Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on August 17, 2025
Overview
Bulging eye disease, often referred to as proptosis or exophthalmos, can be a source of concern for many. It is primarily associated with thyroid-related conditions, especially Graves’ disease. We understand that experiencing symptoms such as eye protrusion, discomfort, and vision problems can be distressing.
Recognizing the importance of early diagnosis is crucial. Tailored treatment options are available, including:
- Medications
- Surgery
- Lifestyle changes
These approaches can effectively manage the condition and help prevent serious complications. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
We are here to help you through this process, offering support and guidance every step of the way. It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but with the right care, you can find relief and regain control of your health.
Introduction
Bulging eye disease, clinically known as proptosis, can understandably raise alarm due to its cosmetic implications and potential underlying health risks. This condition, characterized by the protrusion of one or both eyes, may arise from various causes, including:
- Thyroid disorders
- Tumors
- Infections
Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial, and we understand that this can be a concerning experience. With numerous potential triggers and treatment options available, it’s common to feel overwhelmed. Understanding the complexities of bulging eye disease is essential for effective management and improved outcomes, and we are here to help you through this process.
Define Bulging Eyes: Understanding Proptosis
, also clinically referred to as proptosis or exophthalmos, occurs when one or both eyes protrude from their normal position within the eye socket. We understand that can be both a cosmetic concern and an indication of underlying health issues. Proptosis can arise from various factors, including inflammation, tumors, and glandular disorders, particularly bulging eye disease, which is among the most frequent causes. In fact, studies indicate that bulging eye disease can lead to , including noticeable eye protrusion and discomfort.
Comprehending bulging eye disease is essential for recognizing its symptoms, which may include:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Difficulty closing the eyes
It’s common to feel anxious about these symptoms, as they may signify or tumors. For example, , which may arise from conditions like cataracts or diabetic retinopathy, can also be a sign of eye bulging. Symptoms left untreated can lead to serious health complications, such as bulging eye disease, emphasizing the importance of seeking .
Care for the bulging eye disease is tailored to the root issue. In cases involving gland disorders, anti-gland medications or surgery may be necessary. Surgical intervention is often considered when bulging eye disease threatens vision or causes corneal damage, typically involving the removal of bone from behind the eye socket to relieve pressure. Additionally, eye drops or ointments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and discomfort. We encourage and avoiding irritants, as they are also important for effectively managing symptoms.
Recent case studies, like those assessing the monoclonal antibody veligrotug, have shown encouraging outcomes in addressing . The THRIVE and THRIVE-2 trials demonstrated considerable enhancements in the treatment of bulging eye disease and associated symptoms, with responder rates of 70% for the veligrotug group compared to 5% for the placebo group. This highlights the significance of continuous research and progress in treatment alternatives.
In summary, bulging eye disease is a serious issue that requires careful evaluation and management. Regular follow-ups with an ophthalmologist are essential for monitoring symptoms and ensuring appropriate treatment, as . We are here to help you through this process.
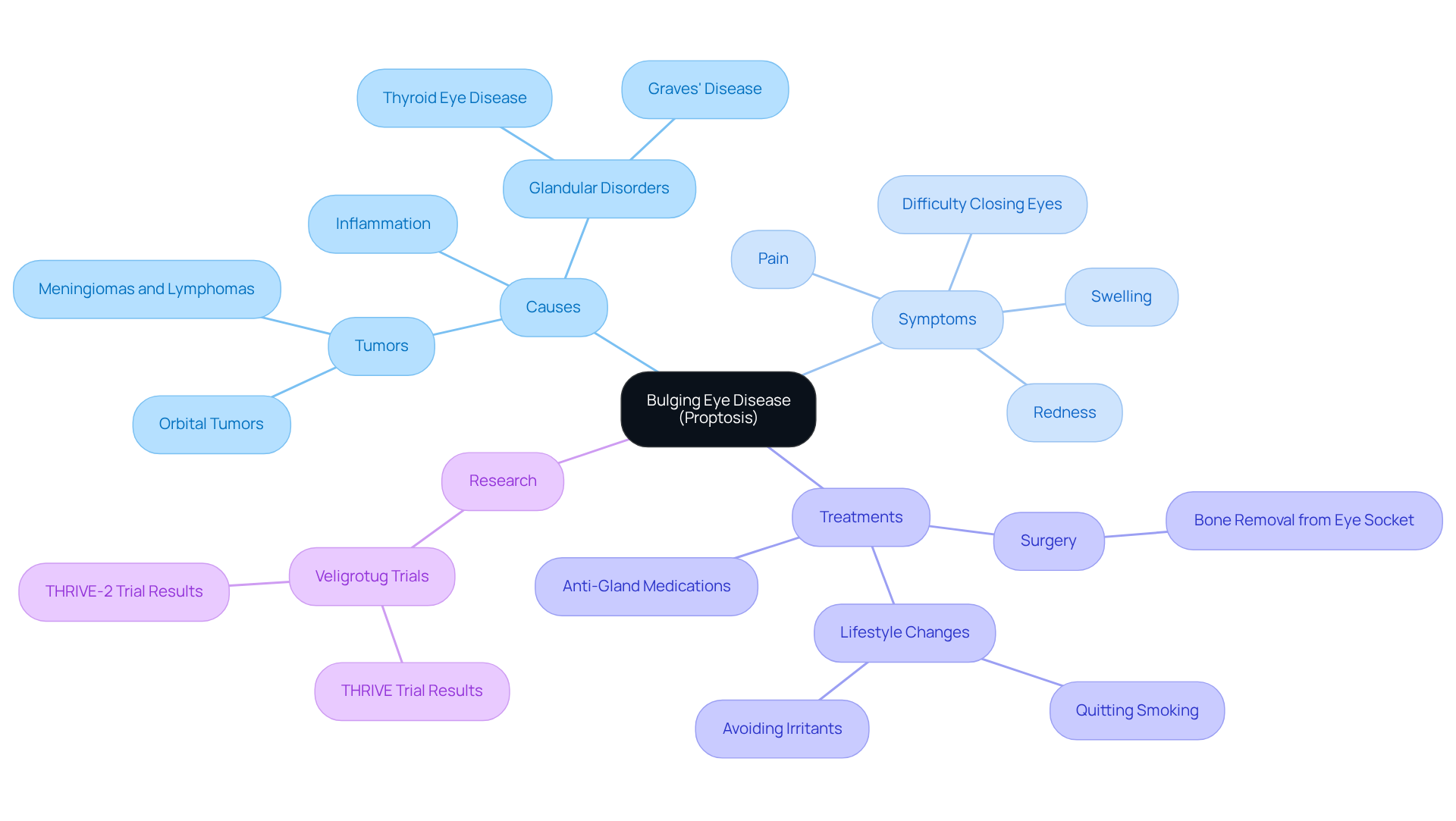
Identify Causes: Thyroid Eye Disease and Beyond
The primary reason for protruding eyes is (TED), primarily associated with , an autoimmune condition affecting the thyroid gland. This condition is characterized by , often leading to visible protrusion. We understand that this can be concerning; in fact, approximately 50% of individuals with Graves’ disease develop TED, highlighting the between these two conditions. Notably, the annual incidence of TED is 16.0 in 100,000 for females and 2.9 in 100,000 for males in the US population, indicating a higher prevalence among women.
Other significant causes of include:
- : An overactive thyroid can lead to swelling behind the eyes, with about 90% of TED cases being hyperthyroid.
- Orbital tumors: Growths within the eye socket can exert pressure on the eyeball, resulting in as they push it forward.
- Infections: Such as orbital cellulitis, can result in inflammation and swelling, which may lead to bulging eye disease with noticeable eye protrusion.
- Injuries: To the eye area may also result in bulging eye disease, necessitating prompt medical evaluation.
Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management and treatment. For instance, a case study involving a 40-year-old woman with Graves’ disease illustrated how can significantly improve patient outcomes. Additionally, statistics indicate that the incidence of TED is notably higher in females, particularly between the ages of 40 and 64. This underscores the importance of awareness and early detection in at-risk populations.
As emphasized by healthcare experts, identifying the signs linked to hyperthyroidism, such as palpitations and weight loss, is crucial for diagnosing underlying thyroid conditions that may result in protruding eyes. It’s common to feel anxious about these symptoms, so prompt medical attention is advised for individuals experiencing them, as they can indicate the onset of TED or other serious conditions. Furthermore, it is important to note that (DON) occurs in 4 to 10% of TED patients, and untreated TED can lead to permanent vision loss, emphasizing the urgency of seeking medical attention. We are here to help you through this process.
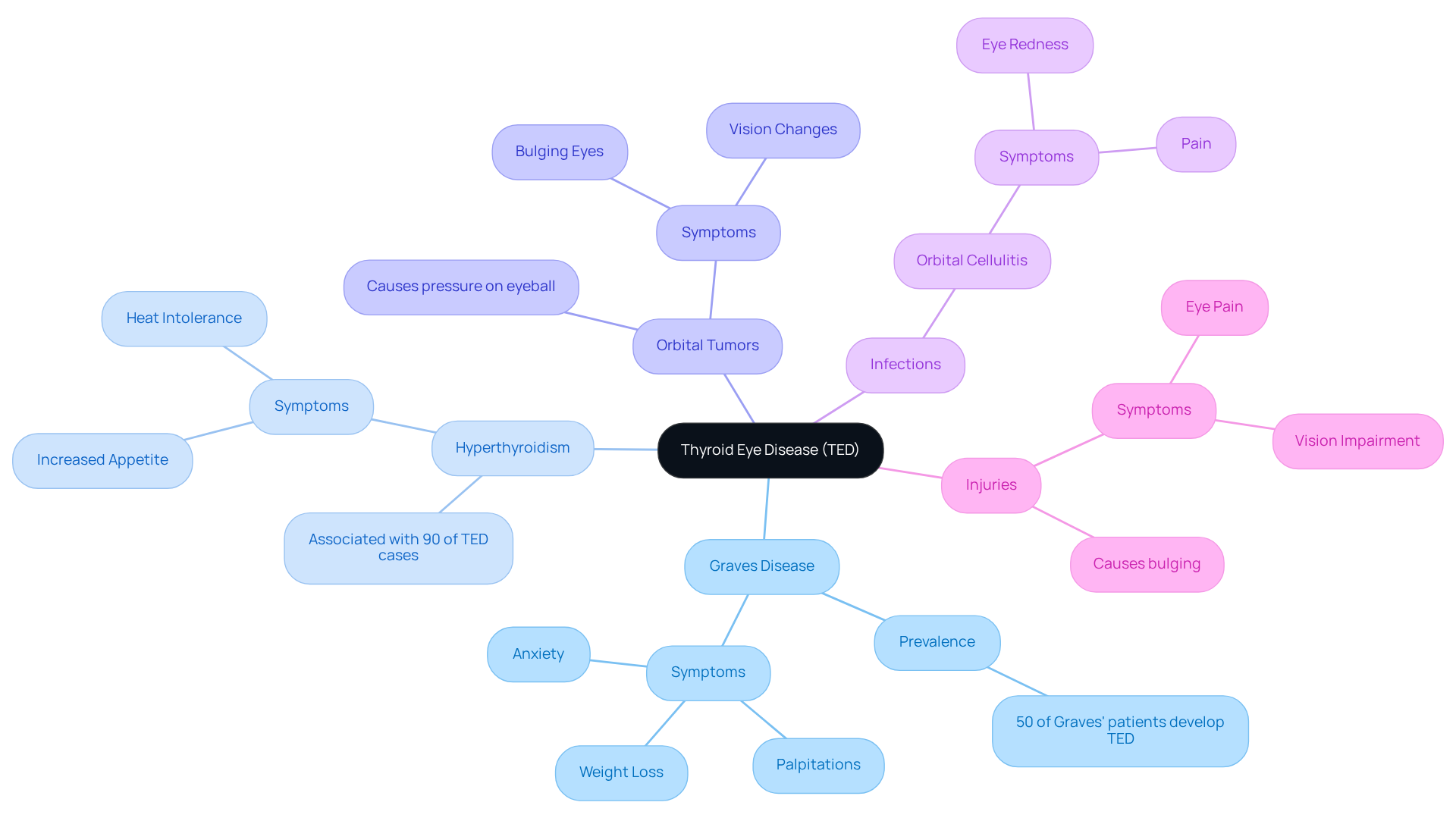
Recognize Symptoms: Signs of Bulging Eyes
Symptoms of bulging eye disease, also known as proptosis, can manifest in various ways, and we understand how concerning this can be for you. Here are some common :
- : The eyeball appears more prominent than usual, which can be alarming for many individuals.
- : Patients often report discomfort or a gritty sensation, which can significantly impact daily activities.
- : Misalignment of the visual organs may lead to visual disturbances, complicating tasks such as reading or driving.
- : This can lead to exposure-related problems, heightening the risk of corneal injury.
- : Some individuals may experience discomfort around the eyes, which can be indicative of underlying issues.
Identifying these symptoms promptly is essential. We understand that seeking help can feel daunting, but can avert complications linked to issues such as (TED). Research indicates that bulging eye disease affects approximately 60% of individuals with TED, highlighting the need for awareness and timely intervention. Furthermore, studies show that can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Remember, we are here to help you through this process, so if you notice any of these signs, please don’t hesitate to seek help.
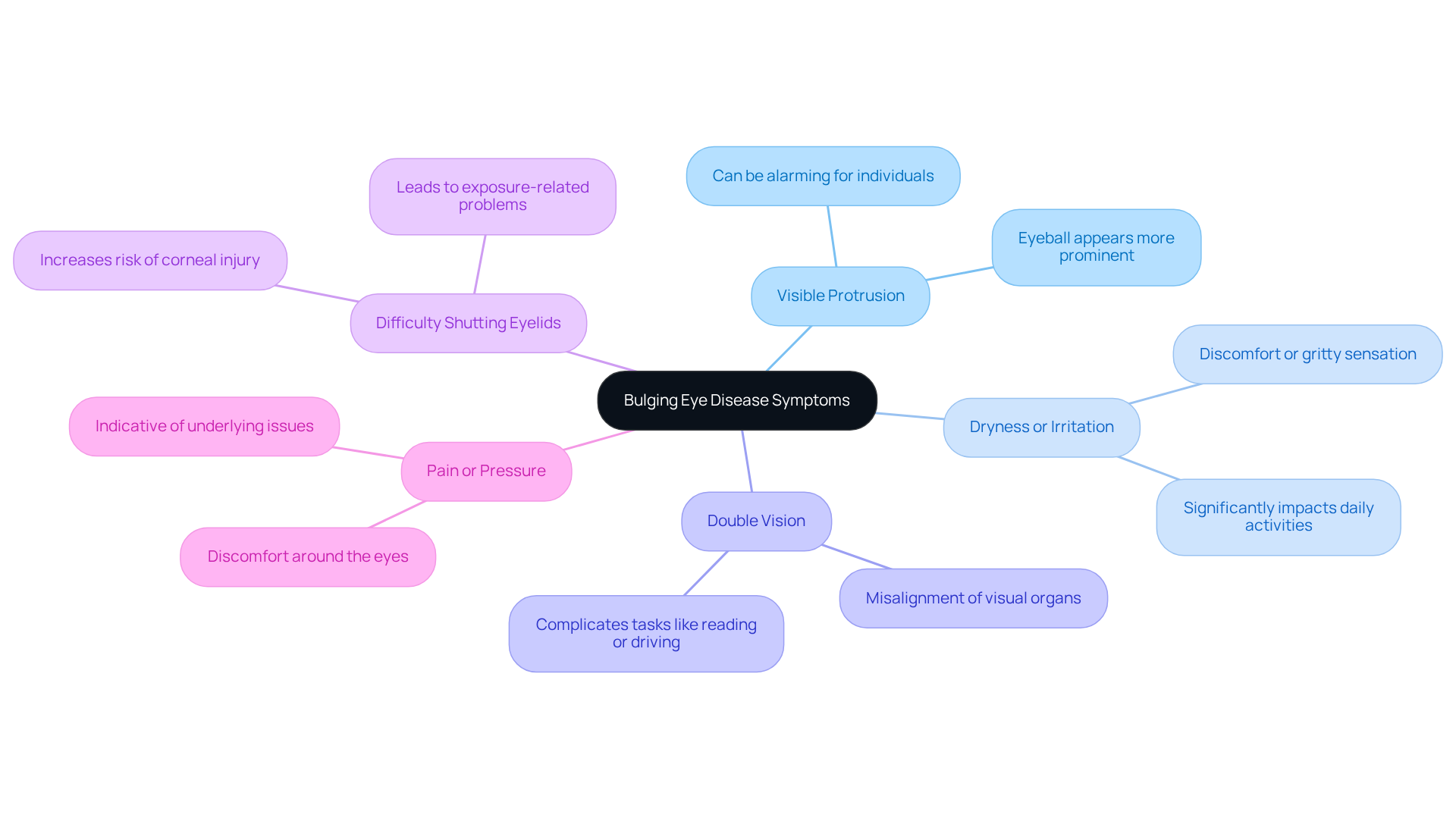
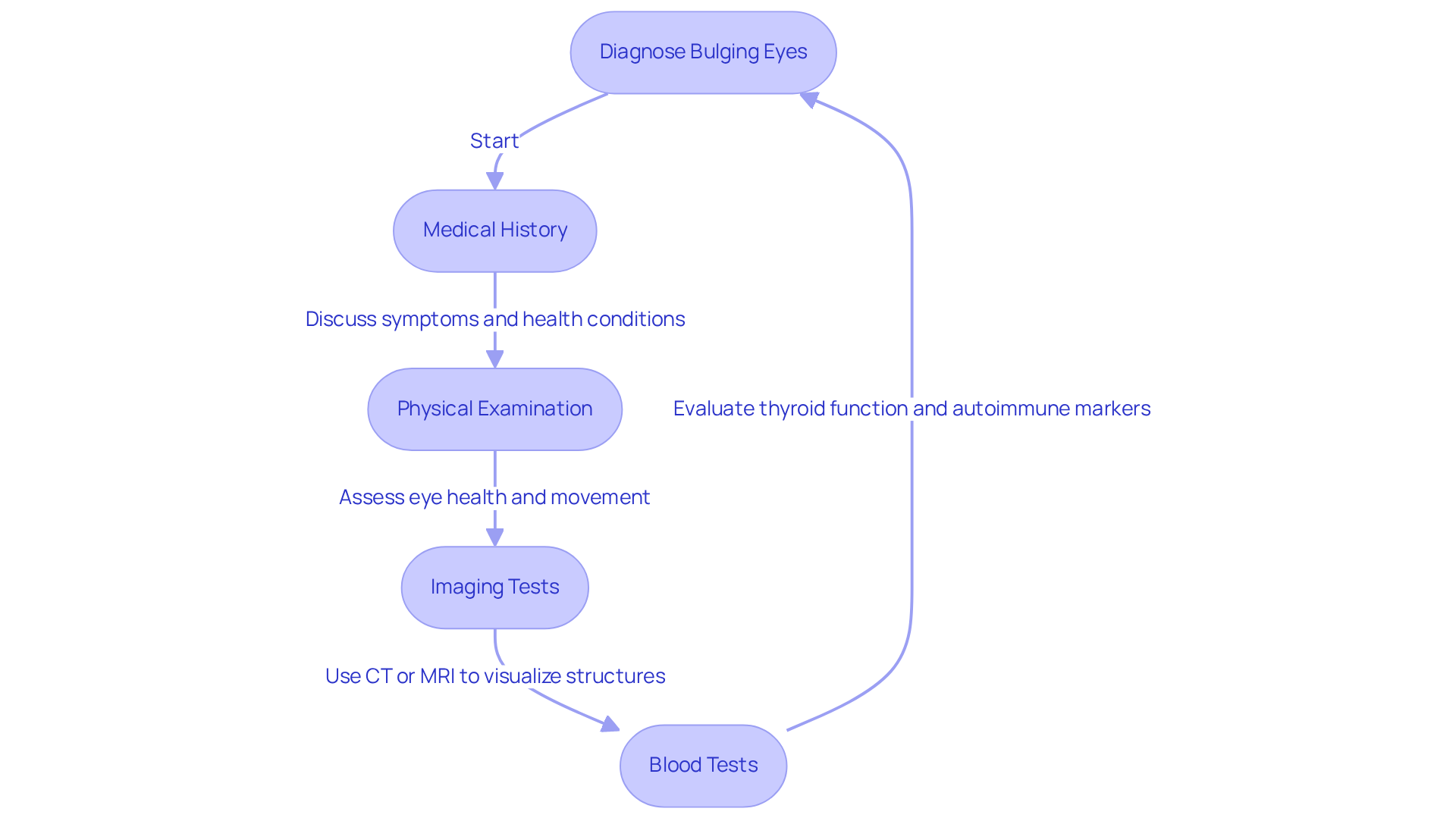
Diagnose Bulging Eyes: Testing and Evaluation
Diagnosing requires a thorough evaluation that encompasses several key components.
We understand that this can be a concerning time for you, so let’s walk through the process together.
- Medical History: A and any is essential. This helps us identify potential causes of proptosis, such as , , or tumors.
- Physical Examination: An eye specialist will assess the degree of protrusion and overall eye health, including eye movement and visual acuity. This examination is crucial for determining the severity of your condition.
- Imaging Tests: , such as contrast-enhanced orbital CT scans or MRIs, are vital for visualizing the structures behind your eyes. These tests can reveal underlying issues like tumors or inflammation, which are common causes of exophthalmos. As noted by specialists, imaging is critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Blood Tests: These tests help evaluate thyroid function and detect autoimmune markers, particularly in cases linked to Graves’ disease, the most prevalent cause of exophthalmos.
This not only ensures an accurate diagnosis but also informs tailored treatment options, enhancing patient outcomes. We want to reassure you that are essential for managing your condition effectively.
It’s important to recognize that bulging eye disease, which is also referred to as exophthalmos, can lead to complications if not diagnosed and treated early, highlighting the urgency of the evaluation process. Additionally, we understand that the emotional effects of eye bulging can influence your confidence and mental well-being, making a comprehensive approach to treatment crucial.
Comprehending the reasons for eye bulging can be supported by the acronym VITAMIN CE, which classifies possible underlying factors. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Explore Treatment Options: Managing Bulging Eyes
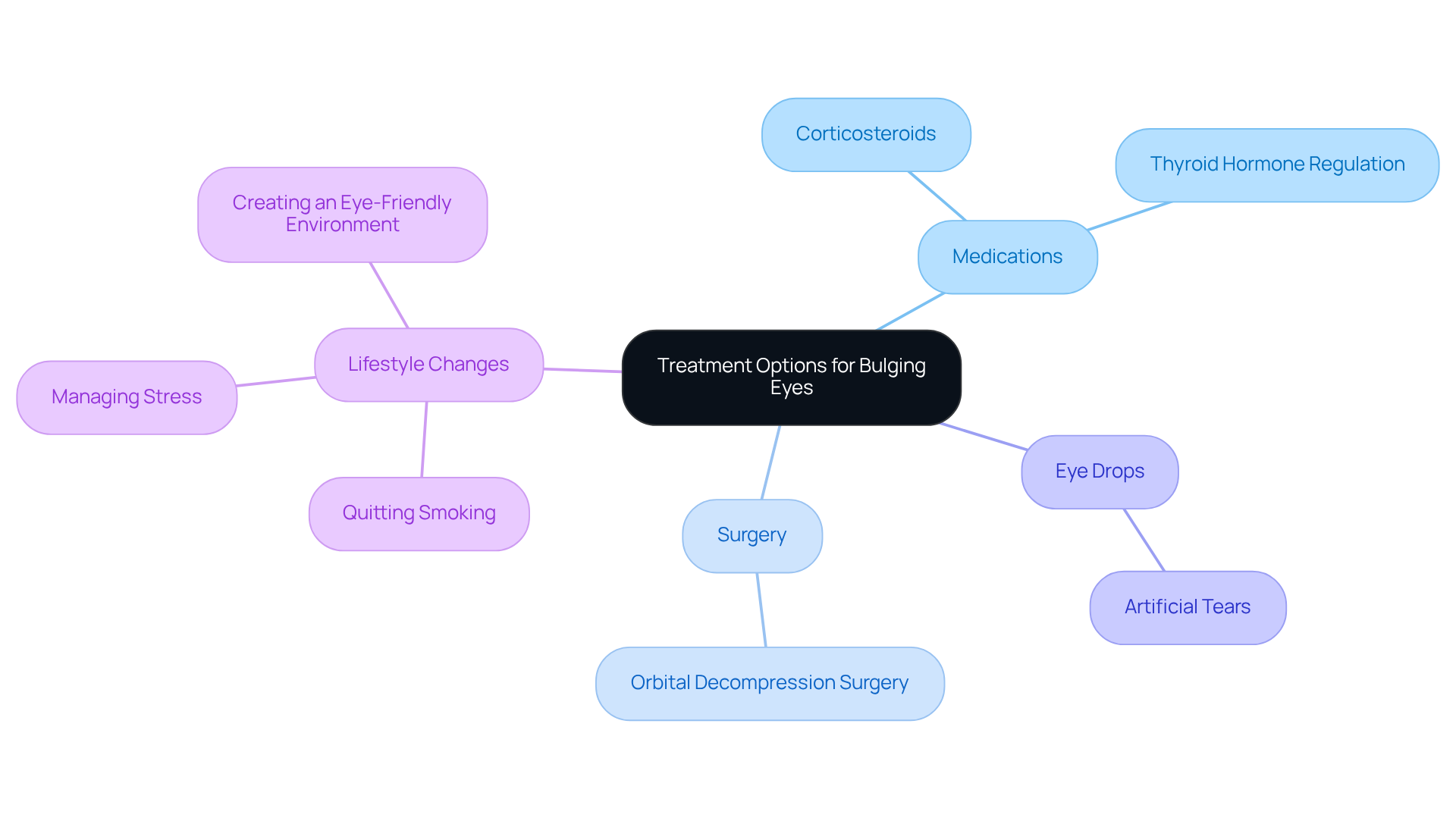
Treatment for , which is also referred to as proptosis, is tailored to the underlying cause and may involve several approaches. We understand that dealing with this condition can be challenging, and we are here to help you through this process.
- Medications: Corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation associated with (TED). Regulating thyroid hormone levels is also crucial for managing symptoms effectively. It’s reassuring to know that recent studies indicate patients who adhere to experience .
- Surgery: In more severe cases, may be performed to relieve pressure within the orbit and enhance the aesthetic appearance of the eyes. Many patients report promising success rates, including improved visual function and reduced proptosis post-surgery.
Eye drops, particularly , can be beneficial for alleviating dryness and irritation, providing immediate relief for those experiencing discomfort due to . It’s common to feel discomfort, and these drops can make a difference.
- Lifestyle Changes: Implementing , such as quitting smoking and managing stress, can significantly improve symptoms. We encourage you to create an eye-friendly environment, which includes maintaining optimal humidity levels and reducing exposure to irritants.
Consulting with an is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses your individual needs and conditions. Regular follow-ups and evaluations are crucial for monitoring progress and adjusting treatment strategies as necessary. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available at every step.
Conclusion
Bulging eye disease, also known as proptosis, is more than just a cosmetic concern; it can signify serious underlying health issues such as thyroid disorders, tumors, or infections. We understand that this condition can be distressing, and recognizing the complexities of bulging eyes is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. This not only supports physical health but also nurtures emotional well-being for those affected.
In this article, we explored various aspects of bulging eye disease, including its causes, symptoms, diagnostic processes, and treatment options. It’s important to be aware of symptoms like visible protrusion, dryness, and discomfort. Early medical intervention plays a critical role in managing this condition. Tailored treatment approaches—whether through medication, surgery, or lifestyle changes—can significantly improve patient outcomes and enhance quality of life.
Ultimately, awareness and understanding of bulging eye disease are paramount. If you are experiencing symptoms, we encourage you to seek professional evaluation promptly. Early detection can prevent complications and enhance treatment efficacy. By staying informed and proactive, you can navigate the challenges associated with bulging eyes, paving the way towards better health and well-being. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is bulging eye disease?
Bulging eye disease, also known as proptosis or exophthalmos, occurs when one or both eyes protrude from their normal position within the eye socket. It can be a cosmetic concern and may indicate underlying health issues.
What are the symptoms of bulging eye disease?
Symptoms of bulging eye disease may include pain, redness, swelling, and difficulty closing the eyes. Blurred vision can also be a sign of eye bulging.
What are the common causes of bulging eyes?
The primary cause of bulging eyes is thyroid-related disease (TED), particularly associated with Graves’ disease. Other causes include hyperthyroidism, orbital tumors, infections like orbital cellulitis, and injuries to the eye area.
How is bulging eye disease treated?
Treatment for bulging eye disease is tailored to the underlying cause. It may involve anti-gland medications, surgery to relieve pressure, eye drops or ointments to reduce inflammation, and lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking.
What recent advancements have been made in treating bulging eye disease?
Recent studies, such as the THRIVE and THRIVE-2 trials, have shown promising results with the monoclonal antibody veligrotug, demonstrating significant improvements in symptoms related to bulging eye disease.
Why is early detection of bulging eye disease important?
Early detection is crucial as it can significantly improve outcomes. Regular follow-ups with an ophthalmologist are essential for monitoring symptoms and ensuring appropriate treatment.
Who is most at risk for developing thyroid eye disease?
Approximately 50% of individuals with Graves’ disease develop thyroid eye disease, with a higher prevalence among women, particularly those aged 40 to 64.
What should individuals do if they experience symptoms of bulging eyes?
Individuals experiencing symptoms such as palpitations, weight loss, or noticeable eye protrusion should seek prompt medical attention, as these can indicate underlying thyroid conditions or other serious issues.






