that learning about this disorder is crucial, especially as its impact is expected to rise significantly in the coming years. By being aware of the symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options, you can empower yourself to seek timely care and manage your condition effectively.
This article highlights key aspects of Fuchs corneal dystrophy, including symptoms such as:
- Blurred vision
- Light sensitivity
- Glare
These symptoms can profoundly affect daily life. Diagnostic methods like slit-lamp examinations and pachymetry play a vital role in confirming the condition. Treatment options range from non-surgical interventions to advanced surgical procedures tailored to the severity of the disease. Regular eye exams and open communication with healthcare providers are essential for optimal management and preserving your vision.
Recognizing the significance of Fuchs corneal dystrophy is imperative, not only for you but also for your family and caregivers. As the prevalence of this condition continues to grow, staying informed about its symptoms, diagnostic techniques, and treatment options will help foster proactive health management. Engaging with healthcare professionals and utilizing available resources can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals navigating this eye disorder. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy (FCD)?
Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy is a progressive eye condition that affects the cornea, particularly the endothelial cells responsible for maintaining corneal clarity by pumping out excess fluid. The deterioration of these cells leads to fluid accumulation, swelling of the cornea, and vision impairment.
Who is most commonly affected by Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy?
Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy typically manifests in individuals over the age of 50, and it is often hereditary. In the U.S., approximately 1.12% of adults in this age group, or around 590,000 individuals, are affected.
What are the common symptoms of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy?
Common symptoms include glare from lights, halos around light sources, and difficulty driving at night, especially in low-light conditions. The presence of guttae, small deposits on the cornea, is also a characteristic feature of the condition.
What is the projected global impact of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy by 2050?
It is estimated that by 2050, over 415 million people globally will be affected by Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy, indicating a significant rise in the number of individuals impacted by this condition.
What was the economic burden of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy in 2019?
In 2019, the economic burden of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy was estimated at USD 291.648 million, underscoring the importance of effective management strategies for this condition.
What treatment options are available for Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy?
Treatment options for Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy range from eye drops to surgical procedures, such as endothelial keratoplasty, which can improve vision in more severe cases.
How does genetics influence the risk of developing Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy?
Genetic factors, particularly alterations in the TCF4 gene, play a crucial role in the development of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy. Family background can elevate the risk of developing this disorder.
Why are regular eye exams important for individuals at risk of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy?
Regular eye exams are essential for early detection and management of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy, allowing for timely interventions to help preserve vision.






