Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on November 19, 2025
Introduction
Understanding the complexities of eye bulging disease, often referred to as exophthalmos or proptosis, is essential. This condition can indicate various underlying health issues, and we recognize that it may raise concerns about serious medical implications.
As you explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options associated with eye bulging, we hope you gain valuable insights into managing this condition effectively. It’s common to feel overwhelmed with so many potential factors at play, from autoimmune disorders to lifestyle choices.
So, what are the key indicators that should prompt immediate medical attention? We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you feel supported and informed every step of the way.
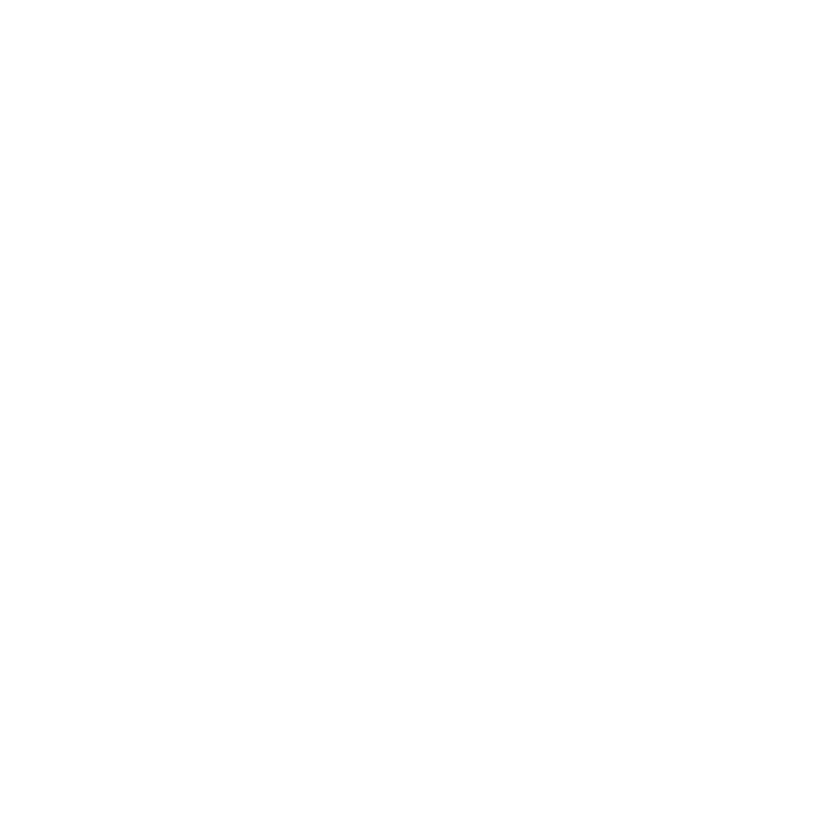
Define Eye Bulging: Understanding Exophthalmos and Proptosis
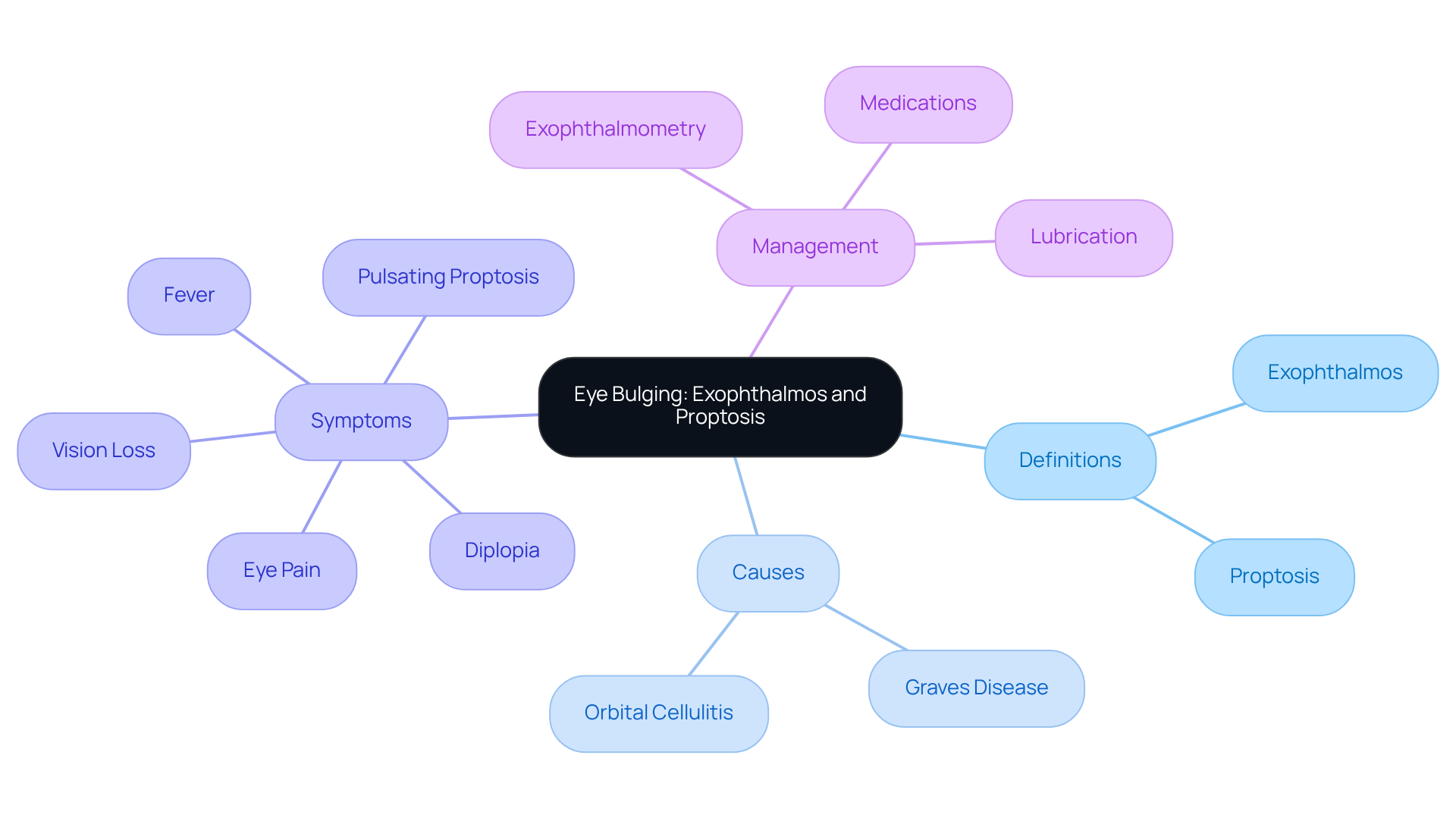
Eye protrusion, also known as exophthalmos or proptosis, can be concerning. It refers to the abnormal extension of one or both eyeballs from their natural position in the eye socket. Understanding these terms is essential, as they can indicate various underlying conditions, ranging from benign to more serious medical issues.
We understand that learning about these conditions can be overwhelming. Recent studies highlight that Graves disease is often the primary cause of proptosis in adults. This autoimmune condition leads to swelling and lymphoid infiltration of the orbital tissues, resulting in noticeable eye protrusion. In children, orbital cellulitis is frequently identified as the main cause of proptosis.
Recognizing the symptoms associated with these conditions is crucial. For example, acute unilateral proptosis may signal serious issues like intraorbital hemorrhage or infections, which require immediate medical attention. Key symptoms to watch for include:
- Eye pain
- Vision loss
- Diplopia (double vision)
- Fever
- Pulsating proptosis
These signs are critical for understanding the urgency of the situation. Prompt intervention can significantly impact health outcomes, especially when these red flags are present.
Current research is focused on understanding the mechanisms behind the eye bulging disease. Clinical trials are exploring innovative solutions for eye bulging disease (Thyroid Eye Disease), aiming to reduce the need for invasive surgeries like orbital decompression. New medications are being assessed for their effectiveness in alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life.
Real-world examples of proptosis management show the evolving landscape of care options. For instance, systemic glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, have been effective in managing edema and orbital congestion in individuals with TED. Additionally, lubrication is vital for protecting the cornea in severe cases of proptosis.
Exophthalmometry, which measures the distance from the lateral angle of the bony orbit to the cornea, plays a key role in diagnosing proptosis and assessing its severity. Normal values are typically around 20 mm, but they can vary by age, sex, and ethnicity. As research progresses, our goal remains to provide effective, minimally invasive solutions that enhance patient care and outcomes. We are here to help you through this process.
Explore Causes of Eye Bulging: From Medical Conditions to Lifestyle Factors
Eye bulging disease can arise from a variety of factors, each with distinct implications for treatment and management. We understand that this can be concerning, and we’re here to help you navigate through it.
Thyroid Eye Disease (Graves’ Disease) is the leading cause of eye bulging disease, which is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the eye muscles that pushes the eyeball forward. About 1 in 3 people with Graves’ disease develop eye-related issues, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and intervention. Symptoms may include dry, gritty, red, or irritated vision, puffy eyelids, eyelids that pull back more than usual or don’t close completely, double vision, sensitivity to light, discomfort or pressure in the eyes, and difficulty moving the eyes.
-
Orbital Tumors: Both benign and malignant growths within the eye socket can lead to displacement of the eye. Recent findings indicate that timely management of these tumors is crucial, as they can significantly impact vision and overall eye health. It’s common to feel anxious about this, but early intervention can make a difference.
-
Inflammation: Conditions such as orbital cellulitis can result in swelling and protrusion of the eyes. This inflammation often requires prompt medical attention to prevent complications, including potential vision loss, as swelling can press on the optic nerve. We understand that seeking help can be daunting, but it’s important to act quickly.
-
Injury: Trauma to the eye area can cause bleeding or swelling behind the eye, resulting in visible protrusion. Immediate evaluation by an eye care professional is essential to assess the extent of the injury and determine appropriate treatment. Remember, you’re not alone in this; professionals are ready to support you.
-
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been shown to worsen conditions that lead to eye protrusion. For instance, smoking increases the risk of developing Graves’ disease and its ocular manifestations. Grasping these lifestyle factors is crucial for individuals aiming to enhance their vision health and reduce risks linked to prominent eyes. We encourage you to consider these factors as part of your journey to better eye health.
Recognizing these causes is crucial for the effective management and treatment of eye bulging disease. By understanding what might be contributing to your symptoms, you can seek timely medical intervention and improve your quality of life. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.

Identify Symptoms of Eye Bulging: Key Indicators and Warning Signs
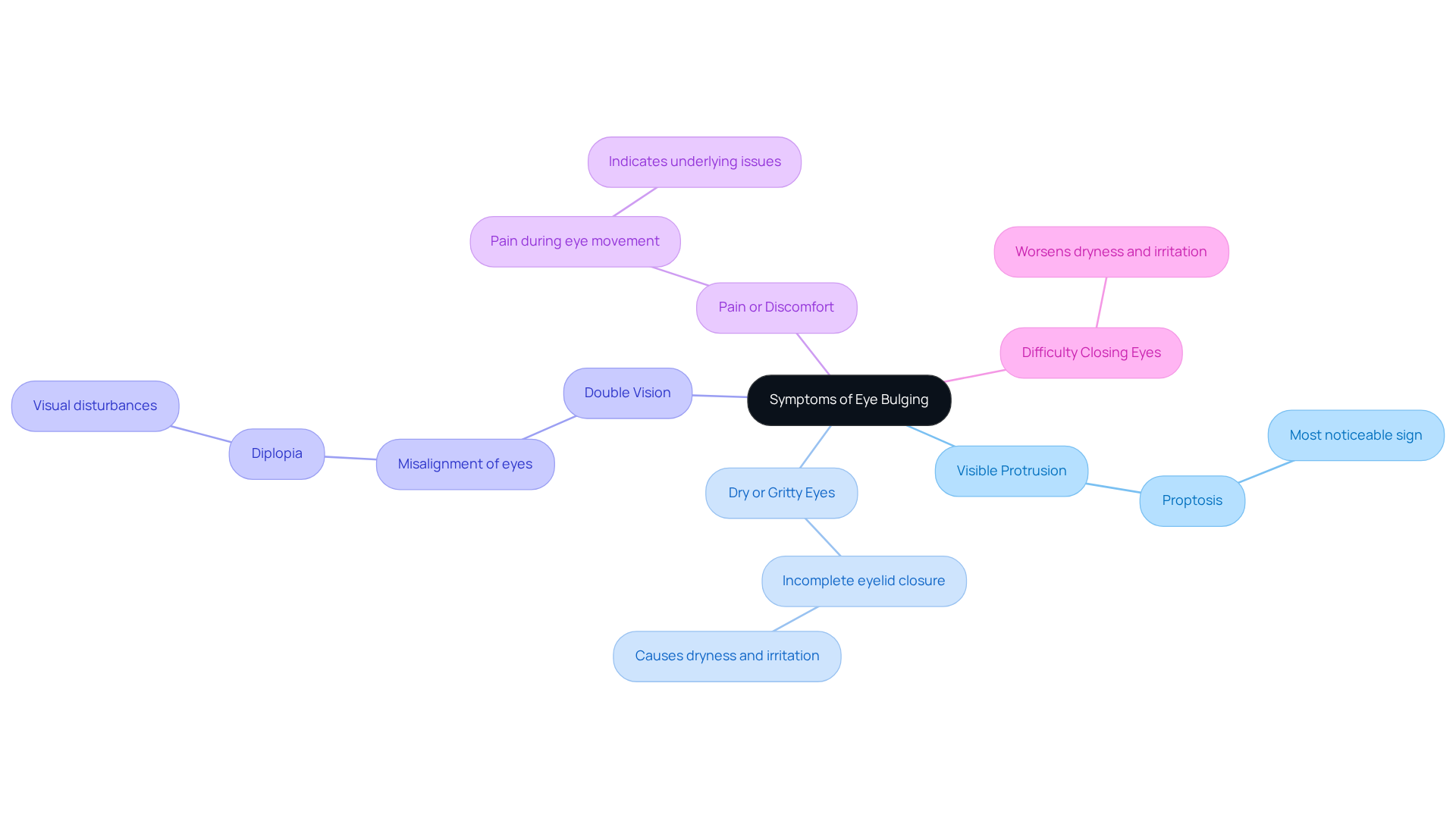
If you’ve noticed changes in your eyes, it’s completely understandable to feel concerned. Common symptoms associated with eye bulging include:
- Visible Protrusion: One or both eyes may seem more prominent than usual, a condition known as proptosis. This is often the most noticeable sign.
- Dry or Gritty Eyes: Many patients report a sensation of dryness or irritation, which can happen due to incomplete eyelid closure.
- Double Vision: Misalignment of the eyes, or diplopia, can occur, leading to visual disturbances that need prompt attention.
- Pain or Discomfort: It’s not uncommon to experience pain, especially during eye movement, which can indicate underlying issues.
- Difficulty Closing Eyes: In some cases, the eyelids may not fully cover the eyeball, worsening dryness and irritation.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial. We understand that timely medical intervention can significantly improve outcomes. Reports indicate that around 13 to 20% of patients with thyroid eye disease (TED) experience dry eye symptoms, highlighting the importance of awareness. Furthermore, ophthalmologists emphasize that any sudden changes in eye appearance, especially those indicating eye bulging disease, warrant immediate evaluation to rule out serious conditions like tumors or infections.
To ensure proper diagnosis and care, we encourage you to schedule an appointment with a Northwest Eye doctor. Real-world cases show that early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications, underscoring the need for vigilance in monitoring your eye health. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Evaluate Eye Bulging: Diagnostic Procedures and Assessments
Evaluating eye bulging disease can be a concerning experience, and we understand that you may have many questions. Here’s a look at the diagnostic procedures that can help clarify your situation:
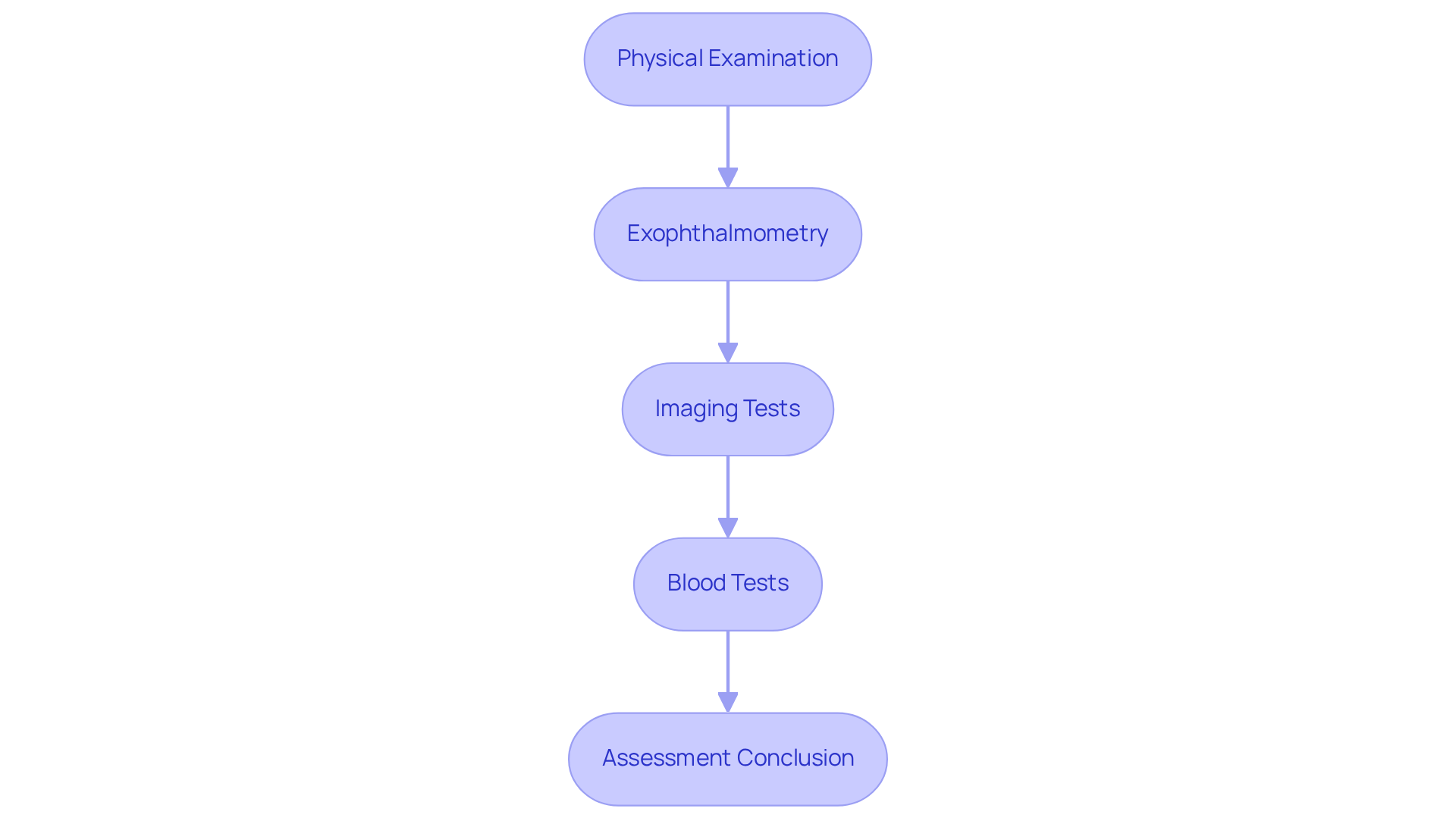
- Physical Examination: An ophthalmologist will conduct a thorough assessment of your eye health, checking for signs of redness, irritation, or other abnormalities. This step is crucial in understanding the degree of protrusion and ensuring your overall well-being.
- Exophthalmometry: This specialized test measures how far your eyes protrude using instruments like the Hertel or Luedde exophthalmometer. The measurement is taken from the lateral orbital margin to the apex of the cornea while you look straight ahead. Normal protrusion measurements range from 12 to 21 mm, with mean measurements of 16.5 mm for Caucasian males and 15.4 mm for females. This method is essential for identifying conditions like Graves’ disease, a common cause of eye bulging disease in adults.
- Imaging Tests: CT scans or MRIs may be ordered to visualize the structures behind your eyes. These tests help identify any abnormalities such as tumors or inflammation, especially when swelling affects just one eye. They provide detailed insights into the underlying causes, which can be reassuring.
- Blood Tests: These tests evaluate thyroid function and other underlying conditions that may lead to eye protrusion. For instance, eye bulging disease, also known as thyroid eye disease (TED), affects approximately one million Americans annually and can lead to significant vision issues if not addressed promptly.
A thorough assessment is crucial for establishing the right care strategy. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring that your unique needs are addressed effectively. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
Treat Eye Bulging: Overview of Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Treatment for eye bulging is tailored to the underlying cause and may encompass several approaches:
-
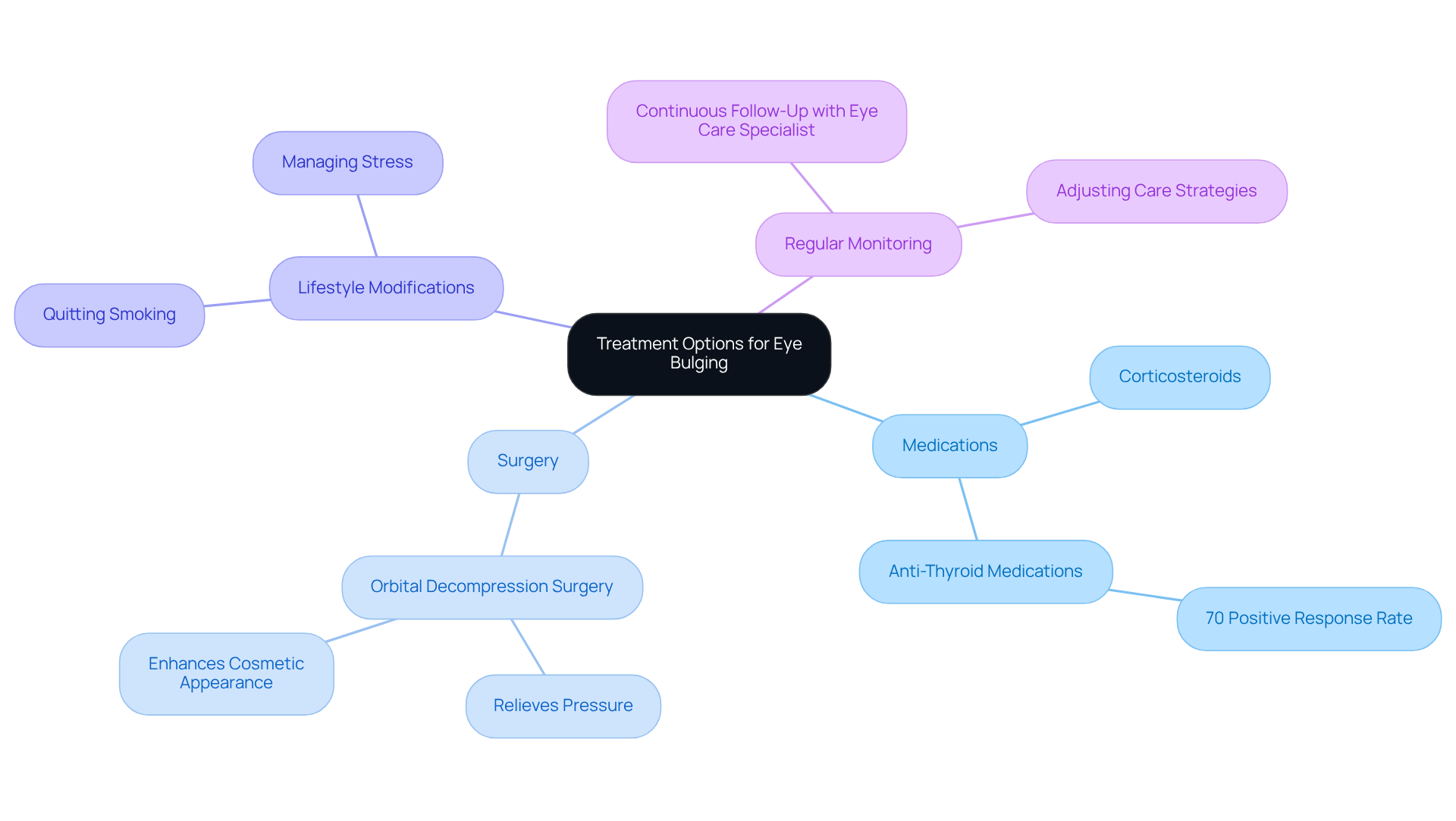
Medications: We understand that managing eye bulging can be challenging. Corticosteroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation, while anti-thyroid medications can effectively address thyroid-related conditions. Recent studies show that these medications can significantly alleviate symptoms, with about 70% of participants responding positively to treatments like Viridian’s drug VRDN-001 for eye bulging disease.
-
Surgery: If you’re experiencing pronounced protrusion, orbital decompression surgery might be an option worth considering. This procedure aims to relieve pressure on the eyes and enhance cosmetic appearance, offering significant relief for many individuals.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but adopting healthier habits can make a difference. Quitting smoking and managing stress are crucial steps in symptom management. Research indicates that individuals who stop smoking often see better results in managing eye protrusion issues.
-
Regular Monitoring: We know that continuous follow-up with an eye care specialist is essential for effectively managing chronic conditions. Regular evaluations allow for prompt adjustments to care strategies, ensuring that your unique needs are met. As Dr. Smith, an ophthalmologist, emphasizes, ‘Regular monitoring is essential for adjusting care strategies and attaining the best results for individuals with eye bulging disease.’
Integrating these strategies is vital for effective management. Personalized care not only enhances treatment outcomes but also fosters patient satisfaction. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Conclusion
Understanding eye bulging disease, or exophthalmos, is essential for recognizing its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. We understand that this condition, characterized by the abnormal protrusion of one or both eyes, can be concerning. It may signify various underlying health issues, ranging from autoimmune disorders like Graves’ disease to lifestyle factors such as smoking. Awareness of these aspects is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
The article highlights key causes, including:
- Thyroid eye disease
- Orbital tumors
- Inflammation
- Trauma
Each of these has specific implications for treatment, and it’s common to feel overwhelmed by the information. Symptoms such as visible protrusion, dry or gritty eyes, and double vision serve as important indicators that warrant prompt medical evaluation. Diagnostic procedures like exophthalmometry and imaging tests are vital for understanding the severity of the condition and guiding treatment decisions.
Ultimately, taking proactive steps in monitoring eye health and seeking medical attention when necessary can significantly impact outcomes. We encourage you to emphasize lifestyle modifications alongside medical interventions to enhance your overall well-being. By staying informed and vigilant, you can navigate the complexities of eye bulging disease, ensuring you receive the appropriate care and support needed for optimal eye health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is eye bulging, and what are its medical terms?
Eye bulging, also known as exophthalmos or proptosis, refers to the abnormal extension of one or both eyeballs from their natural position in the eye socket.
What is the primary cause of proptosis in adults?
The primary cause of proptosis in adults is Graves disease, an autoimmune condition that leads to swelling and lymphoid infiltration of the orbital tissues.
What is the main cause of proptosis in children?
In children, the main cause of proptosis is often orbital cellulitis.
What symptoms should be recognized as potential indicators of serious issues related to eye bulging?
Key symptoms to watch for include eye pain, vision loss, diplopia (double vision), fever, and pulsating proptosis.
Why is it important to recognize these symptoms?
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial because they can indicate serious conditions that require immediate medical attention, and prompt intervention can significantly impact health outcomes.
What current research is being conducted regarding eye bulging disease?
Current research is focused on understanding the mechanisms behind eye bulging disease (Thyroid Eye Disease) and exploring innovative solutions to reduce the need for invasive surgeries like orbital decompression.
What role does exophthalmometry play in diagnosing proptosis?
Exophthalmometry measures the distance from the lateral angle of the bony orbit to the cornea, which helps in diagnosing proptosis and assessing its severity.
What are some lifestyle factors that can contribute to eye bulging?
Lifestyle factors such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen conditions that lead to eye protrusion, including Graves’ disease.
What are some other causes of eye bulging apart from Graves’ disease?
Other causes include orbital tumors (both benign and malignant), inflammation from conditions like orbital cellulitis, and trauma to the eye area.
How can timely management of eye bulging conditions impact health?
Timely management of conditions leading to eye bulging is crucial as it can significantly impact vision and overall eye health, reducing the risk of complications.






