Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on August 25, 2025
Overview
Normal eye pressure is an essential aspect of maintaining your eye health, defined as being between 10 to 21 mmHg, with an average of around 15 mmHg. We understand that fluctuations in this range can be concerning, as both elevated and reduced pressure can lead to serious vision issues. That’s why it’s crucial to keep an eye on these numbers.
Regular eye examinations are vital for monitoring intraocular pressure (IOP). It’s common to feel anxious about what these numbers mean, but understanding the factors that influence eye pressure—like age, genetics, and health conditions—can empower you. This knowledge is key in preventing conditions such as glaucoma and preserving your precious vision.
We are here to help you through this process and encourage you to prioritize your eye health. By staying informed and proactive, you can take significant steps towards ensuring your vision remains clear and vibrant.
Introduction
Understanding the nuances of eye pressure is crucial for maintaining optimal eye health, as it directly influences the risk of serious conditions like glaucoma. We understand that many individuals may feel anxious about their eye health, and that’s completely normal. The normal eye pressure range, typically between 10 to 21 mmHg, serves as a benchmark for assessing ocular well-being. However, it’s important to recognize the factors that can lead to abnormal eye pressure, which can jeopardize vision.
What steps can you take to ensure your eye pressure remains within this vital range? How can you proactively manage your eye health? We are here to help you through this process.
Define Normal Eye Pressure and Its Importance
The normal eye pressure range, measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg), typically falls between 10 to 21 mmHg, with an average around 15 mmHg. We understand that maintaining this range is essential for preserving your eye health. Both increased and reduced eye tension can lead to serious issues, particularly conditions that are primary causes of vision loss among individuals over 60.
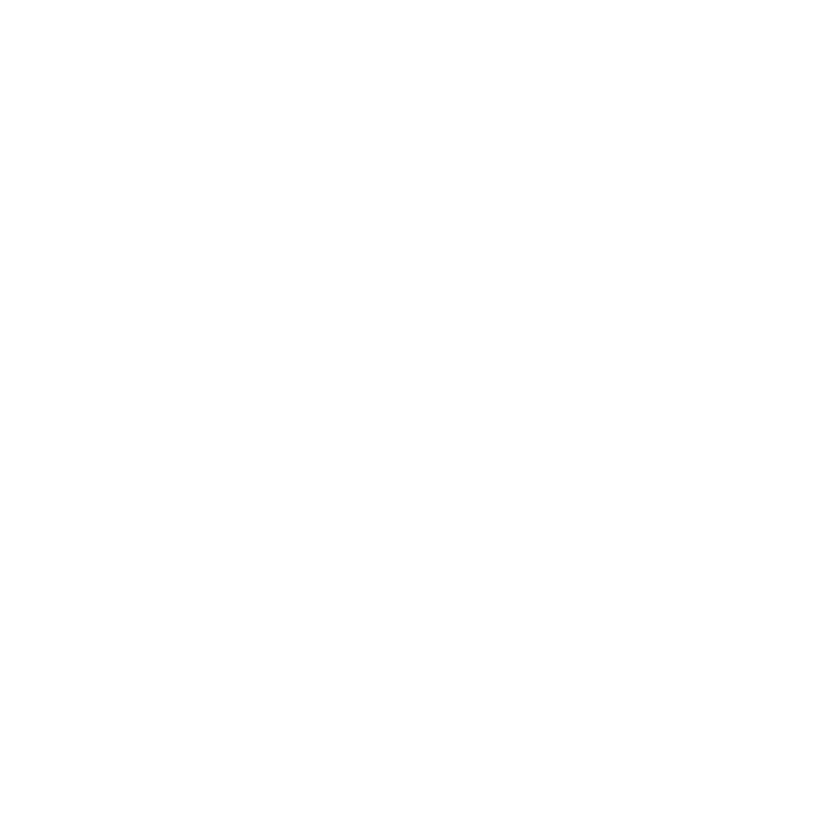
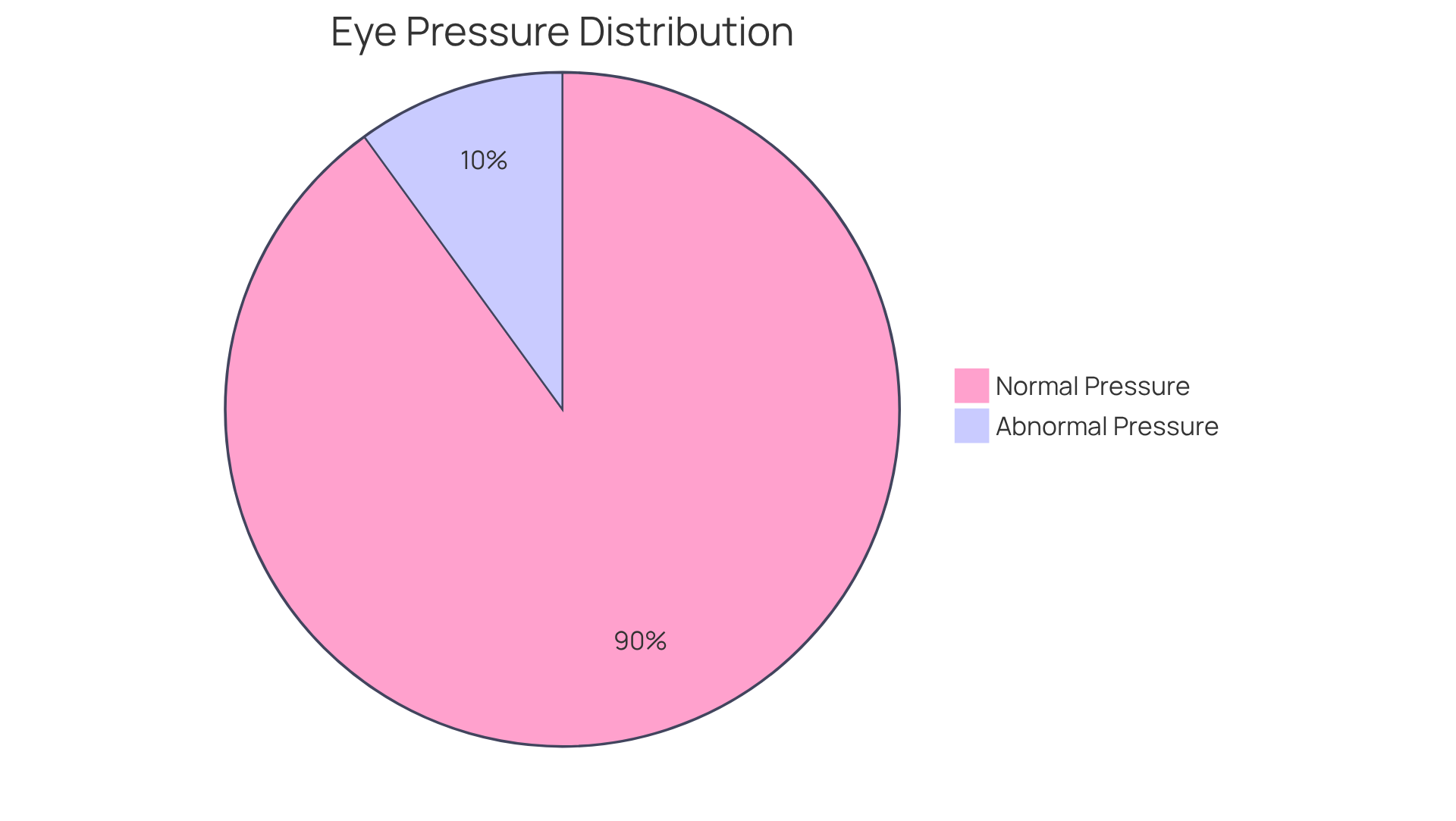
Elevated intraocular tension (IOP) is a significant risk factor for eye disease. Regular observation is crucial for early identification and action. Research indicates that approximately 90 percent of individuals have eye tension that falls within the normal eye pressure range. This highlights the importance of regular eye examinations to evaluate your IOP levels.
Regular monitoring not only helps in the timely identification of potential issues but also allows for effective management strategies to prevent vision loss. It’s common to feel concerned about eye health, and expert opinions emphasize that while elevated eye tension alone does not lead to glaucoma, it can contribute to optic nerve damage over time.
Real-world examples show that patients who adhere to regular eye evaluations often experience improved outcomes. This underscores the essential role of in preserving vision and overall eye health. Remember, we are here to help you through this process and ensure your eyes remain healthy.
Explore Factors Affecting Eye Pressure
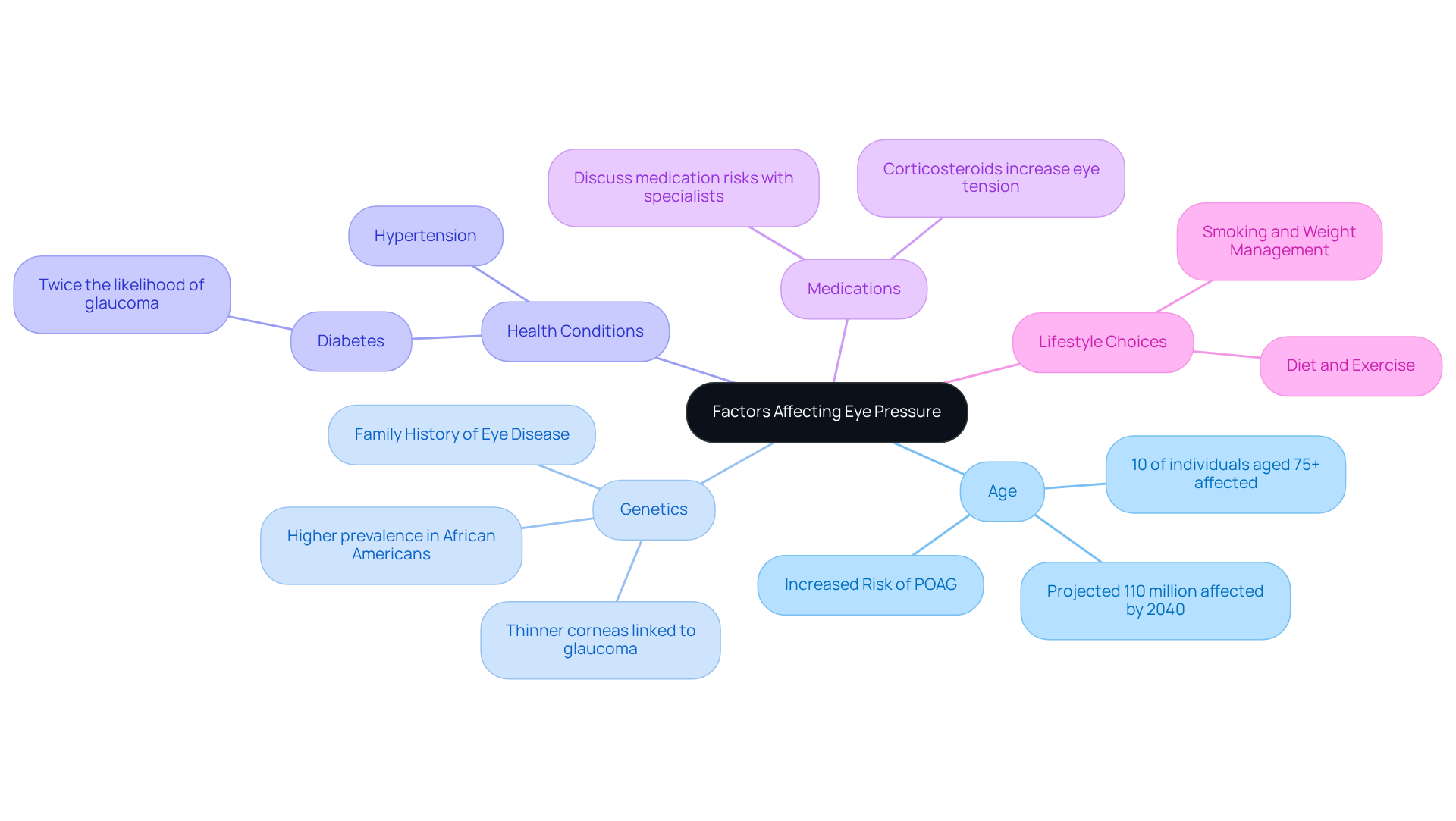
Several factors can significantly influence eye pressure, and understanding them is crucial for maintaining the normal eye pressure range and taking care of your eye health.
- Age: As we age, eye pressure typically increases, making older adults more susceptible to elevated levels. Approximately 10% of individuals aged 75 and older are impacted by primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG). This highlights the importance of regular monitoring as we grow older. With forecasts suggesting that the number of people affected by this condition may exceed 110 million by 2040, the need for vigilant is clear.
- Genetics: If you have a family history of eye disease or high eye pressure, your risk may be elevated. Research indicates that certain genetic differences, particularly those affecting the cornea, can influence susceptibility to eye pressure disorders. For example, studies show that African Americans tend to have thinner corneas and a higher prevalence of glaucoma compared to other groups. Recognizing these genetic factors is crucial for maintaining eye well-being.
- Health Conditions: Chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension can negatively impact the normal eye pressure range. Individuals with diabetes are twice as likely to develop eye conditions, making regular eye examinations essential for monitoring eye health. As Jamie Dietze points out, ‘Elevated IOP is the main risk factor for developing glaucoma and for the advancement of the condition.’ Understanding eye tension in relation to the normal eye pressure range is vital for assessing glaucoma risk.
- Medications: Some medications, especially corticosteroids, can lead to increased eye tension. It’s important to discuss your medication regimen with your eye care specialist to understand any potential risks.
- Lifestyle Choices: Your lifestyle can also play a role in eye health. Factors such as diet, exercise, and smoking can influence your well-being. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity are essential for overall wellness and may help reduce the risk of increased eye tension.
By grasping these elements, you can make informed choices regarding your eye care. Remember, routine eye exams and proactive management of your eye health are crucial steps in safeguarding your vision. We are here to help you through this process.
Review Techniques for Measuring Eye Pressure
Understanding eye pressure is important for maintaining your vision, and there are several techniques available to measure it, each with its own advantages:
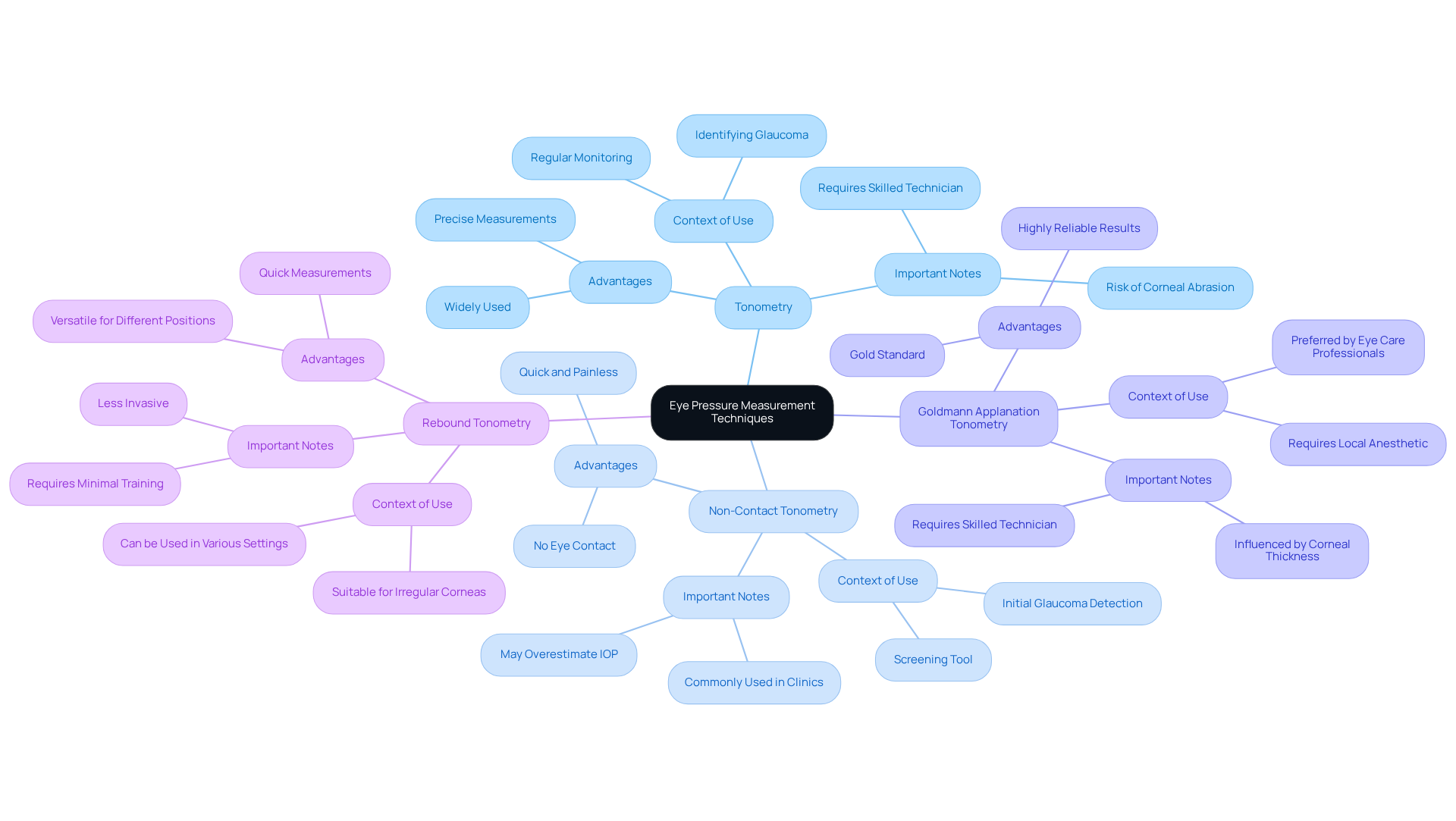
- Tonometry: This widely used method involves a tonometer that gently applies a small amount of pressure to your eye. This helps gauge its resistance, which is crucial for identifying conditions like glaucoma. We know how important precise intraocular measurements are for determining whether your measurements fall within the normal eye pressure range, which is crucial for evaluating your eye health.
- Non-Contact Tonometry: Often referred to as the ‘air puff’ test, this technique assesses eye tension by releasing a quick burst of air onto your eye without any touch. While it’s , it’s common to feel a bit startled. Studies suggest it may sometimes overestimate intraocular pressure (IOP) compared to traditional methods, making it a helpful screening tool, though perhaps not the best for precise measurements.
- Goldmann Applanation Tonometry: Recognized as the gold standard for measuring IOP, this method flattens a small section of the cornea to assess the force accurately. It does require a skilled technician and can be influenced by corneal thickness, but it provides highly reliable results, which many eye care professionals prefer for their patients.
- Rebound Tonometry: This newer method uses a small probe that briefly contacts your eye, providing quick and reliable measurements. It’s particularly beneficial for those with irregular corneas and can be performed in various positions, making it versatile for different clinical settings.
We understand that grasping these methods can prepare you for your eye examinations and highlight the importance of precise measurements in preserving your vision. Regular monitoring of IOP is essential, especially for those over 40, to maintain it within the normal eye pressure range, as increased eye tension can lead to significant vision loss if not addressed promptly. It’s also important to be aware of potential risks associated with tonometry tests, such as corneal abrasion, which can occur due to the delicate nature of the cornea. Remember, we are here to help you through this process and ensure your eye health is prioritized.
Analyze Risks Associated with Abnormal Eye Pressure
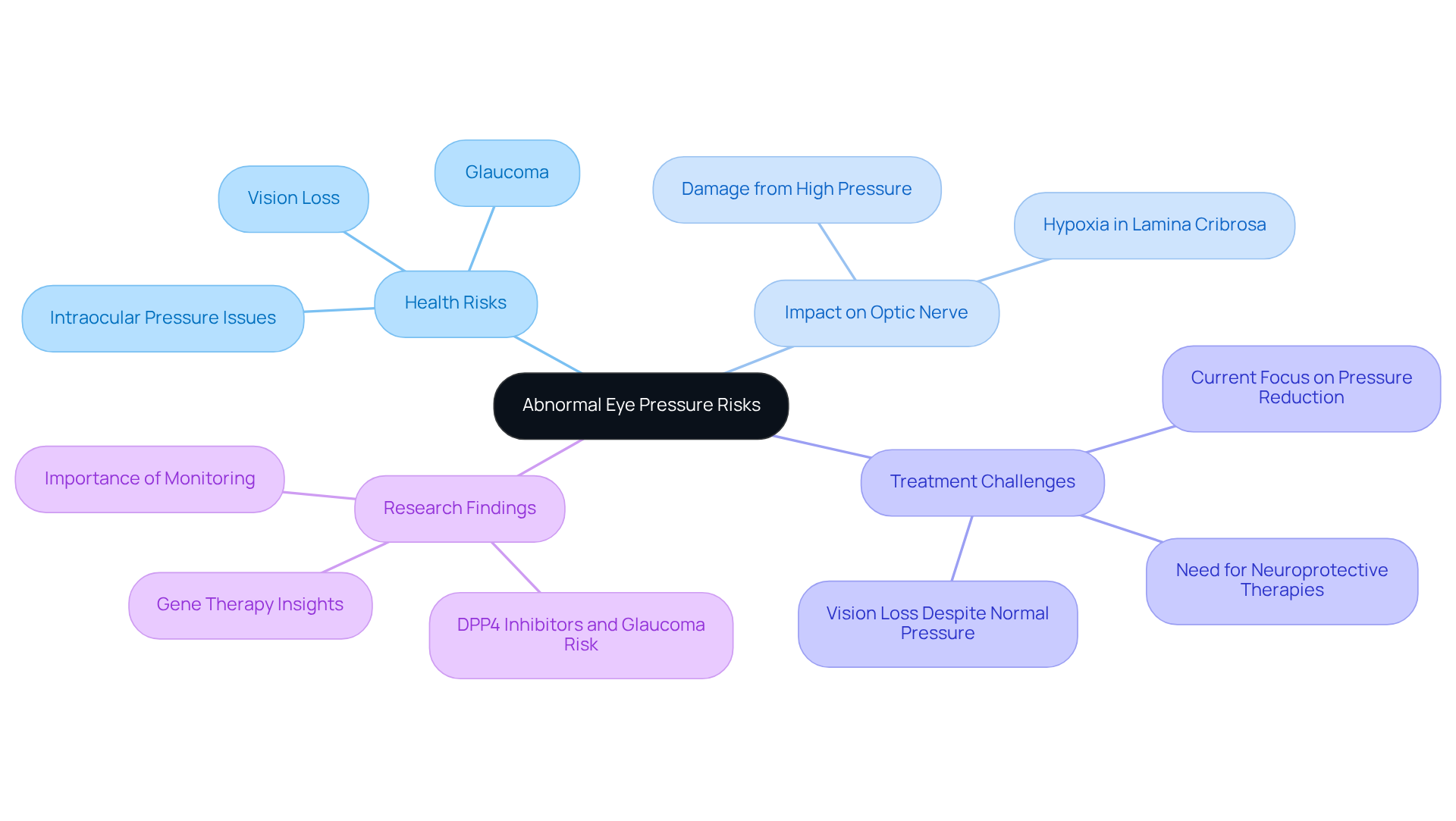
Unusual eye tension poses significant health risks, particularly regarding glaucoma, which is a . Increased intraocular pressure is a critical risk factor for this condition, as it can damage the optic nerve, leading to lasting vision impairment. Research indicates that extreme ocular pressure can result in hypoxia in about 30% of the lamina cribrosa tissue, underscoring the importance of addressing elevated tension levels.
It’s concerning that optic nerve injury due to high eye tension affects millions worldwide. Current treatments primarily focus on lowering elevated eye pressure, yet some patients still experience vision loss even when their eye pressure is within the normal eye pressure range. This complexity highlights the need for ongoing research into neuroprotective therapies that could mitigate damage to retinal ganglion cells.
Real-life examples illustrate the harmful effects of elevated eye tension. For instance, a study involving 582,710 individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus found a link between increased eye pressure and a higher risk of developing primary open-angle glaucoma and glaucoma within the normal eye pressure range. Such findings stress the importance of early detection and timely intervention.
Ophthalmologists highlight the crucial need for monitoring eye pressure. As one specialist noted, “If we can understand the mechanisms behind increased eye tension, we can develop new treatment options to improve blood flow in the back of the eye, potentially slowing the progression of the condition.”
Recent studies further solidify the connection between eye pressure and vision loss. Research shows that even slightly elevated eye tension can distort blood vessels, leading to oxygen shortages that may allow for earlier identification of glaucoma. This reinforces the necessity of regular eye examinations and diligent monitoring of eye pressure to protect long-term eye health and prevent serious complications.
Conclusion
Maintaining normal eye pressure is crucial for safeguarding your vision and overall eye health. With the typical range being between 10 to 21 mmHg, understanding the significance of this range is essential. Regular monitoring and eye examinations are vital to detect any deviations from this norm. Increased or decreased eye pressure can lead to serious conditions, including glaucoma, which is a leading cause of vision loss.
We understand that various factors can influence eye pressure, such as:
- Age
- Genetics
- Health conditions
- Medications
- Lifestyle choices
The importance of regular eye exams cannot be overstated, especially for individuals at higher risk, such as those over 60 or with a family history of eye diseases. It’s common to feel uncertain about the best steps to take, but knowing that there are different techniques for measuring eye pressure, like tonometry and non-contact tonometry, highlights the advancements in eye care that facilitate early detection and management of potential issues.
In conclusion, we encourage you to engage proactively in your eye health through regular check-ups and awareness of your personal risk factors. By prioritizing eye pressure monitoring and understanding its implications, you can take significant steps towards preserving your vision and preventing complications associated with abnormal eye pressure. Taking action today can lead to a healthier future for your eyes and contribute to your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is considered normal eye pressure?
Normal eye pressure typically falls between 10 to 21 mmHg, with an average around 15 mmHg.
Why is maintaining normal eye pressure important?
Maintaining normal eye pressure is essential for preserving eye health and preventing serious issues that can lead to vision loss, particularly in individuals over 60.
What are the risks associated with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP)?
Elevated intraocular pressure is a significant risk factor for eye disease and can contribute to optic nerve damage over time, potentially leading to conditions such as glaucoma.
How common is it for individuals to have normal eye pressure?
Research indicates that approximately 90 percent of individuals have eye pressure that falls within the normal range.
Why are regular eye examinations important?
Regular eye examinations are crucial for early identification of potential issues and for effective management strategies to prevent vision loss.
Can elevated eye tension alone cause glaucoma?
While elevated eye tension alone does not lead to glaucoma, it can contribute to optic nerve damage over time.
What benefits do patients experience from regular eye evaluations?
Patients who adhere to regular eye evaluations often experience improved outcomes in terms of eye health and vision preservation.






