Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on September 5, 2025
Overview
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) is a serious eye condition that can understandably cause concern. This condition arises from the blockage of the central retinal vein, which can lead to potential vision impairment. CRVO is categorized into non-ischemic and ischemic types, with ischemic being more severe. We understand that receiving such news can be overwhelming, but early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. Timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of further vision loss.
It’s common to feel anxious about what comes next. This article will detail the symptoms you may experience, the diagnostic methods used to identify CRVO, and the various treatment options available for managing this condition. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring that you feel supported every step of the way. Remember, seeking care promptly can make a significant difference in your vision health.
Introduction
Understanding Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) is crucial, especially as it poses significant risks to vision, particularly in older adults. We understand that facing such a condition can be overwhelming. CRVO is marked by the blockage of the central retinal vein, which can lead to serious complications, including fluid buildup and potential vision loss. In this article, you will explore the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options available for CRVO. Our goal is to empower you to recognize this condition early and seek timely intervention. However, with various treatment paths and the varying severity of cases, it’s common to feel uncertain about how to navigate the complexities of managing CRVO effectively. We are here to help you through this process.
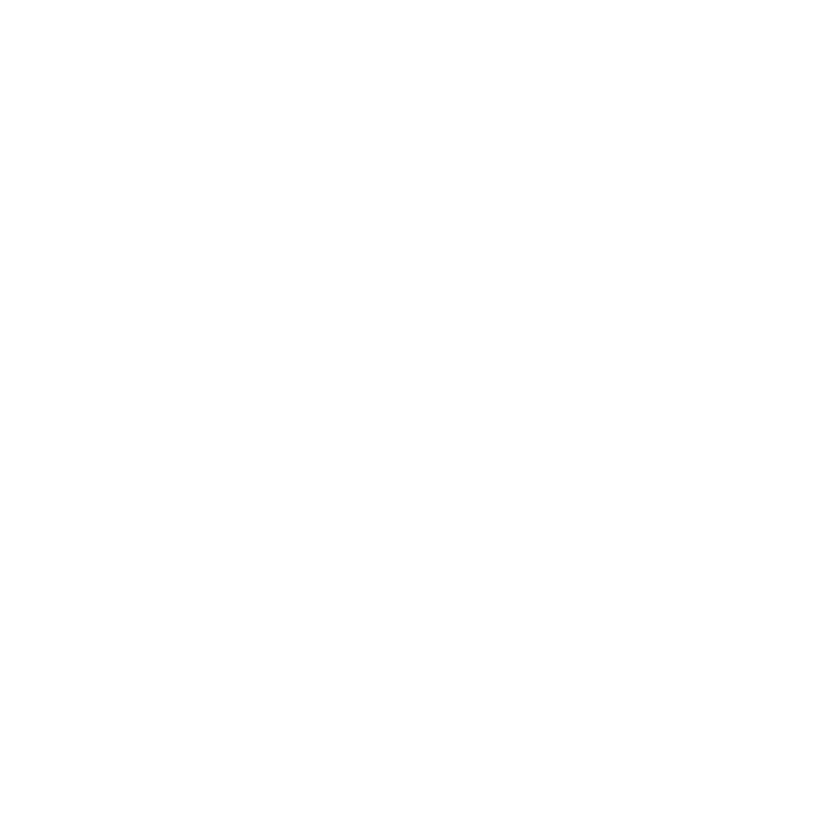
Define Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
CRVO is a significant ocular condition that can understandably cause concern. It is characterized by the blockage of the central retinal vein, known as CRVO, which plays a crucial role in draining blood from the retina. This blockage can lead to fluid and blood buildup in the retina, resulting in varying degrees of sight impairment. We know that learning about this condition can be overwhelming, so it’s important to understand that CRVO is classified into two types: non-ischemic and ischemic. The non-ischemic type is more common and typically linked to a better outlook, while CRVO, which is ischemic central retinal vein occlusion, presents a greater risk of significant vision loss due to insufficient blood flow to the retina. Notably, around 60% of patients with ischemic central retinal vein occlusion develop ocular neovascularization with related complications, highlighting the seriousness of the condition.
Key risk factors for CRVO include:
- Systemic hypertension
- Diabetes
- Glaucoma
- Age-related vascular changes
It’s common for more than 90% of cases of CRVO to occur in people over 50 years, emphasizing the condition’s prevalence in older demographics. As noted by Douglas R Lazzaro, MD, ‘Pooled data from population studies from the United States, Europe, Asia, and Australia indicate that CRVO affects 0.8 per 1000 individuals.’ Recent studies reinforce this, indicating an occurrence rate of approximately 0.8 per 1000 individuals, with significant predictors including elevated blood pressure and signs of atherosclerosis in retinal vessels.
We understand that comprehending CRVO is essential for and action. Early care can greatly reduce the risk of additional sight deterioration. Effective management often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including regular follow-ups with ophthalmologists and primary care providers to monitor and control underlying risk factors associated with CRVO. It’s also important to mention that one-third of older individuals with central retinal vein occlusion improve without intervention. Additionally, approximately 10% of individuals may develop CRVO or other forms of vein blockages in either the same eye or the opposite eye within 2 years. This proactive strategy is vital for preserving perspective and enhancing patient outcomes. Remember, we are here to help you through this process, and seeking care is a positive step towards maintaining your vision.
Identify Symptoms of CRVO
Symptoms of crvo can vary based on the severity of the blockage, and we understand how concerning this can be. Several key indicators are commonly observed, and it’s important to recognize them:
- Sudden vision loss in one eye, which can be either partial or complete.
- Blurred or distorted sight, complicating the ability to see fine details.
- The appearance of floaters or dark spots within the visual field.
- Alterations in color perception, affecting how colors are viewed.
- Loss of peripheral vision and increased sensitivity to light and glare.
Identifying these symptoms is essential, as early intervention can greatly improve recovery results. It’s common to feel anxious about these changes in vision. Research shows that individuals aged 50 and older are especially vulnerable to central retinal vein occlusion (crvo), with an estimated age- and sex-standardized prevalence of this condition being 0.80 per 1000 persons. Approximately 16 million adults may have occlusive venous disease in at least one eye.
We encourage you to seek prompt medical care if you are facing these symptoms. Timely diagnosis and treatment can help prevent additional and enhance your overall prognosis. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to help you through this process.
Explain Diagnosis of CRVO
Diagnosing CRVO can be a concerning experience, and we understand that you may have many questions. A comprehensive eye examination is essential, utilizing advanced techniques to accurately evaluate your CRVO condition. Here are some key diagnostic methods that your ophthalmologist may use:
- Visual Acuity Tests: These tests measure the clarity of your vision, providing essential baseline data for understanding the severity of vision loss associated with CRVO.
- Fundoscopy: This procedure allows your ophthalmologist to inspect your retina with a specialized lens, detecting important signs like swelling and bleeding that suggest central retinal vein occlusion.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): OCT provides high-resolution images of your retina, enabling the assessment of fluid accumulation and the extent of retinal damage. This non-invasive method has shown high accuracy rates in diagnosing central retinal vein occlusion, making it a crucial tool in clinical practice.
- Fluorescein Angiography: In this procedure, a dye is injected into your bloodstream to visualize blood flow in the retina. It helps identify areas of blockage and assess the severity of the occlusion. Fluorescein angiography complements OCT by providing dynamic insights into retinal circulation.
These diagnostic approaches are vital for your ophthalmologist to determine the type and severity of CRVO, as it directly influences treatment decisions. We want to reassure you that can significantly enhance outcomes, particularly in cases where chronic macular edema is a concern. By utilizing these advanced techniques, healthcare providers can ensure that you receive the most effective and personalized care possible.
According to recent studies, the occurrence of CRVO (central retinal vein occlusion) ranges from 0.08% to 0.1%, with a significant association with older age and a family history of stroke. As Evan J Kaufman, OD, FAAO, emphasizes, ‘CRVO is an ocular emergency, and primary care clinicians should consult with the ophthalmologist promptly.’ This highlights the urgency of diagnosis and treatment. Moreover, the occurrence of retinal vein blockages in the developed world is noted at 5.20 per 1000, underscoring the importance of identifying and diagnosing this condition swiftly. Incorporating these statistics and expert insights not only enhances the authority of the content but also provides a broader context for the significance of timely diagnosis. We are here to help you through this process.
Outline Treatment Options for CRVO
Treatment alternatives for can vary based on the type and severity of the condition, and we understand that navigating these options can feel overwhelming. Here are some common approaches that may be considered:
- Observation: If you have non-ischemic CRVO with mild symptoms, your doctor may recommend monitoring your condition over time. This approach allows for timely intervention if your symptoms worsen, providing peace of mind as you move forward.
- Intravitreal Injections: Anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) agents, such as Avastin and Eylea, are often used to help reduce retinal swelling and improve vision. A 2017 study showed that these injections can significantly enhance visual acuity in individuals suffering from CRVO, with many experiencing substantial improvements. In fact, 82% of patients achieved complete clinical remission following anti-VEGF injections, which can be reassuring to those seeking effective treatment.
- Laser Therapy: Focal laser intervention targets specific areas of the retina that are leaking fluid, helping to stabilize vision. Recent advancements in laser technology, such as PASCAL photocoagulation, have demonstrated promising results with minimal pain and effective outcomes. Kenneth C S Fong emphasizes that laser photocoagulation is a fundamental approach for various retinal conditions, particularly in managing CRVO.
- Surgery: In more severe cases, surgical interventions like vitrectomy may be necessary to remove blood and relieve pressure on the retina. This option is typically considered when other approaches have not yielded satisfactory results, and we want you to know that this is a valid path if needed.
Each care plan should be customized to your unique needs, taking into account your specific requirements and overall well-being. Continuous monitoring and follow-up are essential, as many patients may require ongoing treatment to maintain vision improvements. Remember, the integration of personalized care and the latest therapeutic advancements plays a crucial role in effectively managing CRVO. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring that you feel supported every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) is crucial for recognizing its potential impact on vision and overall eye health. This ocular condition, characterized by the blockage of the central retinal vein, can lead to serious complications if not addressed promptly. By familiarizing oneself with the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps towards safeguarding their vision.
We understand that early detection and intervention are vital. Symptoms such as sudden vision loss, blurred sight, and the appearance of floaters should not be overlooked, as they signal the need for immediate medical attention. Diagnostic techniques, including visual acuity tests and optical coherence tomography, play a vital role in accurately assessing the condition. Furthermore, various treatment strategies, ranging from observation to intravitreal injections and laser therapy, provide tailored options to manage CRVO effectively.
Ultimately, raising awareness about CRVO and its implications can empower individuals to seek timely care and support. Whether through regular eye examinations or understanding the risk factors associated with this condition, taking action is essential. For those experiencing symptoms or at risk, consulting with a healthcare professional is a critical step towards preserving vision and enhancing quality of life. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)?
CRVO is a significant ocular condition characterized by the blockage of the central retinal vein, which is responsible for draining blood from the retina. This blockage can lead to fluid and blood buildup in the retina, causing varying degrees of sight impairment.
What are the two types of CRVO?
CRVO is classified into two types: non-ischemic and ischemic. The non-ischemic type is more common and generally has a better outlook, while ischemic CRVO poses a greater risk of significant vision loss due to insufficient blood flow to the retina.
What are the key risk factors for developing CRVO?
Key risk factors for CRVO include systemic hypertension, diabetes, glaucoma, and age-related vascular changes.
Who is most commonly affected by CRVO?
More than 90% of CRVO cases occur in individuals over 50 years old, indicating its prevalence in older demographics.
What is the occurrence rate of CRVO?
CRVO affects approximately 0.8 per 1000 individuals, according to pooled data from population studies across the United States, Europe, Asia, and Australia.
How can CRVO be managed effectively?
Effective management of CRVO often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including regular follow-ups with ophthalmologists and primary care providers to monitor and control underlying risk factors.
Is it possible for individuals with CRVO to improve without intervention?
Yes, about one-third of older individuals with central retinal vein occlusion may improve without any intervention.
What is the likelihood of developing CRVO or other vein blockages in the same or opposite eye within two years?
Approximately 10% of individuals may develop CRVO or other forms of vein blockages in either the same eye or the opposite eye within two years.






