Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on October 22, 2025
Overview
Optic nerve cupping is a condition that can understandably cause concern, as it is characterized by the hollowing of the optic nerve head. This often indicates increased intraocular pressure associated with glaucoma, which can lead to significant vision loss if not identified and managed promptly.
We understand that this may be alarming, but early detection is key. Regular eye exams and advanced diagnostic techniques, such as:
- Optical coherence tomography
- Visual field testing
play a crucial role in differentiating between glaucomatous and nonglaucomatous causes. This differentiation is essential to ensure you receive the appropriate treatment and care you deserve. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Introduction
Understanding the nuances of optic nerve cupping is vital for maintaining your eye health. This condition often signals underlying issues, such as increased intraocular pressure associated with glaucoma. We understand that this can be concerning, but by delving into the causes, diagnostic techniques, and treatment options, you can gain valuable insights into how to manage your eye health effectively.
It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the complexity of differentiating between glaucomatous and nonglaucomatous cupping. This raises an important question: how can you ensure accurate diagnosis and timely intervention to prevent potential vision loss? We are here to help you through this process, providing the support and information you need to navigate these challenges.
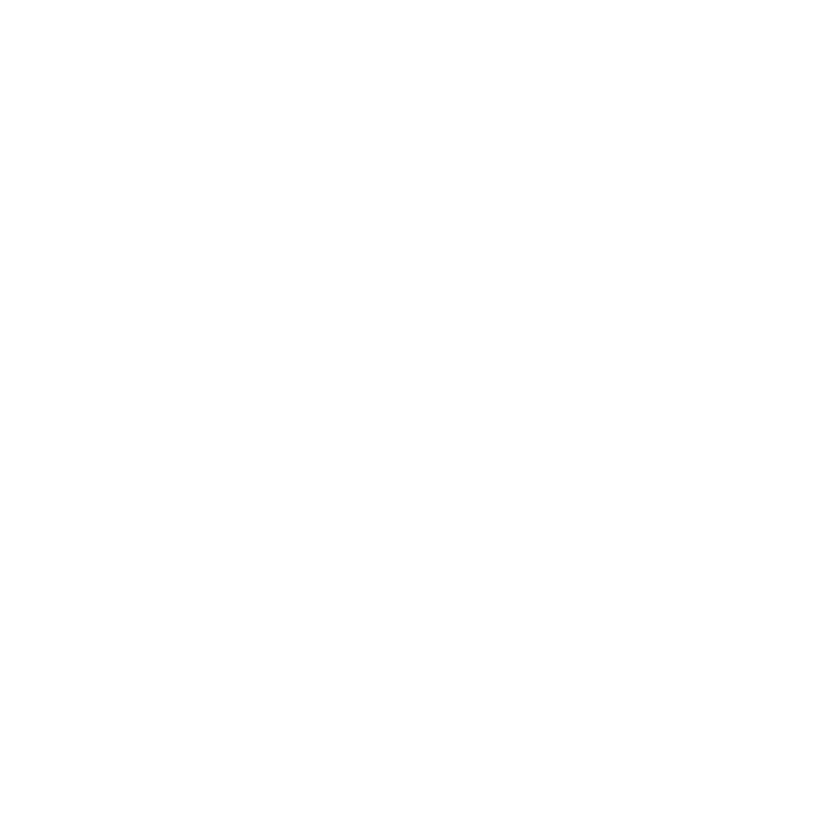
Define Optic Nerve Cupping and Its Importance
The excavation of the eye’s head is marked by the hollowing of the visual pathway, a condition that can be detected during a thorough eye assessment. We understand that this phenomenon can be concerning, especially as it often signals increased intraocular pressure, a hallmark of glaucoma. Prompt identification of eye socket deformation is essential; research shows that swift action can avert permanent vision impairment.
For instance, the area under the curve (AUC) for differentiating glaucoma from non-glaucoma using specific measurements was found to be 0.95 (95% confidence interval: 0.86, 1.00). This underscores the effectiveness of early detection methods, giving you reassurance that timely intervention can make a difference. Eye specialists stress that identifying the indications of eye disc deformation can lead to improved outcomes for individuals. It’s common to feel anxious about the implications of these findings, but remember that neglected instances may advance to significant vision loss.
Regular eye exams are essential, especially for individuals with risk factors for glaucoma or other ocular diseases. These check-ups facilitate monitoring and proactive management of your eye health. Nevertheless, we recognize that distinguishing glaucomatous from non-glaucomatous nerve cupping continues to be difficult. It requires careful evaluation of your medical history, visual function, and eye examination.
Ancillary testing, such as visual field tests and optical coherence tomography (OCT), plays a vital role in accurately diagnosing optic neuropathies. Furthermore, it’s noteworthy that 73.1% of patients referred to neuro-ophthalmology had diagnoses unrelated to glaucoma. This highlights the importance of thorough evaluations to avoid misdiagnosis. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you receive the care and support you need.
Identify Causes of Optic Nerve Cupping: Glaucomatous vs. Nonglaucomatous
Understanding optic nerve cupping can be overwhelming, but it’s important to know that it can arise from various causes, generally categorized into glaucomatous and nonglaucomatous factors.
- Glaucomatous depression primarily arises from increased intraocular pressure, which can harm the nerve fibers.
- On the other hand, nonglaucomatous cupping may be linked to conditions like optic neuritis, ischemic optic neuropathy, or congenital anomalies, all of which can be associated with optic nerve cupping.
Recognizing these differences is crucial for determining the right management and treatment strategies for you, as each cause may require a unique approach to care.
Recent research underscores the importance of precise diagnosis. A study revealed that machine learning algorithms can identify individuals with glaucoma with an impressive accuracy of 88 to 90 percent, significantly outpacing human evaluators. As noted by Anthony Khawaja, PhD, FRCOphth, ‘I was surprised to see the degree to which machine learning outperformed the human testers.’ This advancement highlights the potential for integrating technology into clinical practice, which can lead to improved outcomes and more effective treatment plans.
Moreover, understanding the frequency of glaucomatous versus nonglaucomatous changes, such as optic nerve cupping, in the optic disc is essential. This knowledge guides clinical strategies and helps allocate resources effectively in vision care.
We should also consider the ethical implications of incorporating AI into healthcare, as these factors will undoubtedly influence the future of patient care and treatment effectiveness. Remember, we are here to help you through this process and ensure you receive the best care possible.
Explain Diagnostic Techniques for Assessing Optic Nerve Cupping
We understand that concerns about your vision can be daunting. Several diagnostic techniques are employed to assess optic nerve cupping, and we want to provide you with the information to help ease your mind:
- Fundoscopy: This involves a direct examination of the optic nerve head using an ophthalmoscope, allowing for a visual assessment of cupping. It’s a straightforward process, and your comfort is our priority.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): This non-invasive imaging method offers cross-sectional visuals of the retina and visual pathway. It assists in measuring the extent of depression, providing valuable insights without discomfort.
- Visual Field Testing: This evaluates peripheral vision loss, which can suggest impairment to the visual pathway. We understand that this may feel overwhelming, but it’s an essential step in understanding your eye health.
These techniques are crucial for establishing a diagnosis, monitoring progression, and determining the suitable treatment plan for patients with optic nerve cupping. Remember, we are here to help you through this process and ensure you receive the best care possible.
Outline Treatment Options and Management Strategies
When it comes to treatment options for optic nerve damage, it’s important to understand that they depend on the underlying cause. We know that facing these challenges can be daunting, especially if you are dealing with optic nerve cupping. In such cases, management typically includes:
- Medications: Eye drops that help lower intraocular pressure, like prostaglandin analogs or beta-blockers, can be effective.
- Laser Therapy: Procedures such as selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT) can assist in improving fluid drainage from the eye.
- Surgery: For more advanced situations, surgical options, including trabeculectomy or tube shunt surgery, may be necessary.
If you’re experiencing nonglaucomatous cupping, the focus shifts to addressing the underlying condition. This may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or even surgical interventions. We understand that regular follow-up appointments are crucial; they allow for monitoring your condition and adjusting treatment as needed. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we are here to help you through the process.
Conclusion
Understanding optic nerve cupping is crucial for maintaining eye health. We recognize that this condition often signals underlying issues, such as increased intraocular pressure linked to glaucoma. Characterized by the hollowness of the optic nerve head, it requires prompt identification and intervention to prevent irreversible vision loss. By being aware of the significance of optic nerve cupping, you can seek timely evaluations and engage proactively in your eye care.
This article highlights the multifaceted aspects of optic nerve cupping. From its causes—both glaucomatous and nonglaucomatous—to the diagnostic techniques and treatment options available, we aim to provide comprehensive insights. Advanced technologies, such as machine learning, play a vital role in enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Regular eye exams are essential for those at risk, reinforcing the necessity for tailored management strategies to address individual needs effectively.
Ultimately, understanding optic nerve cupping is not merely an academic exercise; it is a vital component of proactive eye health maintenance. We encourage you to prioritize regular eye examinations, stay informed about the signs and symptoms of optic nerve cupping, and engage with healthcare professionals to ensure optimal care. By doing so, you can significantly mitigate the risks associated with this condition and preserve your vision for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is optic nerve cupping?
Optic nerve cupping is the excavation or hollowing of the eye’s head, which can be detected during a thorough eye assessment and often signals increased intraocular pressure, commonly associated with glaucoma.
Why is optic nerve cupping important?
It is important because it can indicate the presence of glaucoma, and early detection is crucial to prevent permanent vision impairment. Timely identification and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for affected individuals.
How effective are early detection methods for glaucoma?
Early detection methods for glaucoma have shown to be highly effective, with a study indicating an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.95 for differentiating glaucoma from non-glaucoma, suggesting high accuracy in identifying the condition.
What should individuals with risk factors for glaucoma do?
Individuals with risk factors for glaucoma should undergo regular eye exams to facilitate monitoring and proactive management of their eye health.
What challenges exist in distinguishing glaucomatous from non-glaucomatous nerve cupping?
Distinguishing glaucomatous from non-glaucomatous nerve cupping is challenging and requires a careful evaluation of medical history, visual function, and a comprehensive eye examination.
What role does ancillary testing play in diagnosing optic neuropathies?
Ancillary testing, such as visual field tests and optical coherence tomography (OCT), is vital for accurately diagnosing optic neuropathies, aiding in distinguishing between different conditions.
What does the statistic about patients referred to neuro-ophthalmology indicate?
The statistic that 73.1% of patients referred to neuro-ophthalmology had diagnoses unrelated to glaucoma indicates the importance of thorough evaluations to avoid misdiagnosis and ensure appropriate care.






