Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on August 14, 2025
Overview
Graves eye disease, known as Thyroid Eye Disease (TED), is an autoimmune disorder associated with hyperthyroidism. It can bring about symptoms such as:
- bulging eyes
- eyelid retraction
- double vision
We understand that dealing with these symptoms can be challenging and may cause concern.
Early diagnosis is crucial, and we encourage you to seek care as soon as possible. A comprehensive treatment approach is essential, which may include:
- medications
- lifestyle changes
- possibly surgery
These steps can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent complications.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Many patients have navigated similar experiences, and we are here to help you through this process. Together, we can work towards finding the best solutions for your health and well-being.
Introduction
Graves eye disease is an autoimmune disorder closely linked to thyroid dysfunction, and it can pose significant challenges for those affected. We understand that around 40% of individuals with hyperthyroidism may potentially develop this condition, making it crucial to recognize its symptoms and explore treatment options for effective management. Navigating the complexities of diagnosis and treatment while ensuring optimal eye health can feel overwhelming. This article delves into the key aspects of Graves eye disease, from identifying symptoms to exploring the latest therapeutic approaches, providing essential insights for patients and caregivers alike. We are here to help you through this process.
Define Graves’ Eye Disease and Its Connection to Thyroid Disorders
Graves eye disease, also known as Thyroid Eye Disease (TED), is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the tissues surrounding the eyes. We understand that this can be concerning, especially as it is closely linked to thyroid conditions like , which occurs when the thyroid gland produces too many hormones. In the case of Graves eye disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid, leading to increased hormone levels.
This hyperactivity can cause inflammation and swelling in the eye muscles and surrounding tissues. Common symptoms include proptosis, or bulging eyes, eyelid retraction, and double vision. It’s important to know that recent studies indicate around 40% of individuals with hyperthyroidism may develop Graves eye disease, which highlights a significant connection between these conditions.
Moreover, TED is more prevalent in women, particularly those aged 35 to 59. This underscores the importance of targeted awareness and treatment strategies. Recognizing this connection is vital for understanding the systemic nature of the condition and its ocular effects. Untreated TED can lead to serious complications, including vision loss and persistent double vision.
We want to emphasize that consistent observation and timely action are crucial in managing both hyperthyroidism and its ocular implications. By taking these steps, we can help ensure optimal outcomes for your health. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Identify Common Symptoms and Signs of Graves’ Eye Disease
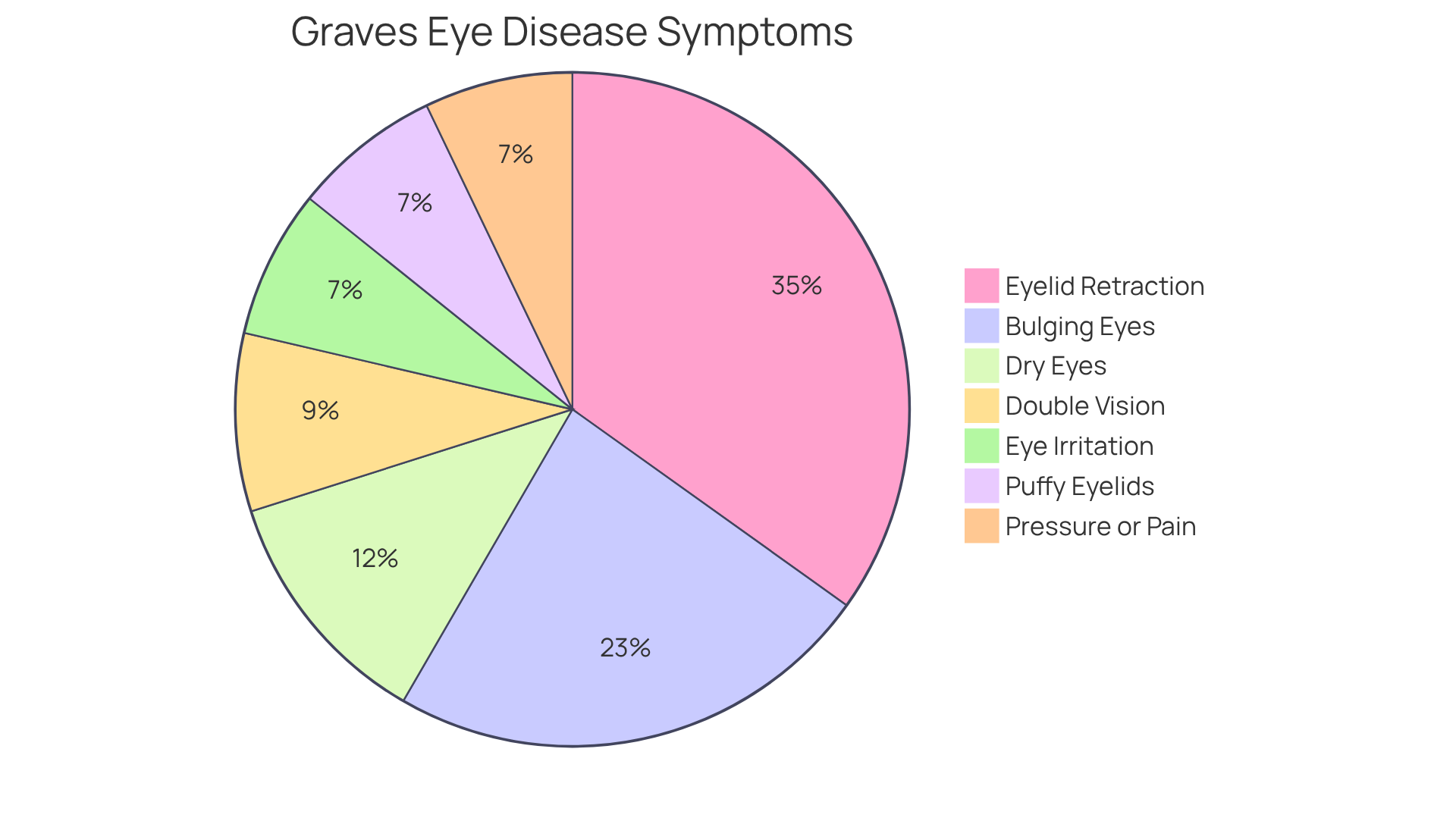
Graves eye disease can bring about several common symptoms that significantly impact your quality of life. We understand that recognizing these signs can be concerning, and we want to help you navigate this journey. Here are some key indicators to be aware of:
- Bulging Eyes (Proptosis): This prominent symptom occurs when your eyes protrude due to inflammation and swelling of the eye muscles. It affects approximately 1 in 3 individuals with the disease, and it’s common to feel self-conscious about this change.
- Eyelid Retraction: You may notice that your upper eyelids retract more than normal, revealing more of your eyeball. This condition is seen in nearly 49% of thyroid eye conditions, and it’s understandable to feel uneasy about these changes.
- Double Vision: Misalignment of your visual organs, resulting from muscle swelling, can lead to diplopia. This affects 6 to 18% of patients at presentation, and it can be quite disorienting.
- Dry Eyes: Inflammation can disrupt tear production, causing dryness and discomfort. Symptoms are reported in 13 to 20% of patients, and it’s important to seek professional evaluation as this condition can also indicate other eye diseases.
- Eye Irritation: Many individuals experience a gritty sensation or heightened sensitivity to light, which can contribute to overall discomfort.
- Puffy Eyelids: Swelling around the eyelids can create a puffy appearance, further impacting your aesthetic and emotional well-being.
- Pressure or Pain in the Eyes: Some patients report a sensation of pressure or discomfort behind the eyes, which can be distressing.
Prompt identification of these symptoms is essential for timely diagnosis and effective management of Graves eye disease. We emphasize the importance of awareness, as early intervention can significantly improve your outcomes and quality of life. Additionally, unmanaged hyperthyroidism can lead to serious health issues, highlighting the need for prompt identification and care. We encourage you to learn about your symptoms and seek to ensure you receive the care you deserve. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, please schedule an appointment for a general eye examination with a Northwest Eye doctor or eye surgeon. We are here to help you through this process.
Explain Diagnostic Methods for Graves’ Eye Disease
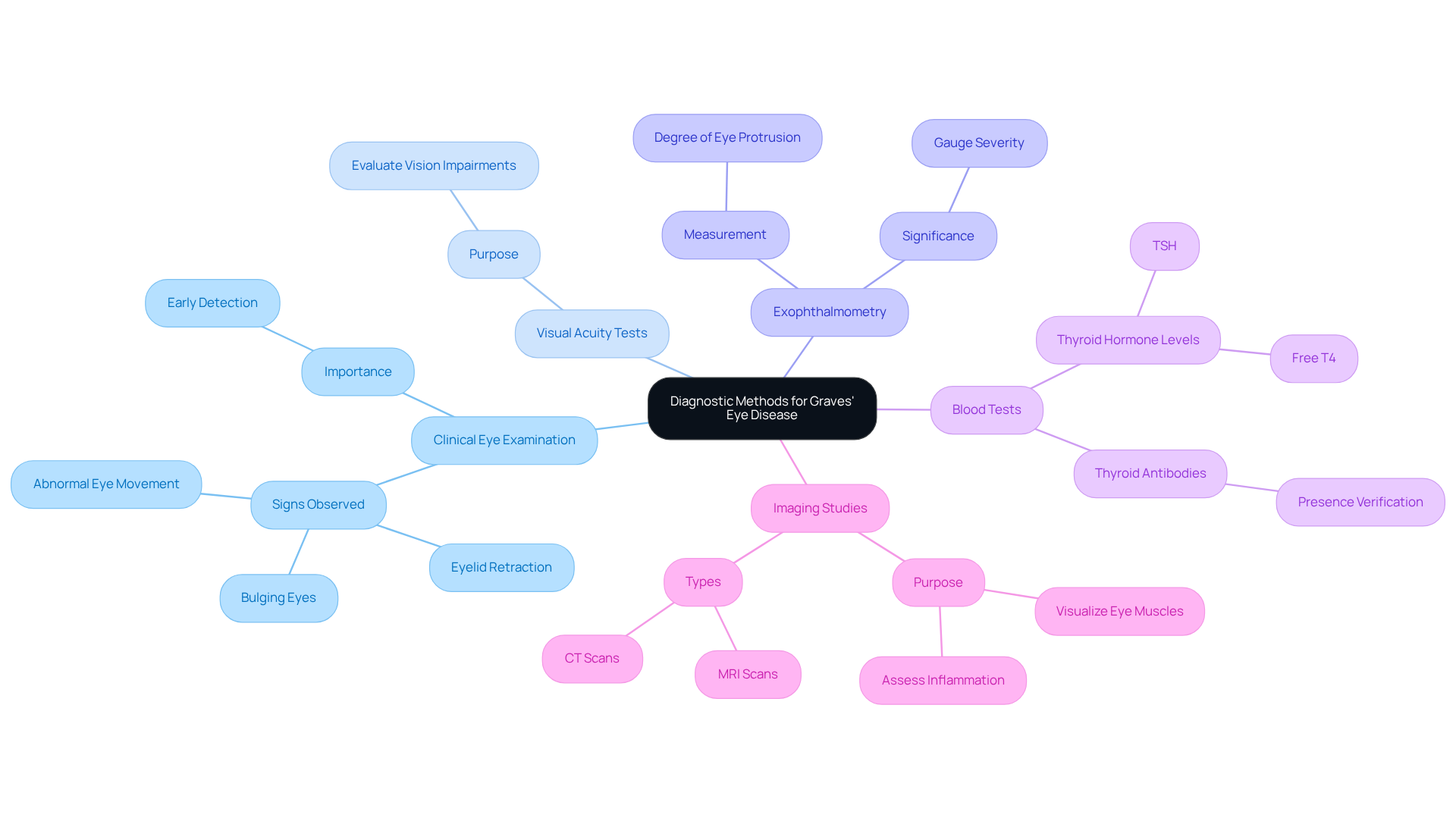
Diagnosing Graves Eye Disease involves a comprehensive approach that combines clinical evaluations and [advanced imaging studies](https://nweyeclinic.com/cornea). We understand that this process can feel overwhelming, but we are here to help you through it.
- Clinical Eye Examination: An ophthalmologist performs a detailed examination, looking for signs such as bulging eyes, eyelid retraction, and abnormalities in eye movement. These are critical indicators of Graves eye disease, and it is essential to address them early.
- Visual Acuity Tests: These assessments evaluate your ability to see at various distances, helping to identify any vision impairments that may arise from the condition.
- Exophthalmometry: This specialized measurement quantifies the degree of eye protrusion, a significant marker for Graves eye disease. Understanding this aspect helps gauge the severity of your condition.
- Blood Tests: Assessing thyroid hormone levels (TSH and Free T4) and the presence of thyroid antibodies is essential for verifying a diagnosis. These factors often change in individuals affected by this condition.
- Imaging Studies: CT or MRI scans visualize the eye muscles and surrounding tissues, providing insights into the extent of inflammation and helping to exclude other potential conditions.
It’s common to feel uncertain about your diagnosis, but statistics show that approximately 1 in 3 individuals with Graves eye disease develop orbitopathy. This emphasizes the necessity of comprehensive ocular evaluations to identify Graves eye disease. Furthermore, a study found that 73.7% of patients with newly diagnosed hyperthyroidism had no ocular involvement at presentation. This highlights the importance of careful monitoring.
These diagnostic methods are vital for establishing an accurate diagnosis of Graves eye disease and for developing an effective treatment plan. We want to ensure that you receive the , and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Outline Treatment Options and Management Strategies for Graves’ Eye Disease
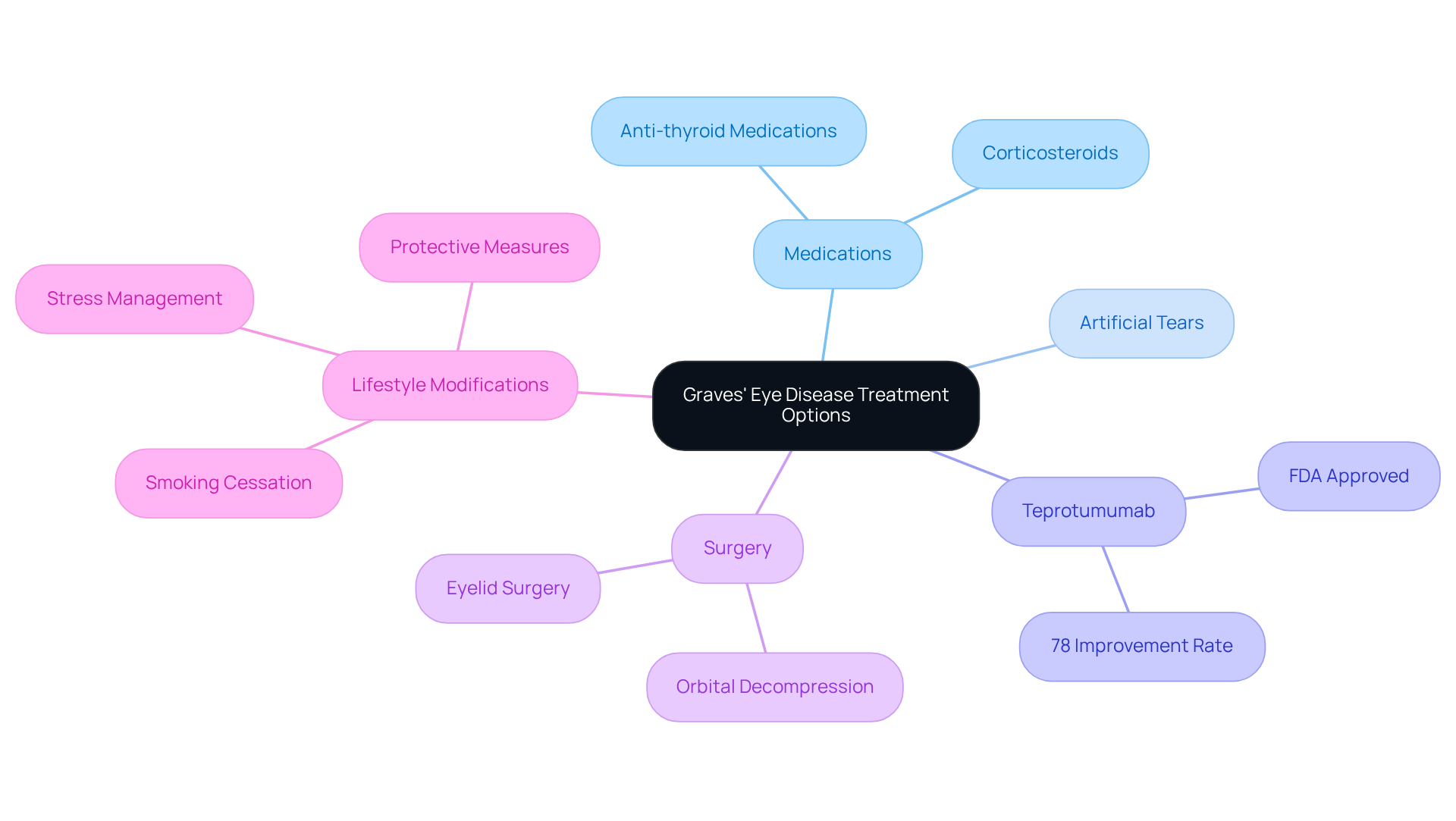
Treatment options for can vary based on the severity of symptoms, and we recognize that navigating these choices can feel overwhelming. Here are some options that may help:
- Medications: Anti-thyroid medications, such as methimazole, can assist in controlling hyperthyroidism. Corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling in the eyes, especially during the active stage of the condition. A cumulative dose of intravenous methylprednisolone (IVMP) for TED treatment typically consists of 4.5 g over about three months.
- Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops can provide relief from dryness and irritation, enhancing comfort for those experiencing ocular symptoms.
- Teprotumumab (Tepezza): This innovative medication, specifically approved for thyroid eye disease, has shown significant success in clinical trials. Approximately 78% of patients experience improvements in eye bulging and double vision. Notably, proptosis decreased by 3.5 mm after treatment with Teprotumumab, demonstrating its effectiveness in managing moderate to severe cases.
- Surgery: In instances of severe symptoms or vision impairment, surgical options such as orbital decompression or eyelid surgery may be necessary. These procedures can relieve pressure on the optic nerve and restore normal eye function, particularly in cases of compressive optic neuropathy.
- Lifestyle Modifications: We encourage patients to adopt healthy lifestyle changes, including smoking cessation, stress management, and protective measures like wearing sunglasses to shield their eyes from irritants.
Effective management of Graves Eye Disease often requires a collaborative approach involving both endocrinologists and ophthalmologists. This partnership ensures comprehensive treatment, addressing both thyroid dysfunction and ocular symptoms. Regular follow-ups and evaluations are crucial for monitoring disease progression and treatment response, allowing for timely adjustments in therapy. Additionally, assessing the psychosocial impact of Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) is essential for informing treatment decisions. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Conclusion
Graves’ Eye Disease is a significant manifestation of thyroid dysfunction, highlighting the intricate relationship between autoimmune disorders and ocular health. We understand that this condition can be challenging, as it not only affects physical appearance but may also lead to serious complications if left untreated. Raising awareness about the symptoms and the importance of early diagnosis empowers individuals to seek timely medical intervention.
In this article, we have explored key aspects of Graves’ Eye Disease, including its connection to thyroid disorders, common symptoms such as proptosis and double vision, diagnostic methods like imaging studies and blood tests, and various treatment options ranging from medications to surgery. Each of these elements is crucial in managing the disease effectively, underscoring the need for a comprehensive approach to care.
As you navigate the journey through Graves’ Eye Disease, it is vital to stay informed and proactive about your health. Seeking professional medical help at the first signs of symptoms can lead to better outcomes and an improved quality of life. By fostering a supportive environment and encouraging open dialogue about thyroid and eye health, we can help you and others affected navigate this complex condition with confidence and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Graves’ Eye Disease?
Graves’ Eye Disease, also known as Thyroid Eye Disease (TED), is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the tissues surrounding the eyes.
How is Graves’ Eye Disease connected to thyroid disorders?
Graves’ Eye Disease is closely linked to thyroid conditions like hyperthyroidism, which occurs when the thyroid gland produces too many hormones. The immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid, leading to increased hormone levels.
What are the common symptoms of Graves’ Eye Disease?
Common symptoms include proptosis (bulging eyes), eyelid retraction, and double vision.
What percentage of individuals with hyperthyroidism may develop Graves’ Eye Disease?
Recent studies indicate that around 40% of individuals with hyperthyroidism may develop Graves’ Eye Disease.
Who is more likely to develop Graves’ Eye Disease?
TED is more prevalent in women, particularly those aged 35 to 59.
What are the potential complications of untreated Graves’ Eye Disease?
Untreated TED can lead to serious complications, including vision loss and persistent double vision.
Why is it important to manage both hyperthyroidism and its ocular implications?
Consistent observation and timely action are crucial in managing both hyperthyroidism and its ocular effects to ensure optimal health outcomes.






