Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on July 22, 2025
Overview
This article is dedicated to helping you understand the causes of eye pain, along with the symptoms and treatment options available. We recognize that experiencing eye pain can be distressing, and it’s important to know that you’re not alone.
Eye pain can arise from various sources, including:
- Dry eye syndrome
- Conjunctivitis
- More serious conditions like glaucoma
By recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical help, you can take proactive steps to prevent complications. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Introduction
Eye pain can be a complex and often distressing experience, signaling a range of underlying conditions, from minor irritations to more serious health issues. We understand that this discomfort can be worrying, and recognizing the various causes of eye discomfort is crucial. By doing so, you empower yourself to identify symptoms and seek appropriate treatment.
However, with so many potential triggers—from dry eyes and infections to more severe conditions like glaucoma—it’s common to feel uncertain about what constitutes a harmless annoyance versus a medical emergency.
This article delves into the fundamentals of eye pain, exploring its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment strategies. We are here to help you navigate this often-overlooked aspect of your health.
Explore the Fundamentals of Eye Pain
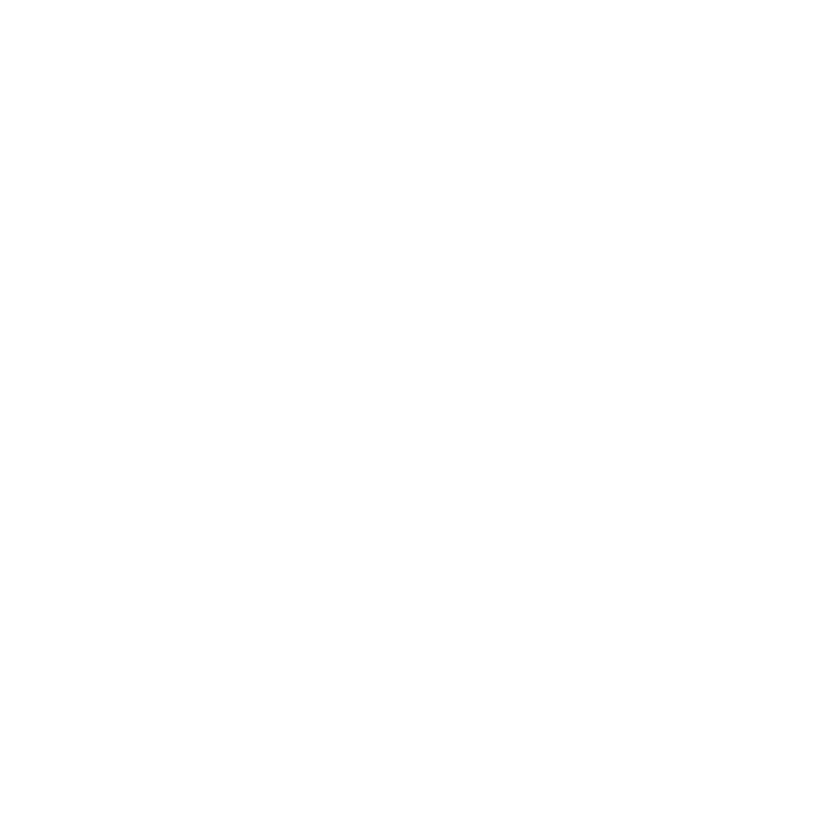
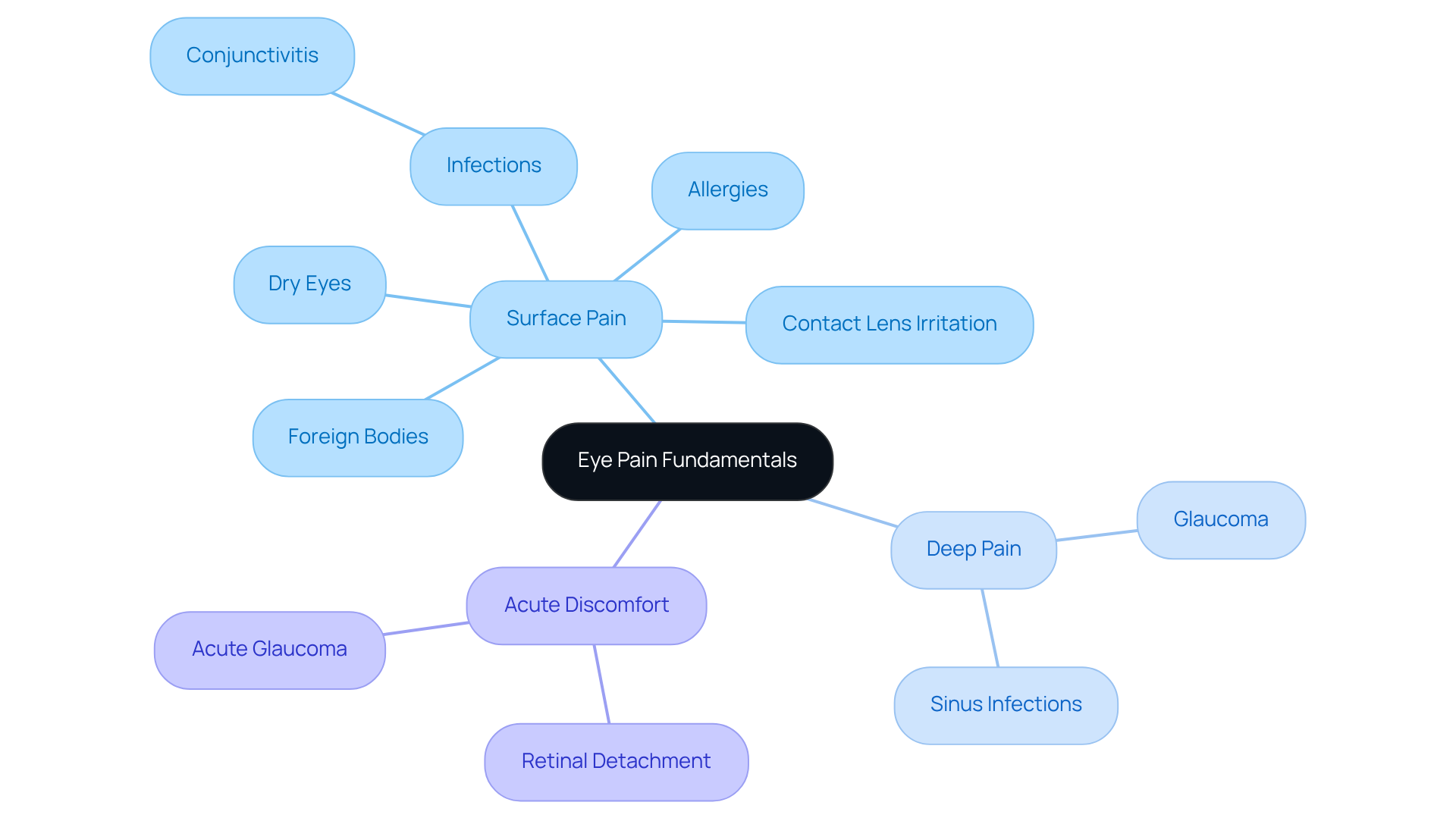
Eye discomfort can manifest in various forms, including sharp, throbbing, or dull sensations. It may originate from the surface of the eye or deeper structures. We understand that comprehending the nature of is essential, as they can indicate underlying conditions ranging from minor irritations to serious health issues. Here are some common types of eye pain you might experience:
- Surface Pain: Often described as burning or stinging, this type of discomfort is typically associated with dry eyes, foreign bodies, or infections such as conjunctivitis. Allergies and eye infections can also lead to sore, red, and itchy eyes, which may worsen with excessive rubbing. Contact lens irritation is another frequent source of surface discomfort.
- Deep Pain: This may feel like pressure or aching and can be linked to various eye pain causes such as glaucoma or sinus infections.
- Acute Discomfort: Sudden and intense distress may suggest emergencies such as retinal detachment, acute glaucoma, or other eye pain causes.
Recognizing these distinctions helps in identifying the urgency of the situation and the need for medical intervention. It’s common to feel overwhelmed by these symptoms, but addressing them is crucial to prevent severe health issues, such as keratoconus and thyroid eye disease. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, please seek professional medical help immediately. We are here to help you through this process.
Identify Common and Uncommon Causes of Eye Pain
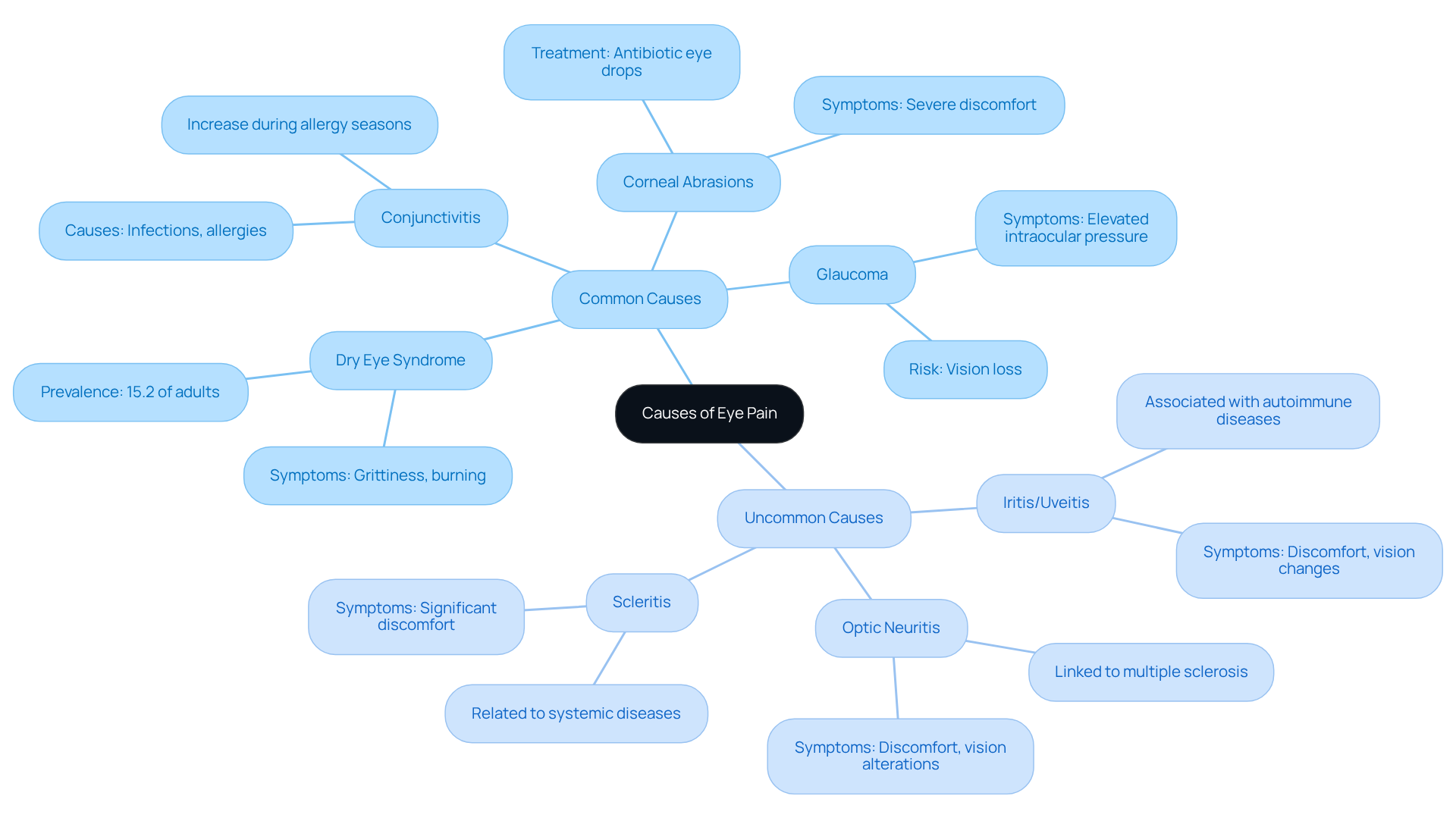
Eye pain causes can arise from various factors, and understanding these can help you identify symptoms and seek the right care. We know that experiencing discomfort in your eyes can be concerning, and it’s important to address these feelings.
Common Causes:
- Dry Eye Syndrome: This condition, characterized by insufficient tear production, affects around 15.2% of adults in the U.S. It often leads to irritation and discomfort, particularly among older adults and women. Symptoms may include feelings of grittiness and burning sensations. It’s noteworthy that the prevalence of dry eye disease (DED) increases with age, especially in women. About 25% of patients visiting ophthalmology clinics experience DED, and we understand how this can impact your daily life.
- Conjunctivitis: This inflammation of the eye’s outer membrane can stem from infections or allergies. We’ve seen a significant rise in cases, especially during allergy seasons, and it’s common to feel frustrated during these times.
- Corneal Abrasions: These scratches on the eye’s surface can cause severe discomfort. If you experience this, it may require medical treatment, such as antibiotic eye drops, to prevent infection. We want you to know that seeking help is a positive step.
- Glaucoma: Elevated intraocular pressure linked with glaucoma can lead to significant discomfort and potential vision loss. Prompt medical intervention is essential, and we encourage you to reach out if you have concerns.
Uncommon Causes:
- Iritis/Uveitis: Inflammation of the inner eye structures, often associated with autoimmune diseases, can lead to significant discomfort and changes in vision. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management, and we are here to support you through this process.
- Optic Neuritis: This condition involves inflammation of the optic nerve, leading to discomfort and possible vision alterations, often linked to multiple sclerosis. We understand this can be alarming, and seeking care is important.
- Scleritis: Inflammation of the sclera, the eye’s white outer layer, is often related to systemic diseases and can cause significant discomfort and vision impairment.
Recognizing the eye pain causes is essential for accurately identifying symptoms and seeking timely medical advice. We are here to help you navigate your eye health and ensure better outcomes. Your well-being is our priority, and we encourage you to .
Recognize Symptoms and When to Seek Help
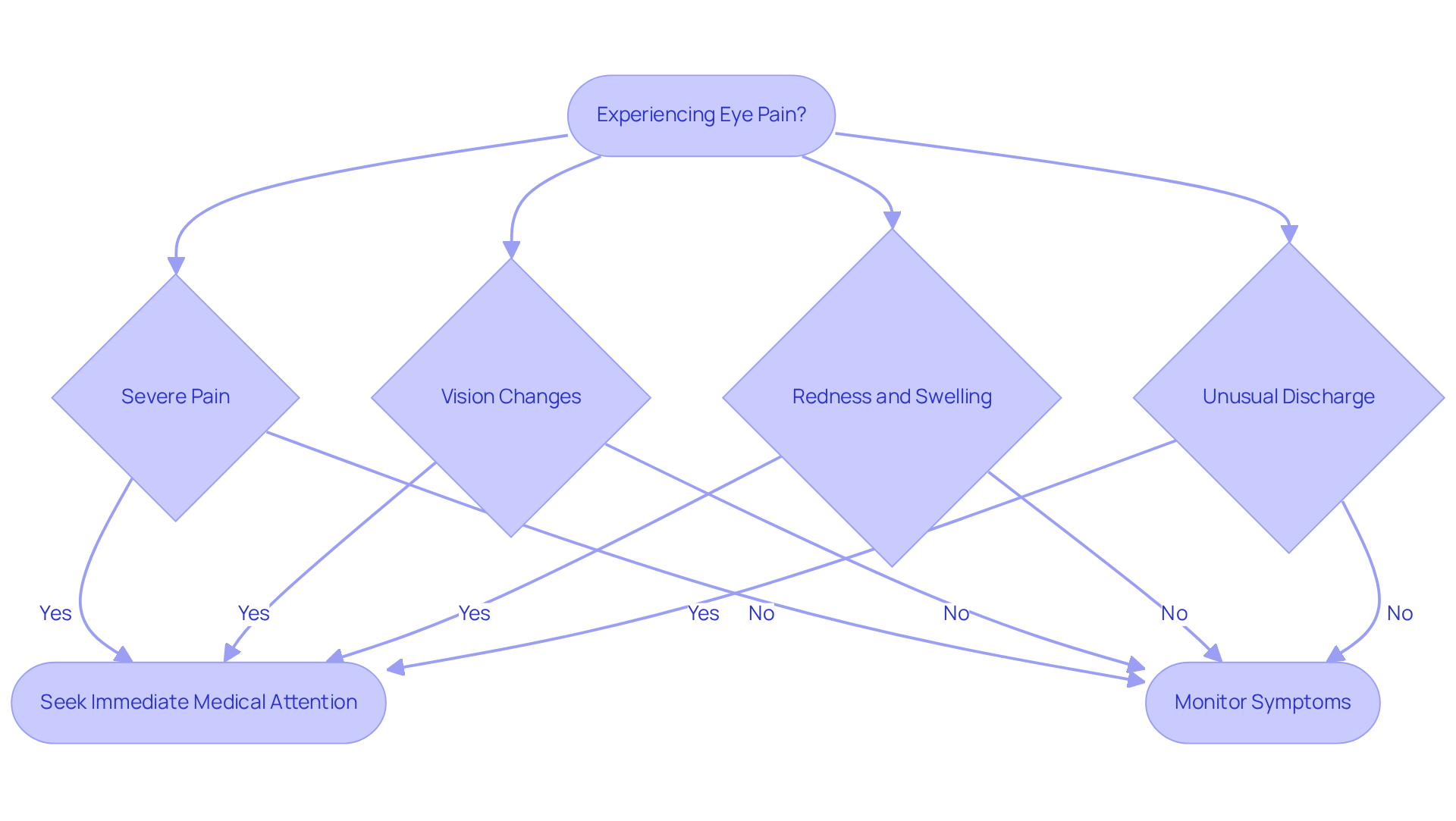
Immediate medical assessment is required for specific symptoms associated with eye pain causes. We understand that experiencing these symptoms can be concerning, and it’s crucial to monitor key indicators, including:
- Severe Pain: Intense pain that disrupts daily activities can signal a serious underlying issue. It’s common to feel anxious when faced with such discomfort.
- Vision Changes: Sudden loss of vision, blurred vision, or seeing halos around lights are that require immediate attention. Blurred sight may arise from issues such as cataracts, diabetic retinopathy, or uncorrected refractive errors, and can indicate the presence of eye disease. We want you to feel reassured that help is available.
- Redness and Swelling: Significant redness or swelling around the eye may indicate inflammation or infection. It’s important to take note of these changes.
- Discharge: Unusual discharge from the eye can be a sign of infection and should not be ignored. We care about your well-being, and prompt action is essential.
Headaches or nausea can accompany severe eye pain causes, especially in cases of acute glaucoma, which is often silent until advanced. We know how overwhelming these experiences can be.
Statistics show that many severe eye issues, such as glaucoma, can remain asymptomatic until they reach an advanced stage, highlighting the significance of regular eye exams. If any of these symptoms are present, seeking medical attention promptly is essential to prevent complications and preserve vision. Remember, only a Northwest Eye doctor can provide an accurate diagnosis. If you experience any of these symptoms, we encourage you to schedule an appointment with Northwest Eye to ensure your eye health is properly evaluated. Resources like the Eye Condition Library and symptom checkers at Northwest Eye empower you to understand your conditions better and seek timely medical intervention. We are here to help you through this process.
Implement Treatment Strategies and Self-Care Tips
Managing eye discomfort can feel overwhelming, but understanding eye pain causes and using a balanced approach that combines medical treatments with self-care strategies can make a significant difference. We understand that it’s essential to address both your immediate needs and the long-term comfort that can result from eye pain causes. Here are some key methods to consider:
-
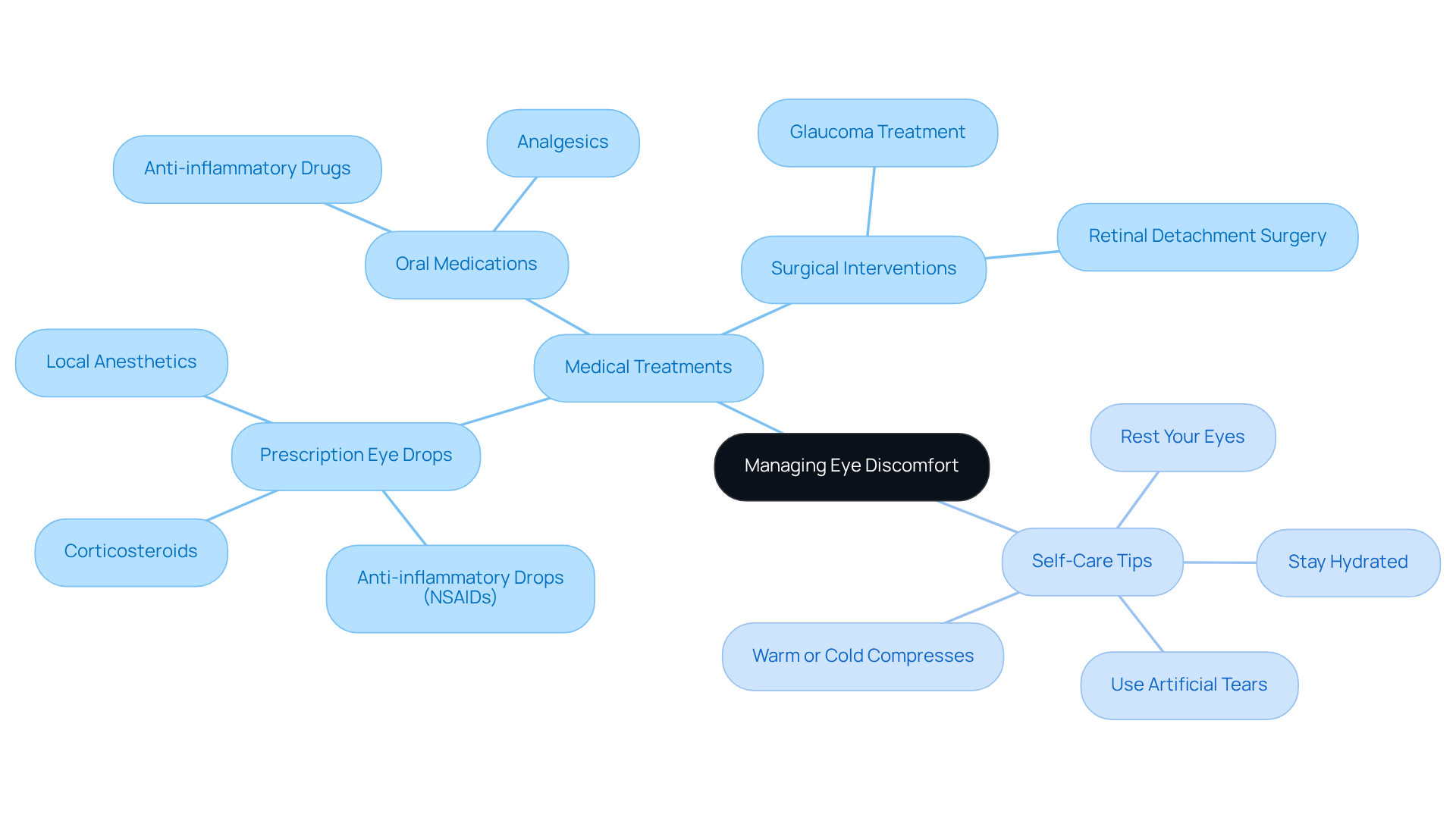
Medical Treatments:
- Prescription Eye Drops: Depending on the underlying cause, these may include anti-inflammatory drops (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or local anesthetics tailored to alleviate specific symptoms. We recognize that finding the right treatment can be a journey.
- Oral Medications: For more intense discomfort, ophthalmologists may suggest analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve symptoms related to eye pain causes. It’s common to seek additional support during this time.
- Surgical Interventions: In situations involving severe conditions such as glaucoma or retinal detachment, surgical options may be necessary to address the underlying eye pain causes. We are here to help you navigate these decisions.
-
Self-Care Tips:
- Warm or Cold Compresses: Applying a warm or cold compress can soothe irritation and reduce swelling, offering immediate comfort. Remember, small actions can lead to significant relief.
- Rest Your Eyes: Regular breaks from screens and bright lights can help alleviate some eye pain causes, promoting relaxation and recovery. It’s important to listen to your body.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for supporting tear production and can help mitigate eye pain causes while maintaining overall eye health. We encourage you to prioritize your well-being.
- Use Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter lubricating drops can provide significant relief for dry eyes, which are one of the eye pain causes, helping to restore moisture and comfort. Simple solutions can often bring great comfort.
Implementing these strategies can greatly enhance your comfort and facilitate healing from various eye pain causes. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you in more effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding the various causes of eye pain is crucial for recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. Eye discomfort can stem from both common and uncommon conditions, ranging from minor irritations to serious health issues. We understand that identifying the type of pain—whether it is surface, deep, or acute—can help you assess the urgency of your situation and the need for professional help.
This article highlights several key causes of eye pain, including:
- Dry eye syndrome
- Conjunctivitis
- Glaucoma
as well as less common issues like:
- Iritis
- Optic neuritis
It’s common to feel concerned about symptoms such as severe pain, vision changes, and unusual discharge, which may indicate serious conditions requiring immediate medical attention. Additionally, effective treatment strategies and self-care tips, such as using warm compresses and staying hydrated, are essential in managing discomfort and promoting eye health.
Ultimately, being proactive about eye health is vital. Regular eye exams and awareness of potential symptoms can lead to early diagnosis and treatment, helping to prevent complications and preserve vision. We are here to help you through this process. Taking action, whether through professional consultation or implementing self-care practices, empowers you to maintain your eye health and address discomfort effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of eye pain?
Eye pain can be categorized into three types: surface pain, deep pain, and acute discomfort. Surface pain is often described as burning or stinging, deep pain may feel like pressure or aching, and acute discomfort is characterized by sudden and intense distress.
What causes surface pain in the eyes?
Surface pain is typically associated with conditions such as dry eyes, foreign bodies, infections like conjunctivitis, allergies, and contact lens irritation.
What might deep eye pain indicate?
Deep eye pain can be linked to conditions such as glaucoma or sinus infections.
What should I do if I experience acute eye discomfort?
Sudden and intense eye discomfort may indicate emergencies such as retinal detachment or acute glaucoma. It is crucial to seek professional medical help immediately.
Why is it important to recognize the type of eye pain I am experiencing?
Recognizing the distinctions between types of eye pain helps identify the urgency of the situation and the need for medical intervention, which is essential to prevent severe health issues.
What are some serious health issues that can arise from untreated eye pain?
Untreated eye pain can lead to severe health issues such as keratoconus and thyroid eye disease.






