Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on May 20, 2025
Overview
Peripheral vision is vital in our daily lives, as it enhances our spatial awareness and safety, especially during activities like driving, walking, and playing sports. We understand that navigating these environments can be challenging, and peripheral vision plays a crucial role in helping us detect motion and hazards outside our direct line of sight. This ability is essential for avoiding accidents, ensuring that everyone, regardless of age, can feel secure in various contexts. It’s common to feel concerned about safety, but knowing how our vision works can provide reassurance.
Introduction
In a world where visual perception is vital for safety and navigation, we want to highlight the importance of peripheral vision. Often overlooked in favor of our central focus, peripheral vision plays a crucial role in how we interact with our surroundings. Whether you’re driving through busy streets or participating in competitive sports, the ability to perceive motion and detect potential hazards outside of your direct line of sight is essential.
This article will explore the intricate workings of peripheral vision, including its anatomical foundations, its impact on our daily activities, and the various conditions that can impair this essential function. By understanding the nuances of peripheral vision, we can better appreciate its role in enhancing our spatial awareness and overall safety in everyday life.
Define Peripheral Vision and Its Role in Visual Perception
, which is often referred to as side sight, is the ability to . This vital visual ability encompasses everything observable without the need to move the head or eyes, allowing individuals to notice motion and shapes in . It plays a crucial role in , which is essential for safely navigating various environments. For example, when operating a vehicle, peripheral vision is key in approaching from the side, thereby .
We understand that side sight significantly impacts everyday tasks, especially in transportation scenarios. A study examining the relationship between age and the effectiveness of side eyesight revealed that while older drivers may experience a decline in processing peripheral vision, they can still identify road dangers similarly to younger drivers. This underscores the across all age groups. The findings suggest that even as external processing may diminish with age, the remains strong, highlighting the need for continued awareness of the role of peripheral vision in maintaining safety.
Statistics indicate that drivers, pedestrians, and pilots rely heavily on surrounding information, which can vary based on situational factors. The capacity to process sight-related information through peripheral vision is essential for effective hazard detection, as distractions—whether auditory or visual—can impede this ability. For instance, various forms of auditory distraction can result in poorer hazard detection, regardless of the hazard’s location. Experts in the field emphasize that peripheral vision is not merely an adjunct to central vision but a fundamental aspect of perception that enhances spatial awareness. Ruth Rosenholtz from MIT notes, “We argue that the key issue in search is the processing of image patches in the periphery, where visual representation is characterized by summary statistics computed over a sizable pooling region.”
In our everyday lives, peripheral vision aids in numerous activities beyond driving, including walking and engaging in sports, where awareness of the environment is paramount. The ability to detect movement and changes in the surroundings without direct attention through peripheral vision allows individuals to respond swiftly to potential dangers, reinforcing the importance of preserving this aspect of vision as one ages. Ultimately, understanding the function of peripheral vision is essential for recognizing its in our daily lives.
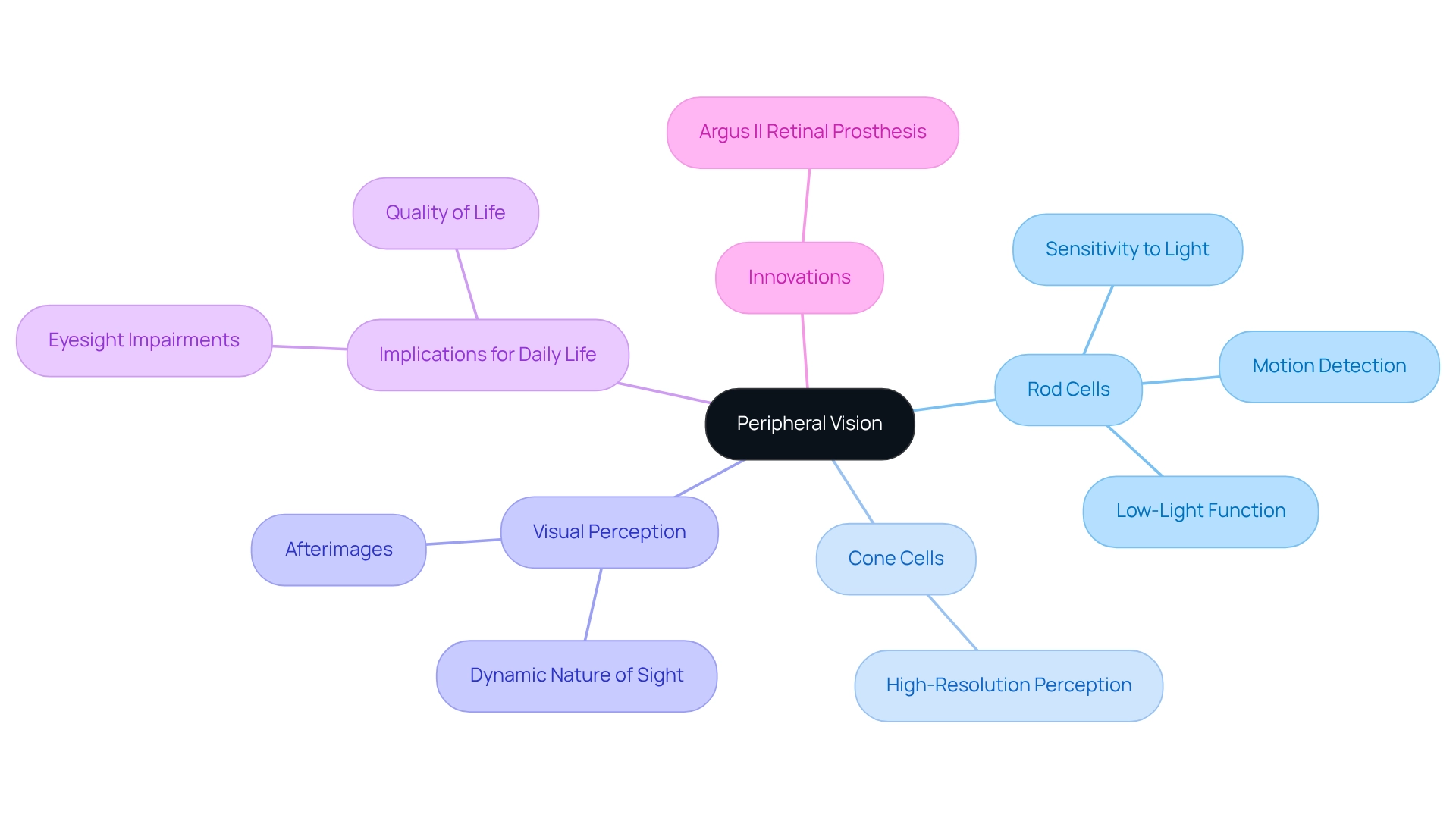
Explore the Anatomy and Physiology of Peripheral Vision
Side eyesight is primarily governed by the , which contains a significantly greater concentration of compared to cone cells. Rods are highly sensitive to light and motion, making them in dimly lit environments. This sensitivity allows individuals to perceive movement and shapes through their peripheral vision outside their direct line of sight, which is crucial for overall spatial awareness and safety. The imagery captured by these rod cells is relayed through the optic nerve to the brain, where it is synthesized into a comprehensive sight field.
Understanding this anatomical distinction helps clarify why side sight lacks the detail found in central vision, which relies on cone cells for high-resolution perception. Recent studies emphasize the , highlighting their vital importance for and their significant contribution to motion detection and . Research indicates that the density of rod cells in the outer retina is approximately 20 times higher than that of cone cells, underscoring their importance in low-light situations.
Comprehending the structure and physiological foundation of side sight is essential, especially for individuals facing eyesight impairment. We understand that this can be a challenging experience. Case studies, such as ‘Afterimages and Visual Perception,’ have shown that disruptions in rod cell function can lead to , affecting daily activities and overall quality of life. This reality highlights the dynamic nature of sight perception and the role of .
Furthermore, innovations like the Argus II retinal prosthesis, often referred to as the ‘bionic eye,’ symbolize modern solutions for individuals experiencing . By examining these factors, we invite you to gain a deeper understanding of the intricacies of and the potential impacts of conditions affecting side sight. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
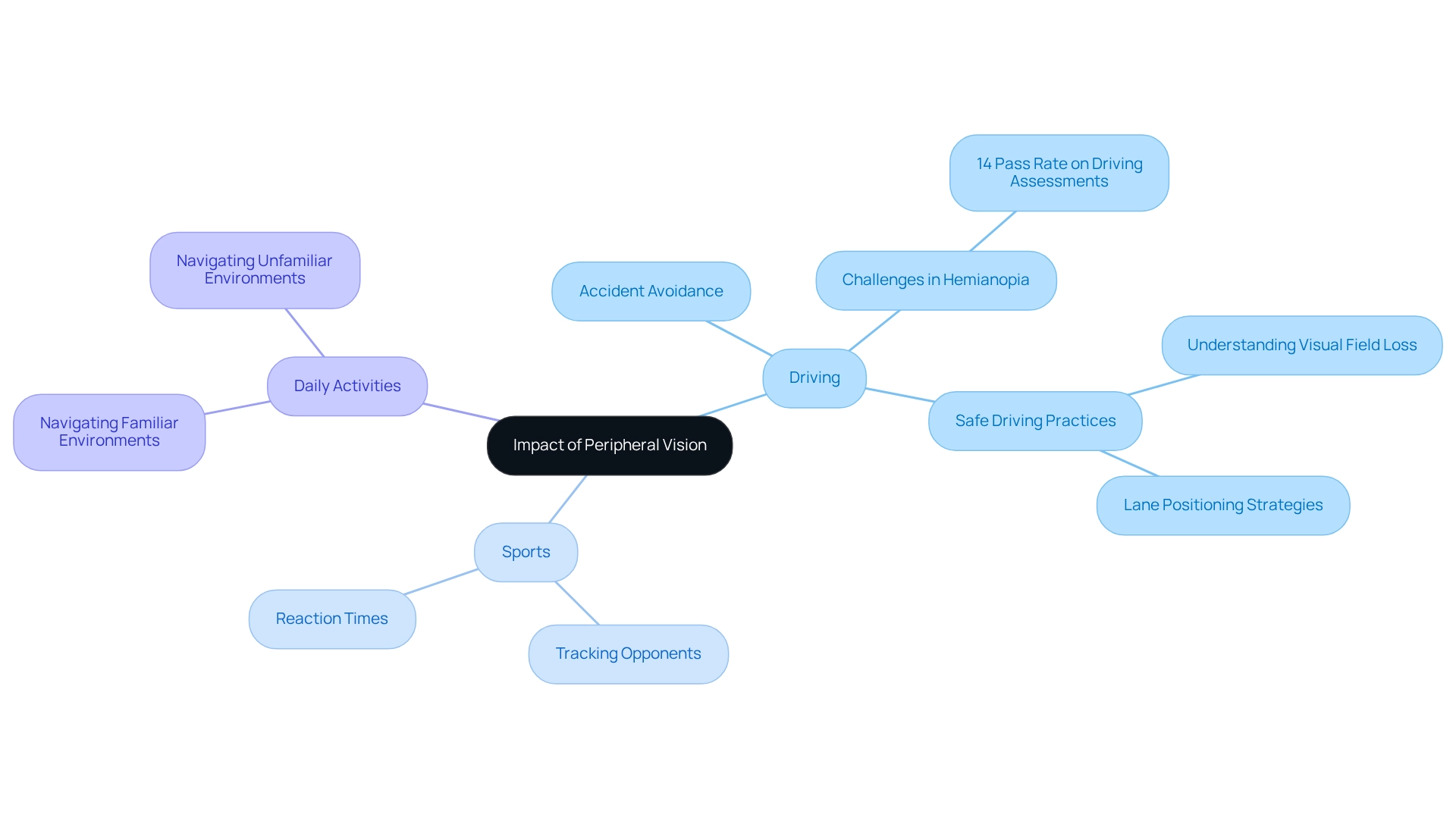
Assess the Impact of Peripheral Vision on Daily Activities and Safety
Having good is vital in many everyday tasks, such as walking, driving, and playing sports. We understand that navigating busy areas can be overwhelming, and people often rely on their side sight to avoid accidents. This ability allows for smoother movement and a .
In driving, having is essential for spotting cars or pedestrians that might not be directly in front, significantly reducing the risk of collisions. It’s concerning to note that pass on-road evaluations, highlighting the challenges faced by those with field loss.
Athletes, too, depend heavily on their peripheral vision to track opponents and the ball, which . Research indicates that sight field loss can alter . For instance, studies have shown that drivers with right field loss may shift their lane positioning to the left. This points to the need for further exploration into for individuals affected by such conditions.
, a research associate at Western Australia University, emphasizes the importance of that allow for safe driving, highlighting that peripheral vision is crucial for perceiving motion and spatial relationships without direct focus to ensure safety and effectiveness in these activities.
Therefore, it is essential to understand how side sight impacts daily living. This understanding is key to enhancing awareness and developing strategies to mitigate risks associated with . It’s not just about driving; it also involves navigating familiar and unfamiliar environments, where peripheral vision is crucial for maintaining overall situational awareness.
Identify Conditions Affecting Peripheral Vision and Their Treatments
Various conditions, notably and retinitis pigmentosa, can significantly affect peripheral vision. Glaucoma, often called the ‘,’ can insidiously reduce side vision, potentially leading to tunnel vision if not addressed. We understand that this condition can be particularly concerning, especially since it disproportionately affects older adults, individuals with a family history of glaucoma, diabetics, and those with severe nearsightedness. Efficient management typically involves medications and surgical options aimed at regulating intraocular pressure, which is vital for maintaining your sight.
Retinitis pigmentosa, a hereditary condition, primarily impacts side vision in its early stages, resulting in a gradual decline of . While there is currently no cure for this condition, many patients find and genetic counseling that can help them adapt to sight loss. Dr. Elise Héon’s research into identifying new genetic causes of inherited retinal diseases underscores the importance of understanding these conditions, paving the way for improved diagnosis and treatment development.
are crucial for the early detection and management of these conditions. Eye care specialists emphasize that . As Dr. Sidhu from the University of Waterloo notes, funding from Fighting Blindness Canada has been instrumental in , leading to promising clinical trials. We recognize that understanding the implications of peripheral vision is essential for maintaining overall eye health and quality of life. Furthermore, ongoing research continues to illuminate , reminding us of the importance of staying informed about advancements in eye care.
Conclusion
Peripheral vision plays a vital role in our daily lives and safety. We understand that recognizing its importance in detecting motion and hazards outside our direct line of sight can be enlightening. From driving to sports, peripheral vision enhances our spatial awareness, allowing us to navigate various environments more safely.
Moreover, understanding the anatomy and physiology of peripheral vision can be quite revealing. It highlights how rod cells function in low-light conditions, which is crucial for those who may be experiencing vision impairments. This knowledge underscores the importance of taking proactive measures to maintain visual health. Conditions like glaucoma and retinitis pigmentosa remind us of the challenges that can arise from peripheral vision loss, making regular eye examinations and advancements in treatment options all the more essential.
Ultimately, peripheral vision is not just an added benefit; it is a fundamental part of our overall visual experience. By prioritizing awareness of its significance, we can enhance our safety, improve daily interactions, and foster a more informed approach to eye health. Understanding and valuing peripheral vision is crucial for effectively navigating the complexities of our visual world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is peripheral vision?
Peripheral vision, also known as side sight, is the ability to detect objects outside of one’s direct line of sight. It allows individuals to notice motion and shapes without needing to move their head or eyes.
Why is peripheral vision important?
Peripheral vision is crucial for spatial awareness, which is essential for safely navigating various environments. For example, it helps drivers recognize pedestrians or cars approaching from the side, enhancing overall situational awareness.
How does age affect peripheral vision in drivers?
A study found that older drivers may experience a decline in processing peripheral vision, but they can still identify road dangers similarly to younger drivers. This indicates that maintaining peripheral vision is important for safe driving across all age groups.
What role does peripheral vision play in hazard detection?
Peripheral vision is essential for effective hazard detection, as it allows individuals to process sight-related information in their surroundings. Distractions, whether auditory or visual, can impede this ability.
How does auditory distraction affect peripheral vision?
Various forms of auditory distraction can lead to poorer hazard detection, regardless of the location of the hazards. This emphasizes the importance of maintaining focus to enhance peripheral vision capabilities.
In what other activities is peripheral vision important?
Beyond driving, peripheral vision aids in activities like walking and engaging in sports, where awareness of the environment is crucial for responding swiftly to potential dangers.
What do experts say about the significance of peripheral vision?
Experts emphasize that peripheral vision is not just an adjunct to central vision but a fundamental aspect of perception that enhances spatial awareness. It plays a key role in processing visual information in the periphery.
Why is it important to preserve peripheral vision as one ages?
Preserving peripheral vision is vital as it allows individuals to detect movement and changes in their surroundings without direct attention, helping them respond quickly to potential dangers as they age.






