Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on October 18, 2025
Overview
This article highlights the importance of understanding external eye anatomy for cataract patients. We recognize that navigating this journey can be overwhelming, and knowing how these structures influence surgical outcomes and recovery is essential. Key components like the cornea, eyelids, and conjunctiva serve vital roles in protecting your eyes and ensuring their proper function. These elements are critical for successful cataract surgery and overall eye health.
We understand that you may have concerns about the procedure and what to expect during recovery. It’s common to feel apprehensive, but rest assured that having a solid grasp of these anatomical features can empower you in your healing process. By being informed, you can approach your surgery with confidence and peace of mind.
Remember, we are here to help you through this process. Your well-being is our priority, and we want you to feel supported every step of the way.
Introduction
Understanding the intricate structures of external eye anatomy is essential, especially for those facing cataract surgery. We recognize that this can be a daunting experience. The visible components, including the eyelids, cornea, and conjunctiva, play pivotal roles in protecting the eye and ensuring optimal vision.
It’s common to feel uncertain about how these elements influence surgical outcomes and recovery. Exploring this connection can empower you to take control of your eye health. We are here to help you navigate the complexities of your upcoming procedure with confidence.
Define External Eye Anatomy
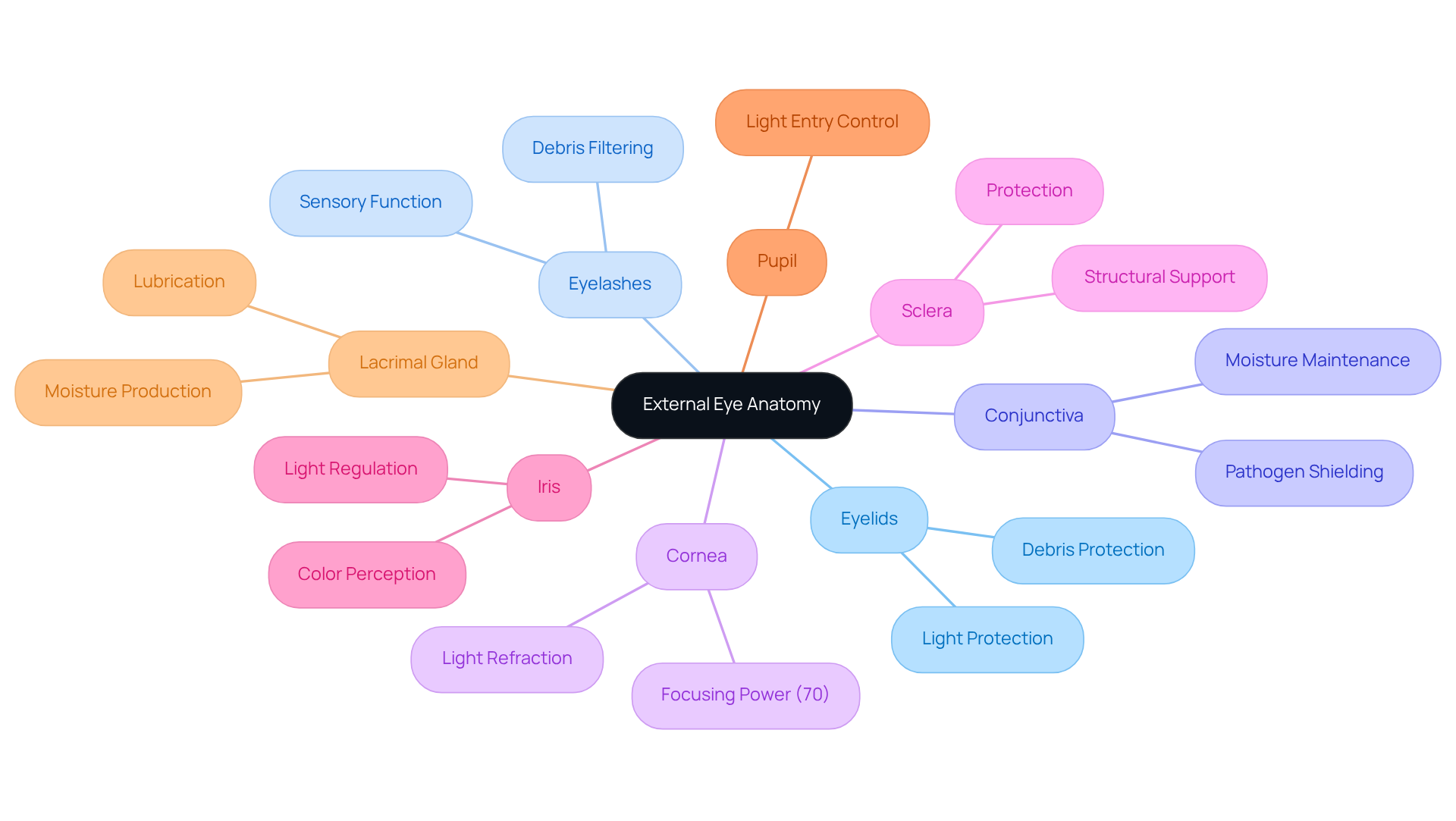
External eye anatomy encompasses the visible structures that are crucial for eye function and protection. These include the eyelids, eyelashes, conjunctiva, cornea, sclera, iris, and pupil. Each component plays a critical role in safeguarding the eye and facilitating vision. For instance, the cornea serves as the clear front layer that refracts light, contributing significantly to the eye’s focusing power. In fact, approximately 70% of this power comes from the cornea.
We understand that the eyelids protect the eye from debris and excessive light, while the conjunctiva helps maintain moisture and shields against pathogens. Additionally, the lacrimal gland, located under the outside edge of the eyebrow, plays a vital role in keeping the eye lubricated. For individuals facing cataracts, comprehending these structures is essential, as they can affect surgical results and recovery.
It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the thought of surgery. The integrity of the external eye anatomy is crucial for influencing the precision of cataract surgery, making it important for individuals to understand how these components interact during the procedure. Current insights from ophthalmologists highlight that a thorough understanding of external eye anatomy aids not only in surgical planning but also enhances patient education and expectations regarding recovery and visual outcomes.
As Wayne Chirisa aptly states, ‘Clear vision is not just a gift, it’s a responsibility to protect through conscious care.’ We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you feel supported and informed every step of the way.
Importance of External Eye Anatomy in Eye Health
The external structure of the eye plays a crucial role in maintaining eye wellness and functionality. We understand that structures such as the eyelids and eyelashes act as the primary barrier against environmental threats, effectively preventing foreign particles from entering the eye. The conjunctiva, a fragile membrane that covers the eye, not only retains moisture but also acts as a barrier against infections. This emphasizes its significance in overall eye well-being.
For patients with lens opacity, understanding the protective roles of these external structures is essential. Any disruption can complicate both the surgical procedure and the recovery process. Maintaining optimal vision condition is vital for achieving successful surgical outcomes, which underscores the importance of awareness regarding external eye anatomy. As vision care experts note, ‘The integrity of these structures significantly influences the effectiveness of lens surgery.’ This underscores their essential role in overall eye wellness.
Moreover, it’s common to feel concerned about the inappropriate application of eye cosmetics, which can pose dangers to eyelash condition. This is especially significant for individuals preparing for cataract surgery. Comprehending these factors can assist patients in taking proactive measures to safeguard their vision. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you feel supported every step of the way.
Components of External Eye Anatomy and Their Functions
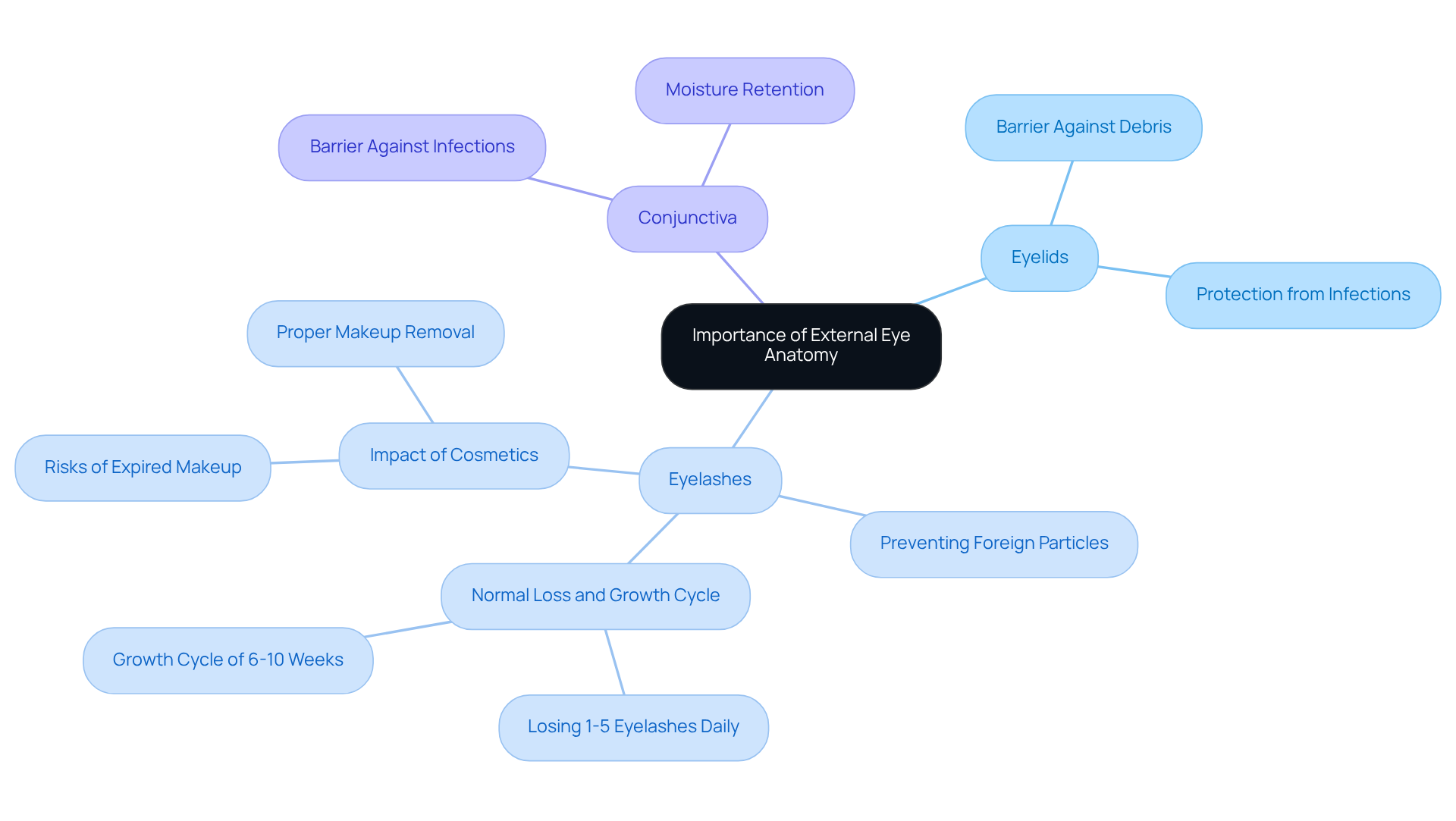
The main components of external eye anatomy include:
-
Eyelids: These structures protect the eye from injury and facilitate the distribution of tears across the eye’s surface, ensuring proper lubrication and comfort. We understand how important it is for your eyes to feel comfortable and safe.
-
Eyelashes: Acting as a barrier against dust and debris, eyelashes trigger a blink reflex when touched, which helps to protect the external eye anatomy from potential harm. It’s common to feel concerned about the smallest irritants, but your eyelashes are there to help keep your eyes protected.
-
Conjunctiva: This mucous membrane maintains moisture in the eye and serves as a protective layer against pathogens, contributing to the overall health of the external eye anatomy. Knowing that your eyes have this additional layer of defense can be reassuring.
-
Cornea: The transparent front part of the eye, the cornea is essential for refracting light and is a crucial element of the external eye anatomy that plays a pivotal role in focusing vision. Its refractive index, usually about 1.376, is crucial for ideal light bending, especially during lens surgery. The introduction of advanced intraocular lenses, such as the Light Adjustable Lens (LAL), allows for post-operative adjustments, enhancing refractive outcomes and providing a personalized approach to vision correction. We are here to support you through this process, ensuring you understand how these advancements can benefit your vision.
-
Sclera: The sclera, or the white outer layer of the eye, provides structural integrity and protection, which is essential for the external eye anatomy and safeguarding its internal components. This sturdy layer is vital for maintaining the overall health of your eyes.
The external eye anatomy features the iris, the colored part of the eye that regulates the size of the pupil, controlling the amount of light that enters the eye and is vital for clear vision. The LAL technology works in conjunction with the iris to optimize light entry and improve visual outcomes post-surgery. We recognize that understanding these interactions can help ease your mind.
- Pupil: This opening in the center of the iris adjusts in size to manage light entry, playing a critical role in visual acuity. The adaptability of the pupil enhances the modifications facilitated by the LAL, ensuring that individuals attain optimal vision. It’s comforting to know that your body has such intricate systems in place to support your sight.
Each of these elements works together to guarantee clear sight and safeguard the eye, which is particularly relevant for individuals undergoing lens surgery in relation to the external eye anatomy. Comprehending the complex functions of these anatomical characteristics, along with the advantages of advanced technologies like the LAL, can improve individual awareness and readiness for their procedures. Remember, we are here to help you navigate this journey, ensuring you feel informed and supported every step of the way.
Common Conditions Affecting External Eye Anatomy
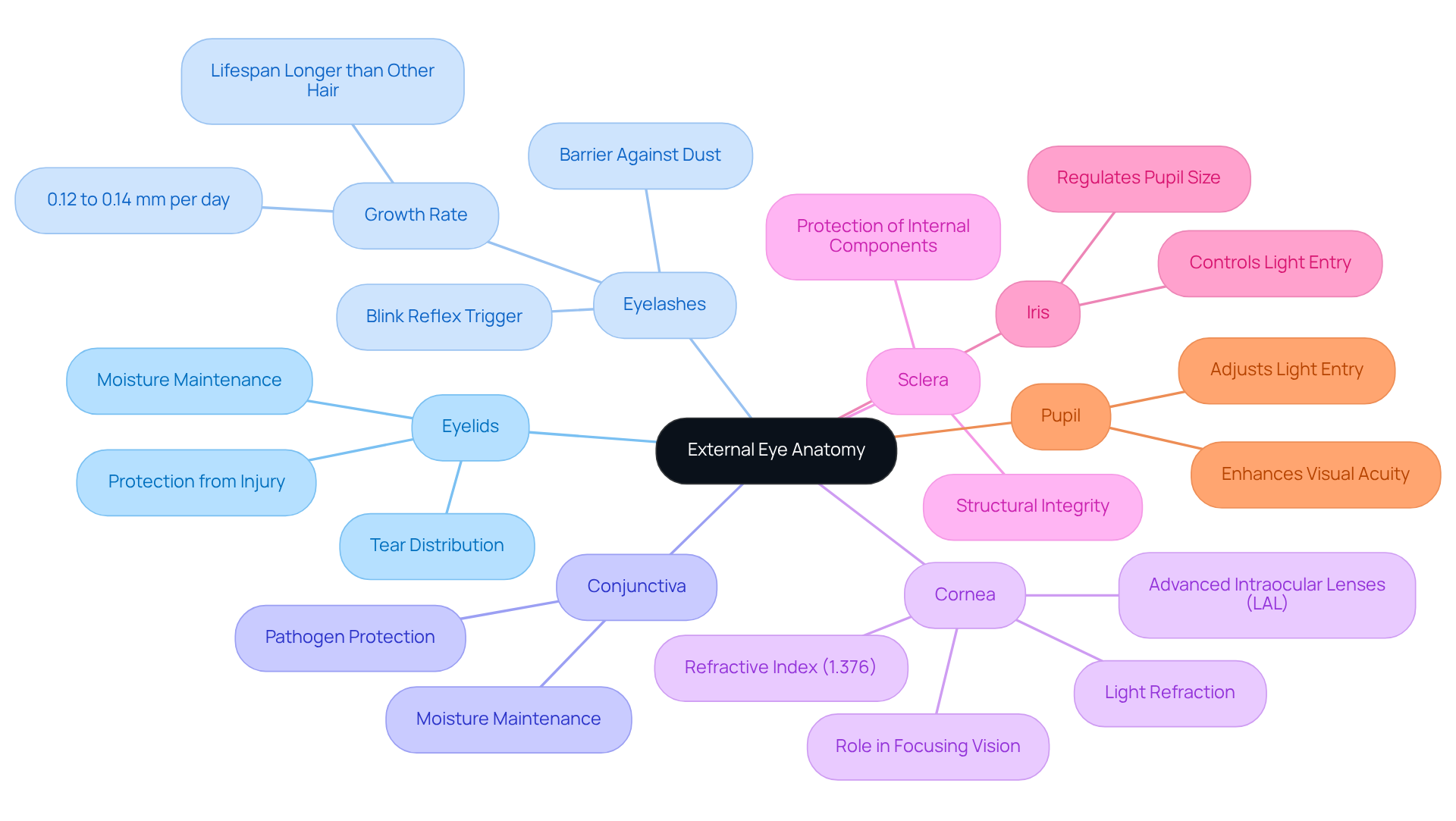
Several prevalent conditions can significantly affect external eye anatomy, especially in cataract patients. It’s important to be aware of these issues, as they can affect your comfort and recovery. Here are a few conditions you should know about:
-
Blepharitis: This inflammation of the eyelids often results in irritation, redness, and discomfort. We understand that dealing with this common issue can be frustrating; studies indicate that 37% to 47% of individuals seen by eye care professionals are diagnosed with this condition. Managing blepharitis is essential, as it can complicate lens surgery and recovery.
-
Conjunctivitis: Known as pink eye, conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the conjunctiva and can arise from infections or allergies. It’s prevalent, with approximately 6 million cases reported annually in the U.S. The condition peaks in spring, particularly among children, highlighting the need for awareness and preventive measures. We recognize that this can be concerning for parents.
-
Dry Eye Syndrome: This condition occurs when the eyes fail to produce sufficient tears, leading to discomfort and potential damage to the ocular surface. It’s estimated that 10-20% of individuals over 40 experience moderate to severe symptoms. We understand how uncomfortable this can be, and it’s crucial to manage dry eye effectively, especially during lens surgery.
-
Pterygium: A growth of tissue on the conjunctiva that may extend onto the cornea, pterygium can affect vision and is often associated with prolonged sun exposure. Comprehending its consequences is essential for individuals with lens opacities, as we want to ensure you have all the information you need.
-
Corneal Abrasions: Scratches on the cornea can cause significant pain and sensitivity to light. These abrasions can complicate the surgical process and recovery, necessitating prompt medical attention. We understand that this can be alarming, but seeking help quickly can make a difference.
For individuals with cataracts, understanding external eye anatomy and awareness of these conditions is crucial. By understanding potential complications, you can seek timely medical intervention. Remember, we are here to help you through this process, ultimately enhancing your overall eye health and surgical outcomes.
Conclusion
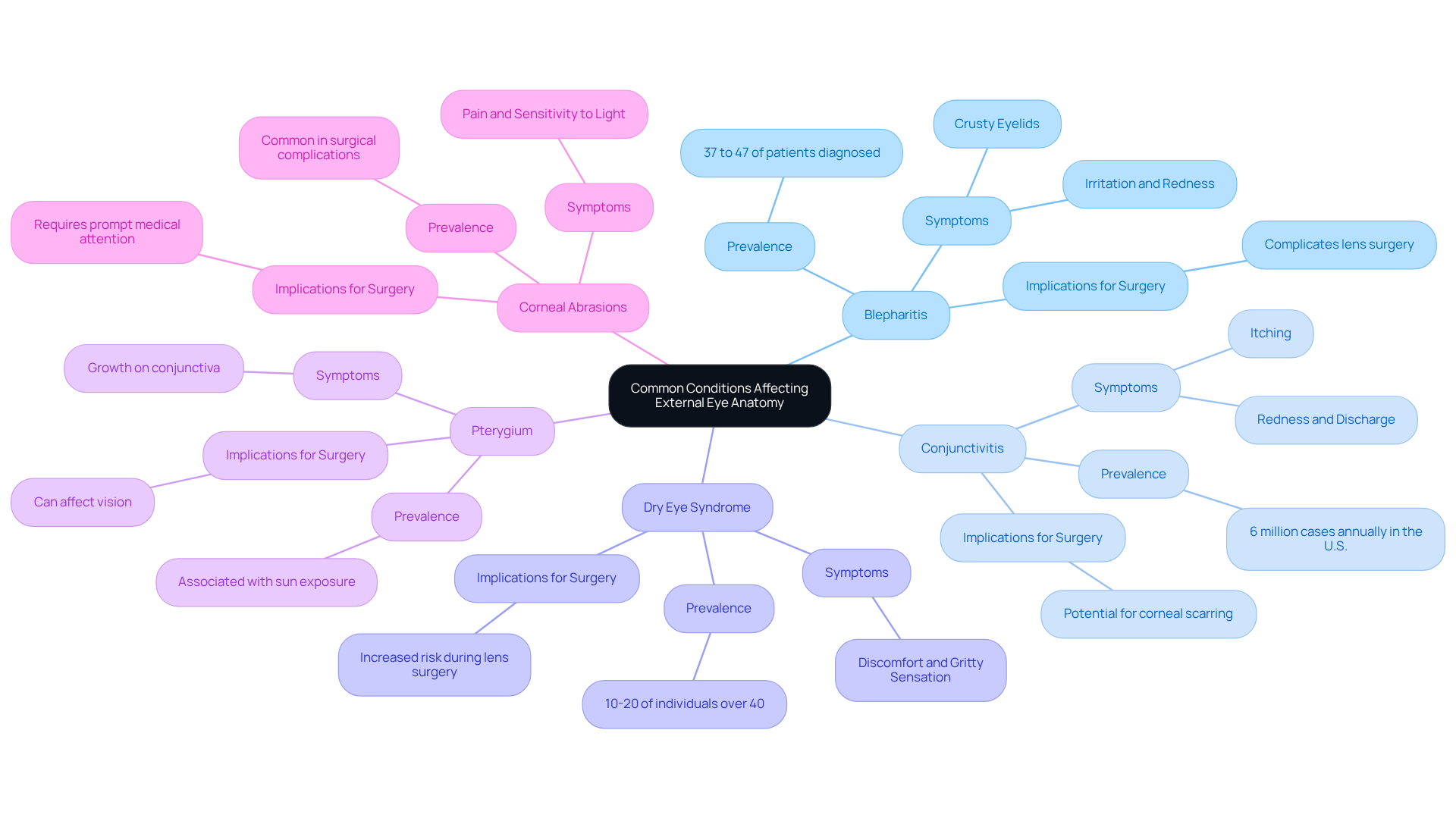
Understanding external eye anatomy is vital for cataract patients. It encompasses the protective and functional structures of the eye that play a crucial role in vision and overall eye health. By grasping the significance of components such as the eyelids, eyelashes, conjunctiva, cornea, and sclera, individuals can better appreciate how these elements contribute to maintaining clear sight and safeguarding the eye during surgical procedures.
We understand that navigating this information can feel overwhelming. The article highlights the intricate interrelationship between these anatomical structures and their functions. Each component is essential for optimal eye wellness, from the protective barriers provided by the eyelids and eyelashes to the critical refractive role of the cornea. Additionally, awareness of common conditions like blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and dry eye syndrome underscores the need for patients to be informed and proactive about their eye health.
In light of this information, it is clear that a comprehensive understanding of external eye anatomy enhances patient education. It empowers individuals to take charge of their eye health. As you prepare for cataract surgery, fostering this knowledge can lead to improved outcomes and a more confident approach to your vision care journey. Embracing the responsibility of eye health through education and awareness can make a significant difference in achieving clear and comfortable vision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is external eye anatomy?
External eye anatomy refers to the visible structures of the eye that are essential for its function and protection, including the eyelids, eyelashes, conjunctiva, cornea, sclera, iris, and pupil.
What role does the cornea play in eye function?
The cornea is the clear front layer of the eye that refracts light, contributing significantly to the eye’s focusing power, with approximately 70% of this power coming from the cornea.
How do the eyelids and conjunctiva protect the eye?
The eyelids protect the eye from debris and excessive light, while the conjunctiva helps maintain moisture and shields against pathogens.
What is the function of the lacrimal gland?
The lacrimal gland, located under the outside edge of the eyebrow, is responsible for keeping the eye lubricated.
Why is understanding external eye anatomy important for individuals facing cataract surgery?
Understanding external eye anatomy is crucial for individuals facing cataract surgery as it influences the precision of the surgery and impacts recovery outcomes.
How does knowledge of external eye anatomy benefit surgical planning and patient education?
A thorough understanding of external eye anatomy aids in surgical planning and enhances patient education and expectations regarding recovery and visual outcomes.
What is the significance of the quote by Wayne Chirisa regarding vision?
Wayne Chirisa’s quote emphasizes that clear vision is a responsibility that requires conscious care to protect one’s eye health.






