Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on August 22, 2025
Overview
This article aims to nurture your understanding of the sclera, exploring its anatomy, functions, and the common conditions that may affect it. We recognize that eye health is a significant concern for many, and the sclera plays a vital role in maintaining the shape of your eye while protecting its inner structures. Conditions such as scleritis and episcleritis can impact vision, and it’s common to feel anxious about these potential issues.
Therefore, we emphasize the importance of being aware of these conditions and taking care of your eye health. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to help you through it.
Introduction
The sclera, often called the “white part” of the eye, is more than just a surface; it acts as a crucial protective barrier that helps maintain the eye’s shape and integrity. We understand that eye health can be a concern for many, and recognizing the anatomy and function of the sclera can illuminate its vital role in supporting vision and safeguarding delicate internal structures. Unfortunately, many individuals may not be aware of the potential conditions that can affect the sclera, which could lead to serious implications for both vision and comfort.
What are the signs of scleral issues, and how can you recognize when it’s time to seek help? This exploration will delve into the anatomy, function, and common conditions of the sclera, providing essential insights to help you maintain optimal eye health. Remember, we are here to help you through this process, ensuring you feel supported every step of the way.
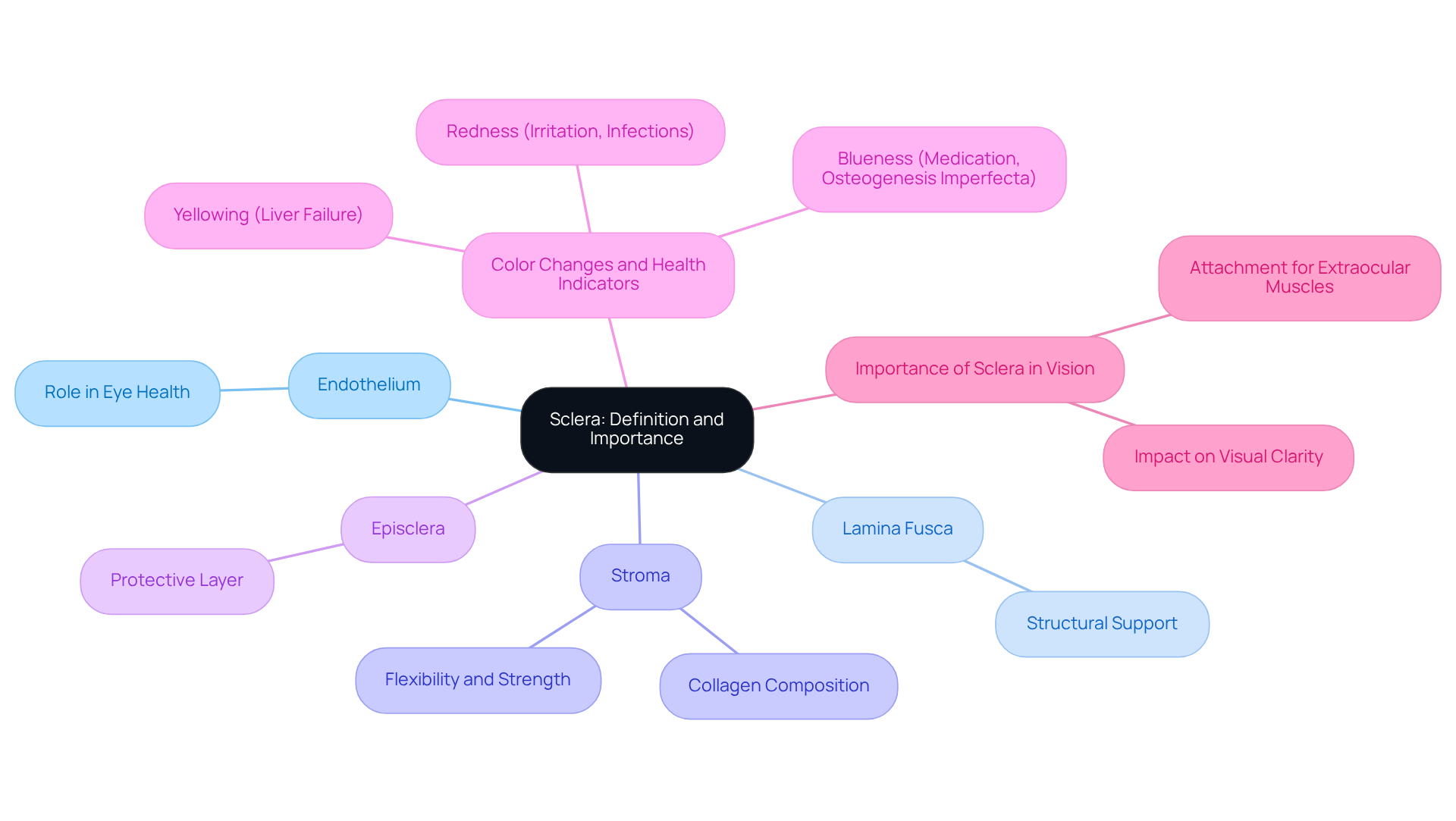
Explore the Sclera: Definition and Importance in Eye Anatomy
The , commonly known as the ‘white part,’ is a strong, fibrous covering that encases the eyeball. At about 1 mm thick, it plays a vital role in maintaining the eye’s shape and providing a . Composed mainly of collagen and elastic fibers, this outer layer offers both strength and flexibility, which are crucial for its structural integrity.
This outer layer consists of four components:
- Endothelium
- Lamina fusca
- Stroma
- Episclera
Each of these layers contributes to the overall function of the eye. It’s important to understand that the condition of the sclera eye is essential for . Any changes in the outer layer can significantly impact visual clarity. For instance, liver failure can cause the eyes to turn yellow, while prolonged medication use may lead to a blue appearance. Both of these signs can indicate underlying medical issues.
We understand that irritation can cause the sclera eye, the white part of the eye, to appear red, and can also affect its health. Additionally, the outer white layer serves as an attachment point for the , which are responsible for eye movement and focus. Recognizing the is crucial for effective eye care. It not only supports the eye’s structure but also plays a pivotal role in .
We are here to help you through this process, ensuring that you feel supported and informed about your .
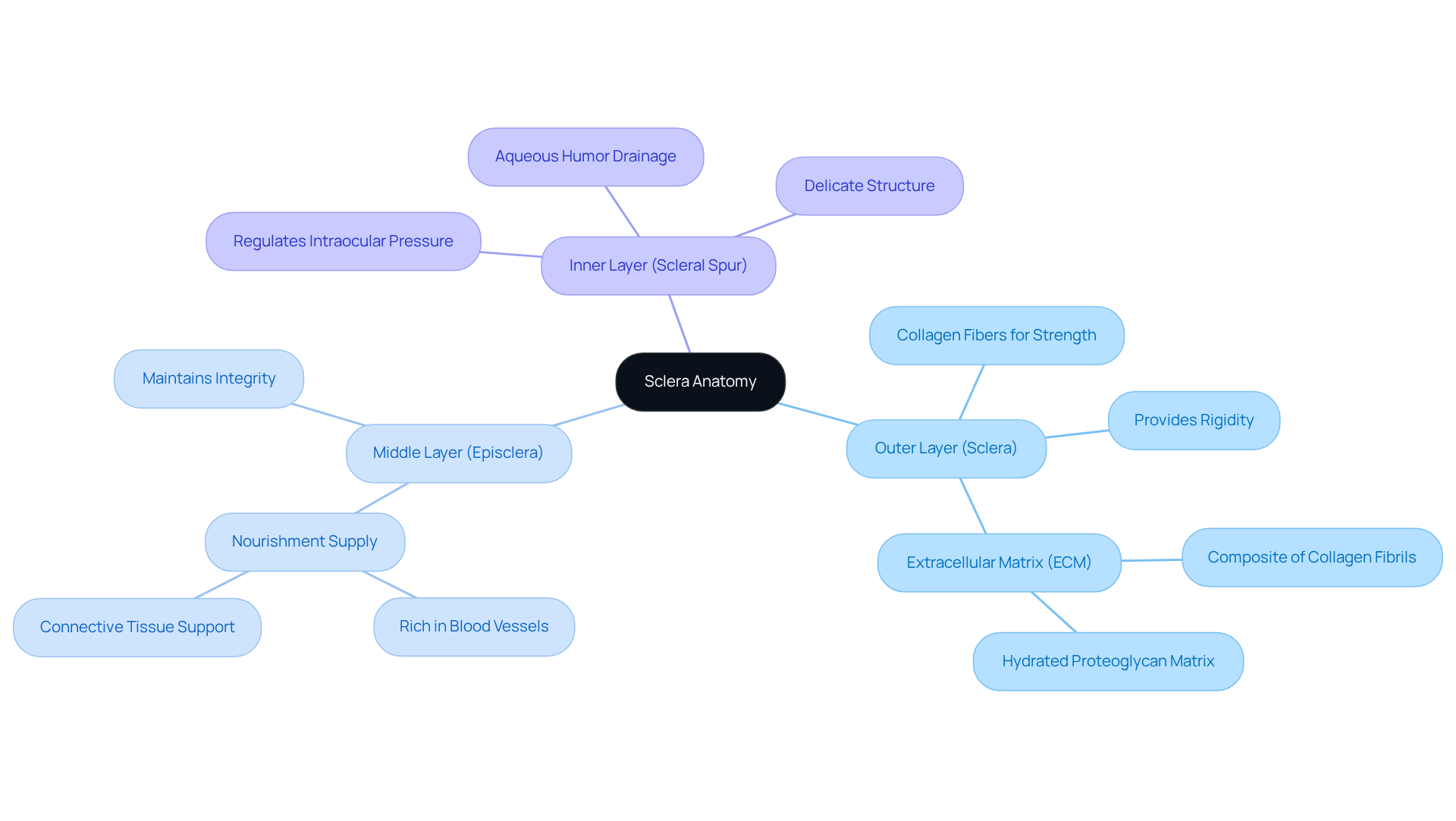
Examine the Anatomy of the Sclera: Structure and Composition
The outer layer of the eye, known as the , consists of three distinct layers, each playing a vital role in your . The sclera eye, which is the outer layer, is dense and fibrous, primarily made up of collagen fibers that provide strength and rigidity to the eye. This collagenous structure is crucial. Studies show that the sclera eye’s (ECM) acts as a composite of collagen fibrils embedded in a hydrated proteoglycan matrix, influencing its biomechanical properties.
The middle layer, known as the episclera, is rich in blood vessels and connective tissue, supplying essential nourishment to the outer layer and surrounding tissues. This is important for maintaining the integrity of the sclera eye and supporting its functions.
The inner layer, or , is more delicate and plays a significant role in draining , which is vital for regulating intraocular pressure. We understand that comprehending the and composition of the eye’s outer layer can feel overwhelming. However, it is crucial for recognizing how different conditions, like and , can impact overall . Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
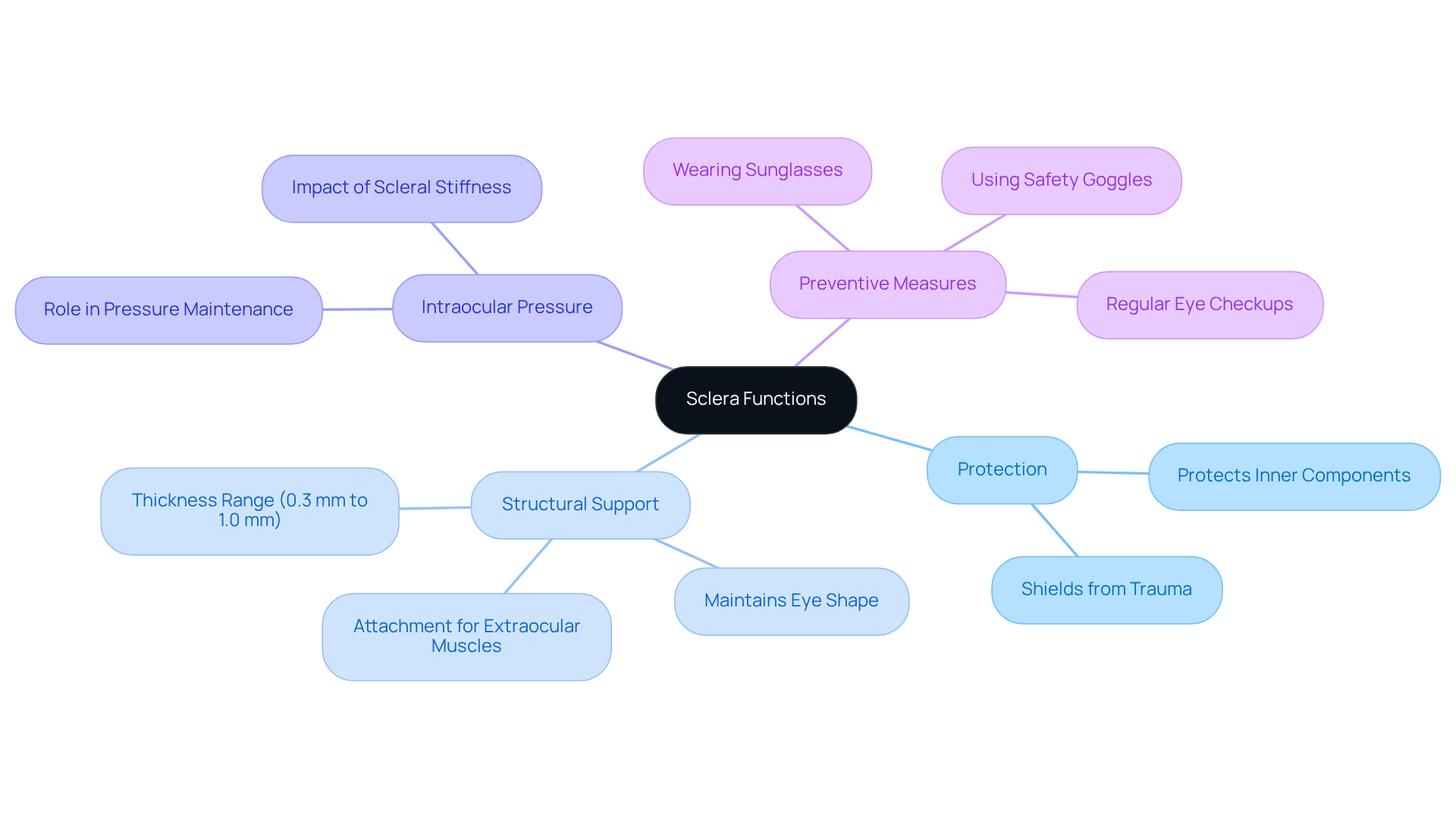
Understand the Function of the Sclera: Protection and Support
The sclera eye, known as the white outer layer of the eye, serves several vital functions. It provides , protects inner components from injury, and acts as an attachment point for the . Its robust exterior is crucial for shielding delicate internal structures, such as the retina and lens, from trauma.
We understand that maintaining is a concern for many. The outer layer of the eye also plays a significant role in maintaining , essential for optimal eye function. Studies show that can affect intraocular pressure dynamics, emphasizing the significance of in preventing issues like .
The thickness of the sclera ranges from about 0.3 mm to 1.0 mm, underscoring its structural integrity. By acknowledging these functions, patients can better understand the and the potential effects of different eye issues on their vision. It’s common to feel anxious about these matters, but knowing the facts can empower you.
Moreover, understanding the difficulties that can arise from neglected sclera eye issues—such as vision loss or globe rupture—is crucial. , can help preserve the health of the sclera eye and prevent injury. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you have the .
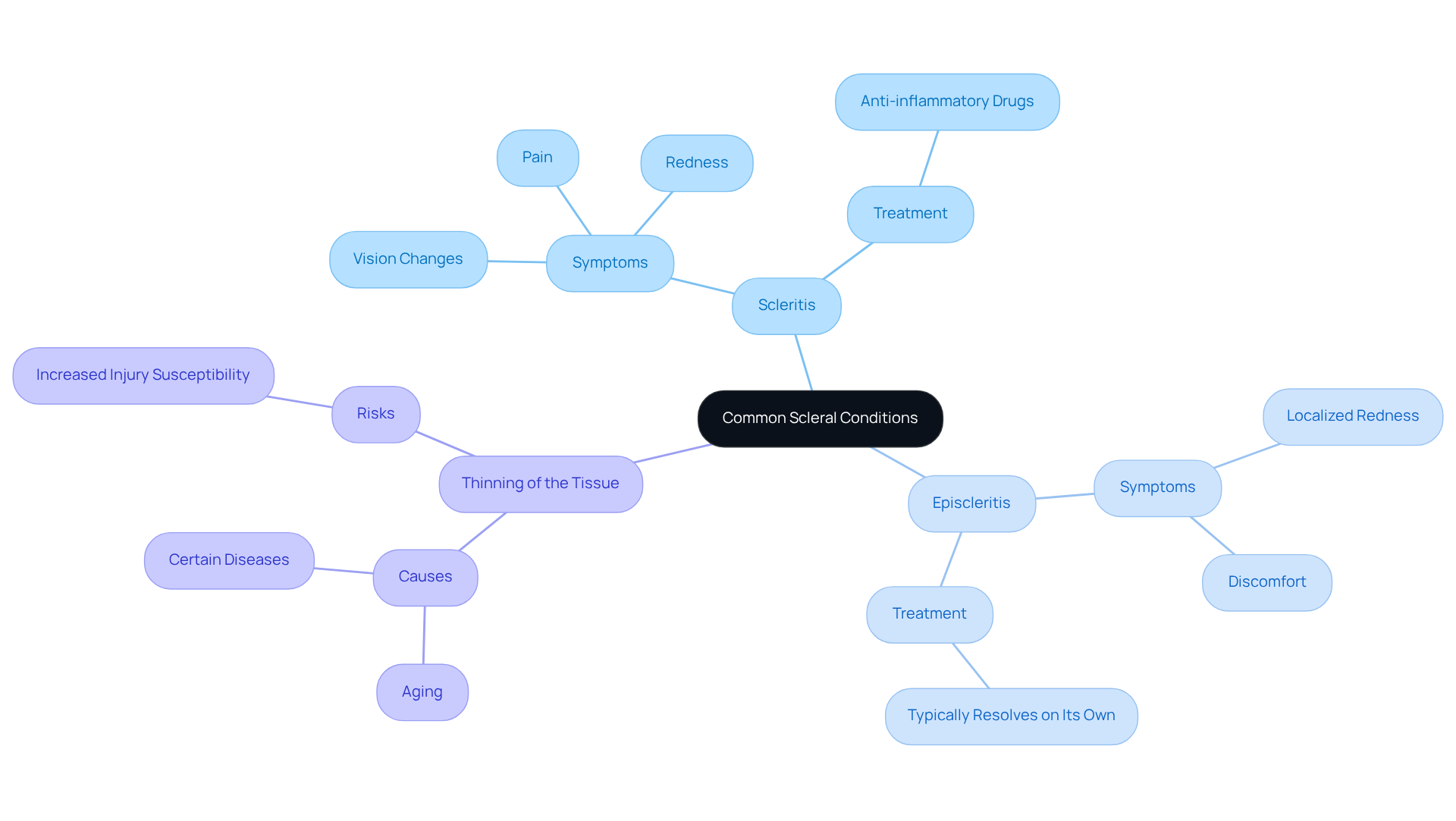
Identify Common Scleral Conditions: Symptoms and Treatments
We understand that concerns about can be worrisome. Typical issues impacting the outer layer of the include:
- Scleritis
- Episcleritis
- Thinning of the tissue
Scleritis is characterized by eye, often resulting in pain, redness, and changes in vision. It’s common to feel anxious when facing these symptoms.
Episcleritis, a milder form of inflammation, typically presents with localized redness and discomfort. The good news is that it usually resolves without significant treatment, offering some reassurance during this time. Scleral thinning can occur due to aging or certain diseases, which may lead to increased susceptibility to injury in the sclera eye.
and their symptoms is crucial for . vary based on the ailment; for instance, scleritis may necessitate , while episcleritis often resolves independently. We are here to help you through this process and ensure you feel supported in your journey to better eye health.
Conclusion
The sclera, often known as the “white part” of the eye, is a vital component of ocular anatomy that provides essential structural support and protection. Its fibrous nature and layered composition are significant in maintaining the eye’s integrity, ensuring optimal vision while safeguarding delicate internal structures. Understanding the anatomy, function, and associated conditions of the sclera is crucial for appreciating its role in overall eye health.
Key insights highlight the sclera’s multifaceted role in eye protection, support, and vision clarity. The various layers, including the episclera and scleral spur, contribute to its strength and functionality. Conditions such as scleritis and episcleritis remind us of the importance of being aware of our eye health. Recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment can help prevent complications and preserve vision.
In light of this knowledge, prioritizing scleral health through protective measures and regular eye examinations is vital. Being aware of the sclera’s significance empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their eye health. It also emphasizes the interconnectedness of the eye’s anatomy and its overall function. By fostering a deeper understanding of the sclera, we can appreciate the importance of maintaining our eye health for a lifetime of clear vision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the sclera, and what is its common name?
The sclera, commonly known as the ‘white part’ of the eye, is a strong, fibrous covering that encases the eyeball.
What is the thickness of the sclera, and what are its primary functions?
The sclera is about 1 mm thick and plays a vital role in maintaining the eye’s shape and providing a protective barrier against injury.
What materials make up the sclera?
The sclera is composed mainly of collagen and elastic fibers, which provide strength and flexibility.
What are the four components of the sclera?
The four components of the sclera are the endothelium, lamina fusca, stroma, and episclera.
How does the condition of the sclera affect vision?
The condition of the sclera is essential for overall vision quality; any changes can significantly impact visual clarity.
What health issues can affect the appearance of the sclera?
Health issues such as liver failure can cause the sclera to turn yellow, while prolonged medication use may lead to a blue appearance.
What can cause the sclera to appear red?
Irritation and eye infections can cause the sclera to appear red.
What role does the sclera play in eye movement?
The sclera serves as an attachment point for the extraocular muscles, which are responsible for eye movement and focus.
Why is it important to understand the significance of the sclera?
Understanding the significance of the sclera is crucial for effective eye care, as it supports the eye’s structure and maintains optimal vision.






