Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on June 17, 2025
Overview
Ocular melanoma, often referred to as uveal cancer, can be a daunting diagnosis. We understand that learning about this condition may raise many concerns. This type of cancer is primarily linked to genetic factors, prolonged exposure to UV light, and age, with risk factors including inherited mutations and fair skin.
Understanding these causes is crucial for early detection. It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but knowing the signs can empower you. Effective diagnosis and treatment options, such as surgery and radiation therapy, can significantly improve patient outcomes.
We want you to feel reassured that there are paths to recovery. Many patients have successfully navigated this journey, and we are here to help you through this process. Remember, you are not alone in this; support is available every step of the way.
Introduction
Ocular melanoma is a rare yet formidable form of cancer affecting the eye, and we understand that this diagnosis can bring about a whirlwind of emotions and concerns for patients and their families. Recognizing its causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and improved outcomes. As the landscape of ocular melanoma continues to evolve with new research and innovations, it’s common to feel overwhelmed by the information available.
How can you ensure that you are equipped with the knowledge and resources necessary to navigate this complex condition? This article delves into the essential aspects of ocular melanoma, offering insights that empower you and your loved ones on your journey toward recovery.
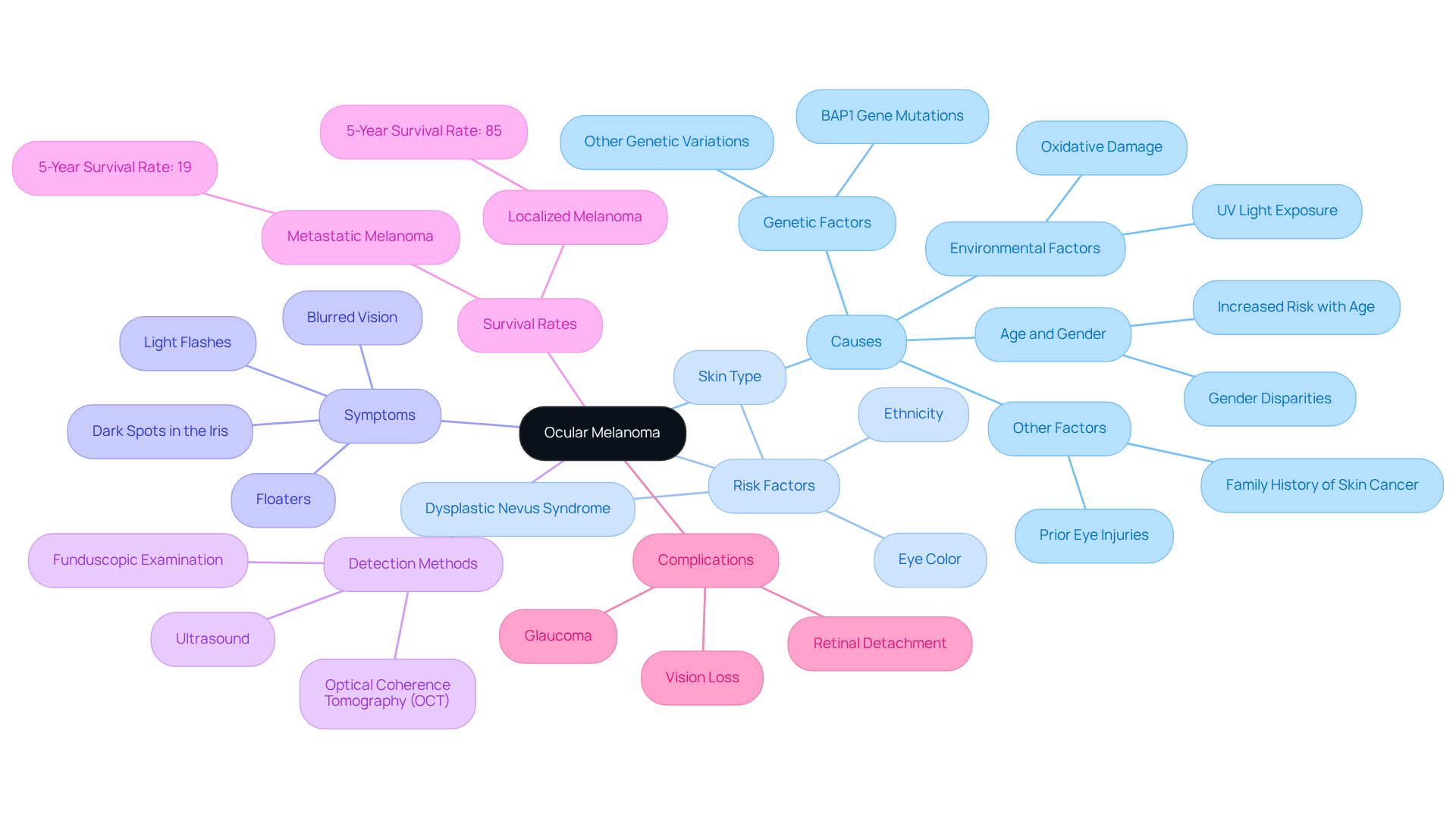
Define Ocular Melanoma: Causes and Risk Factors
Ocular melanoma, which is also referred to as uveal cancer, is a rare yet serious condition that arises from melanocytes in the eye. While the exact causes remain unclear, we understand that several key risk factors can contribute to this condition, and being aware of them is important for your health.
- Genetic Factors: Inherited mutations, especially in the BAP1 gene, significantly heighten the risk of developing ocular melanoma. These genetic variations can influence the likelihood of developing the disease and its potential for metastasis.
- Environmental Factors: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light is a notable risk, especially for individuals with light-colored eyes and fair skin. This exposure can result in oxidative harm in pigmented tissues, aiding in the formation of skin cancer.
- Age and Gender: It’s common to feel concerned as the occurrence of ocular melanoma increases with age, reaching its highest point between 70 and 79 years. Men are slightly more affected than women, with a reported incidence rate of 5.8 cases per million for males compared to 4.4 for females.
- Other Factors: Prior eye injuries, specific skin disorders, and a family history of skin cancer can further increase risk levels.
Symptoms: We understand that noticing changes can be alarming. Patients may experience dark spots in the iris, light flashes, blurred vision, and floaters, which are crucial for early detection.
Detection Methods: Diagnosis typically involves funduscopic examination and imaging modalities such as ultrasound and optical coherence tomography (OCT). Knowing the methods can help ease your concerns about the process.
Survival Rates: Statistics indicate that nearly half of patients with ocular melanoma may experience metastasis, and the 5-year relative survival rate is approximately 85% if the disease has not spread beyond the eye. This information can provide some reassurance during a challenging time.
Complications: We recognize that treatment for eye cancer can lead to issues such as vision loss and glaucoma, making awareness of these risks essential. It’s important to discuss these concerns with your healthcare provider.
Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing effective early detection and prevention strategies. We encourage regular eye examinations, particularly for those at higher risk due to genetic predispositions or environmental exposures. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Diagnose Ocular Melanoma: Techniques and Procedures
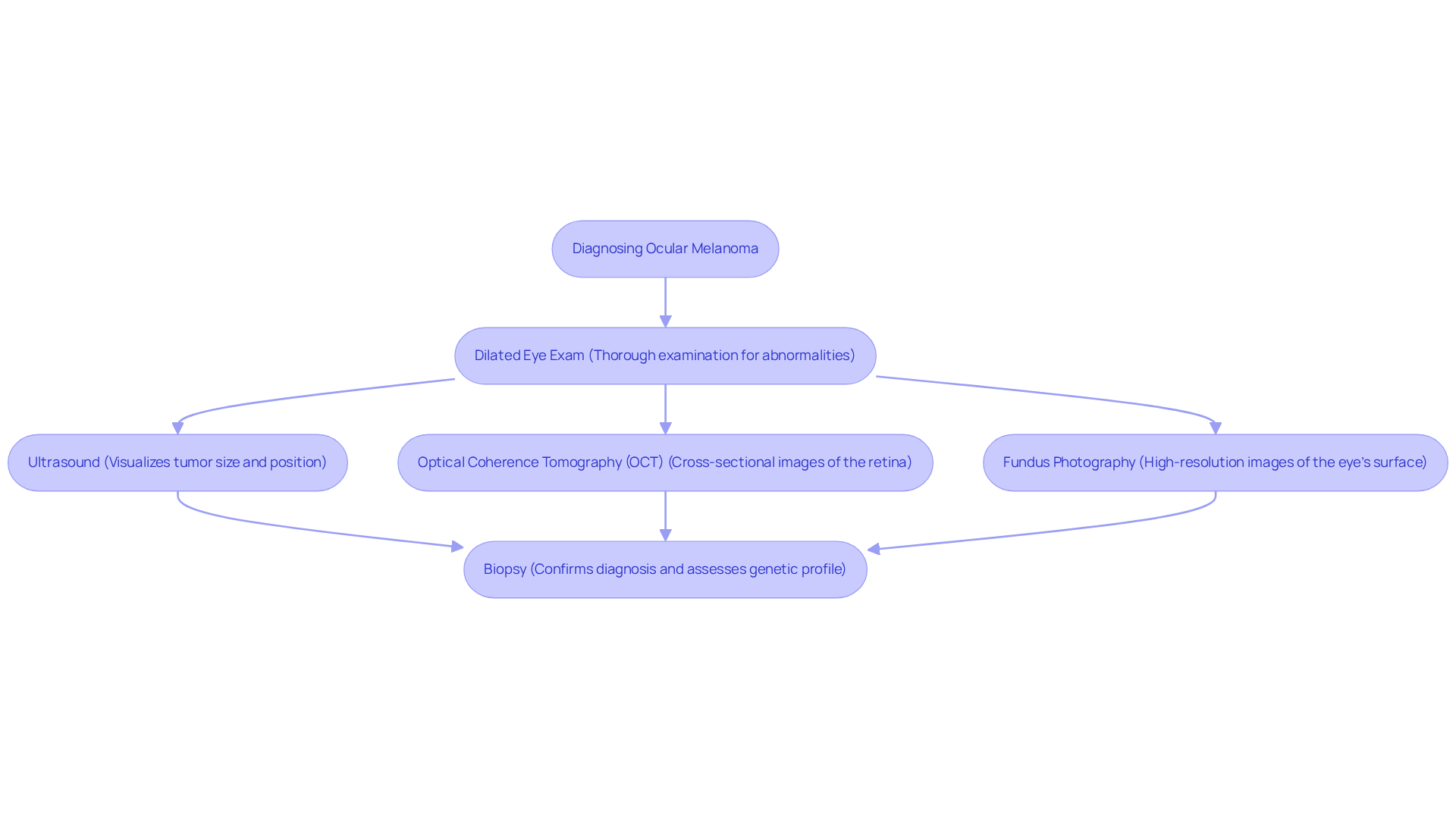
Diagnosing ocular melanoma necessitates a multifaceted approach that integrates clinical examination with advanced imaging techniques. We understand that this can be a concerning time for you, and we are here to help you through this process.
- Dilated Eye Exam: An ophthalmologist conducts a thorough examination using specialized lenses to detect any abnormalities in the eye. This step is crucial for the early identification of ocular melanoma, which is often discovered during routine eye exams. Regular check-ups are essential for maintaining your eye health.
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique is vital for visualizing the tumor’s size and exact position within the eye, offering important information for planning your care.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): OCT provides cross-sectional images of the retina, allowing for a detailed assessment of the tumor’s characteristics and its impact on surrounding structures.
- Fundus Photography: This method captures high-resolution images of the eye’s internal surface, assisting in the detection of abnormal growths that may suggest cancer.
- Biopsy: Although not always necessary, a biopsy can verify the diagnosis and assess the tumor’s genetic profile. This information is becoming increasingly significant for personalized care strategies. Types of biopsies may include shave, punch, and excisional biopsies, each serving a specific purpose in confirming skin cancer diagnoses.
These diagnostic techniques are essential for precisely identifying the existence and severity of ocular melanoma, ultimately guiding effective treatment choices. We want to reassure you that the integration of advanced imaging technologies enhances the accuracy of diagnoses, ensuring timely intervention and improved patient outcomes. Moreover, tumor mutation testing is advised for advanced skin cancer cases, and a cooperative strategy involving a multidisciplinary group of experts is crucial for thorough evaluations of intricate cases. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Treat Ocular Melanoma: Current Approaches and Innovations
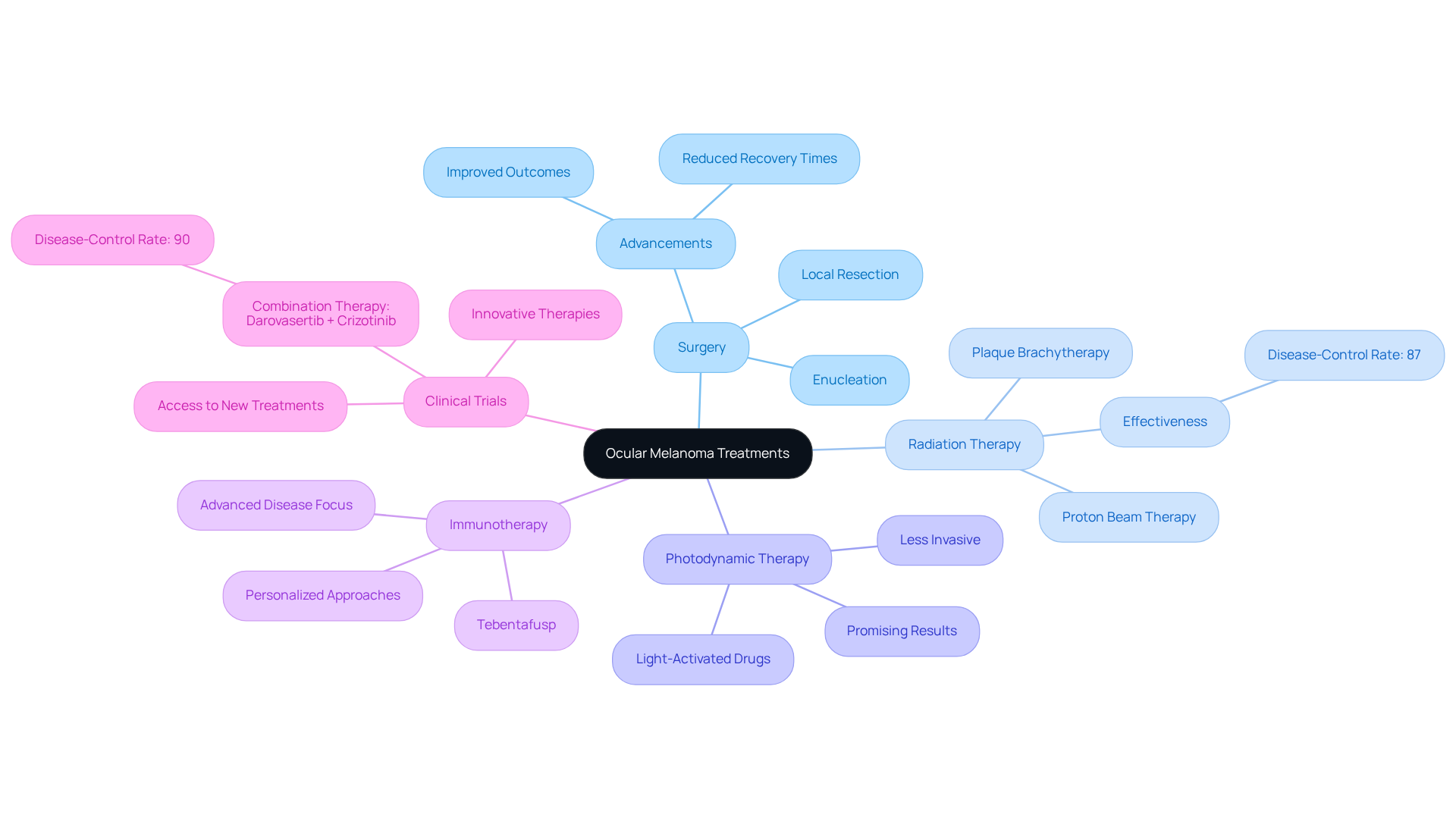
Treatment for ocular melanoma is customized based on the tumor’s size, location, and stage. We understand that navigating this condition can be overwhelming, but several current approaches demonstrate promise in managing it effectively:
- Surgery: Surgical options range from local resection of the tumor to enucleation, which involves the removal of the eye in more advanced cases. Recent advancements in surgical techniques have improved outcomes and reduced recovery times, offering hope for many.
- Radiation Therapy: Techniques such as plaque brachytherapy and proton beam therapy are widely utilized to precisely target tumors while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. These methods have shown significant success rates in controlling tumor growth, with studies indicating a disease-control rate of approximately 87% for combination therapies. It’s common to feel anxious about these treatments, but many have found them effective.
- Photodynamic Therapy: This innovative approach employs light-activated drugs to selectively destroy cancer cells, offering a less invasive alternative with promising results in early studies. Many patients appreciate this option for its gentler approach.
- Immunotherapy: Emerging therapies, including tebentafusp, are being explored to boost the immune system’s capacity to fight cancer cells. Dr. Benjamin Switzer observes that these therapies signify a shift towards more personalized approaches, especially for individuals with advanced disease. We are here to help you understand these options and find the right path for you.
- Clinical Trials: Ongoing research is vital for the development of new therapies and the refinement of existing protocols. Involvement in clinical trials can offer access to innovative therapies and aid in the progress of eye cancer care. For instance, a recent phase 2/3 clinical trial evaluating a combination of darovasertib and crizotinib demonstrated a disease-control rate of 90% in early results. Participating in these trials can be a courageous step towards better treatment.
These varied therapeutic options highlight the importance of a multidisciplinary strategy to effectively manage ocular melanoma, ensuring that patients receive thorough care customized to their individual requirements. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; support is available every step of the way.
Manage Post-Treatment Care: Follow-Up and Support Strategies
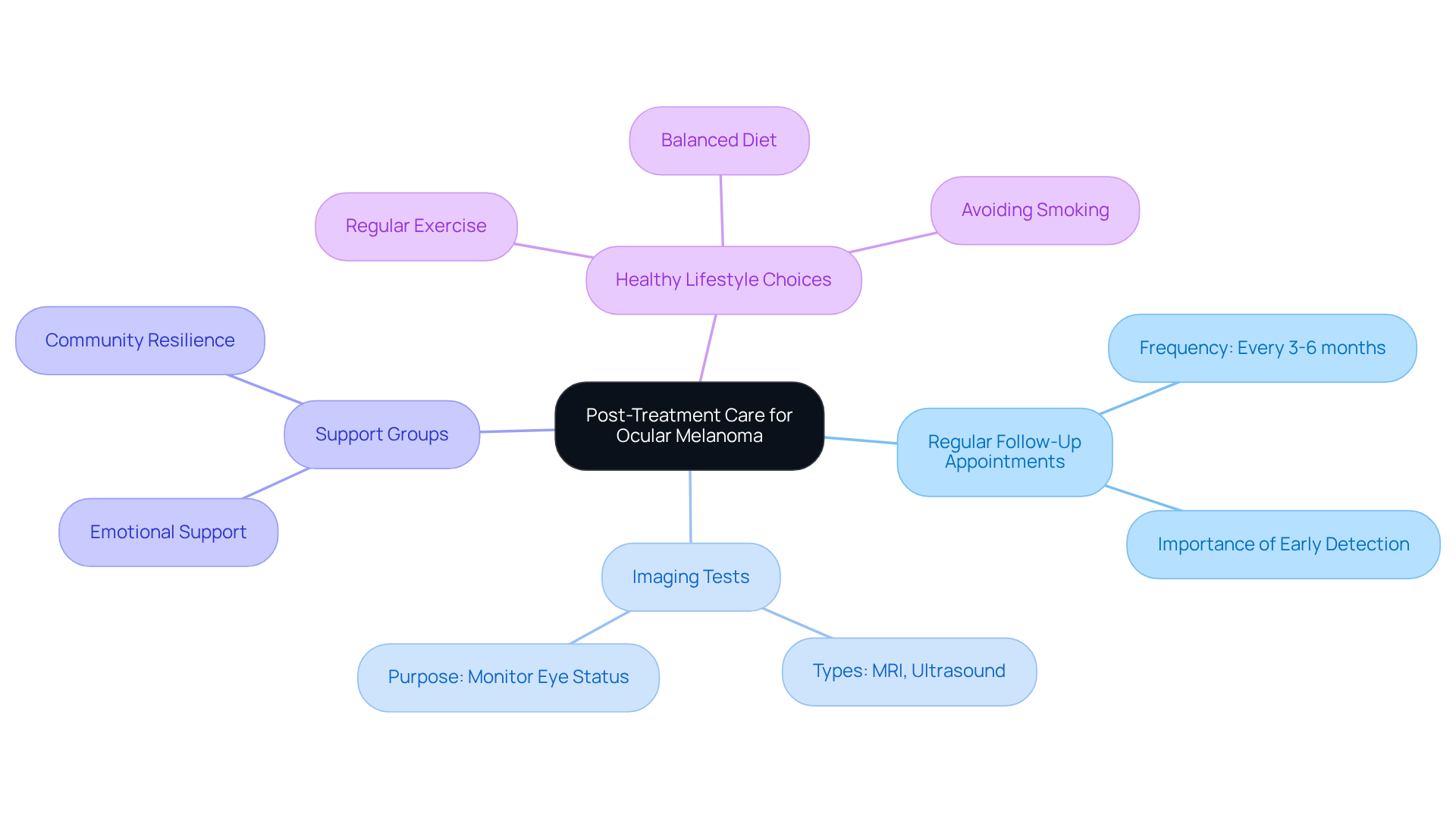
Post-treatment care for ocular melanoma is essential for ensuring your long-term health and monitoring for any recurrence. We understand that this journey can be challenging, and we want to provide you with key strategies to support your recovery:
- Regular Follow-Up Appointments: It’s important to schedule follow-ups every 3-6 months for the first few years after treatment to monitor for any signs of recurrence. This proactive approach is crucial; early identification of changes can significantly influence your recovery results. As healthcare professionals emphasize, consistent follow-up is essential for managing your health post-treatment.
- Imaging Tests: Periodic imaging, such as MRI or ultrasound, may be necessary to assess the status of your eye and surrounding tissues. These tests help identify potential issues before they develop into more serious complications, reinforcing the importance of regular monitoring.
- Engaging with support groups can provide you with emotional support and resources for coping with the challenges of living with ocular melanoma. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges fosters a sense of community and resilience. As one cancer survivor beautifully stated, “Cancer is just a chapter in our lives and not the whole story,” highlighting the importance of support during recovery.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can contribute to your overall health and well-being. These lifestyle modifications not only enhance your physical health but also improve mental well-being, which is crucial during recovery. Statistics show that patients who adopt healthier lifestyles tend to have better outcomes.
These strategies empower you to take an active role in your recovery and health management. Remember, ongoing care and support are essential in your journey after treatment, and we are here to help you through this process.
Conclusion
Ocular melanoma, while rare, brings forth significant challenges that can feel overwhelming. Understanding its causes, diagnostic techniques, and treatment options is essential for navigating this complex journey. By exploring the multifaceted nature of this condition, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions that lead to improved health outcomes.
In this article, we have highlighted key points that matter to you, including the genetic and environmental risk factors associated with ocular melanoma, the importance of early detection through various diagnostic methods, and the diverse treatment options available. Innovations in therapy, such as immunotherapy and photodynamic therapy, along with the vital role of post-treatment care and support, emphasize the need for a proactive and informed approach to managing this condition.
Embracing knowledge about ocular melanoma allows you and your family to take charge of your health journey. Regular eye examinations, understanding the significance of follow-up care, and seeking support from communities can greatly enhance recovery and improve your quality of life. We understand that staying informed about the latest developments in ocular melanoma is crucial for those affected, as it equips you with the necessary tools to face this formidable challenge head-on. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to help you through the process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ocular melanoma?
Ocular melanoma, also known as uveal cancer, is a rare but serious condition that originates from melanocytes in the eye.
What are the main causes of ocular melanoma?
The exact causes of ocular melanoma are unclear, but several key risk factors, including genetic and environmental factors, can contribute to its development.
What genetic factors increase the risk of developing ocular melanoma?
Inherited mutations, particularly in the BAP1 gene, significantly increase the risk of developing ocular melanoma and can influence the disease’s potential for metastasis.
How does UV light exposure relate to ocular melanoma?
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light is a notable risk factor for ocular melanoma, especially for individuals with light-colored eyes and fair skin, as it can cause oxidative damage in pigmented tissues.
What demographic factors are associated with higher rates of ocular melanoma?
The incidence of ocular melanoma increases with age, peaking between 70 and 79 years. Additionally, men are slightly more affected than women, with reported rates of 5.8 cases per million for males compared to 4.4 for females.
What other factors may increase the risk of ocular melanoma?
Prior eye injuries, certain skin disorders, and a family history of skin cancer can further elevate the risk of developing ocular melanoma.
What symptoms should one look out for regarding ocular melanoma?
Symptoms may include dark spots in the iris, light flashes, blurred vision, and floaters, which are important for early detection.
How is ocular melanoma diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a funduscopic examination and imaging techniques such as ultrasound and optical coherence tomography (OCT).
What are the survival rates for ocular melanoma?
The 5-year relative survival rate for ocular melanoma is approximately 85% if the disease has not spread beyond the eye, although nearly half of patients may experience metastasis.
What complications can arise from treatment for ocular melanoma?
Treatment can lead to complications such as vision loss and glaucoma, making it essential to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider.
How can individuals at higher risk manage their health regarding ocular melanoma?
Regular eye examinations are encouraged for those at higher risk due to genetic predispositions or environmental exposures to facilitate early detection and prevention strategies.






