Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on May 31, 2025
Overview
We understand that concerns about eye health can be daunting. This article focuses on elevated eye pressure, also known as intraocular pressure (IOP), and aims to provide you with the information you need to feel reassured.
High eye pressure can arise from various factors, such as excessive fluid production or inadequate drainage. It’s common to feel uncertain about what this means for your vision. Regular monitoring is crucial, as it helps prevent damage to the optic nerve and preserves your sight.
Treatment options are available, including medications and laser therapy. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you have the support you need. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are steps you can take to manage your eye health effectively.
Introduction
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is crucial for maintaining eye health, yet many may not recognize its importance until they experience symptoms. We understand that this can be concerning. It’s essential to grasp the significance of IOP, not only to prevent vision loss but also to identify the underlying causes and symptoms of elevated pressure. This article will explore the intricacies of IOP, including its definition, risk factors, and the potential consequences of neglecting your eye health.
We aim to provide you with effective treatment options, ranging from medications to advanced surgical interventions. Regular monitoring and proactive care are vital in this journey. By shedding light on these critical aspects, we hope to empower you to navigate your eye health with confidence and take informed steps toward preserving your vision.
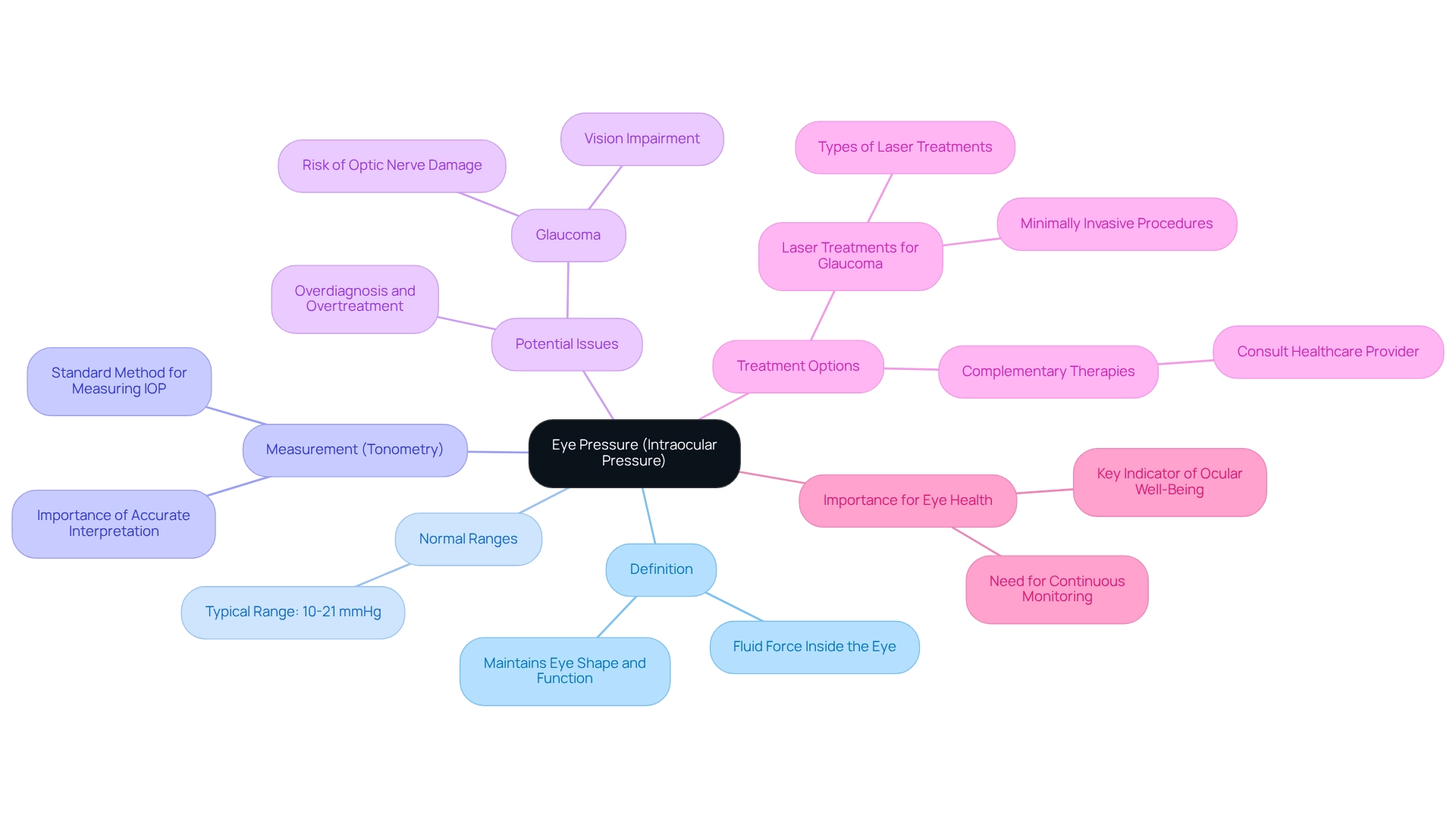
Define Eye Pressure: Understanding Intraocular Pressure Basics
Eye pressure, also known as intraocular tension (IOP), refers to the fluid force inside the eye, which is crucial for maintaining its shape and ensuring proper function. We understand that concerns about eye health can be overwhelming, but knowing that IOP is typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) can provide some reassurance. Normal eye pressure ranges from 10 to 21 mmHg, and measurements above this range may indicate potential issues, such as glaucoma. The tension is sustained by a balance between the production and drainage of aqueous humor, the fluid within the eye. Consistent observation of eye pressure is crucial, particularly for those susceptible to glaucoma, as increased levels can result in optic nerve harm and vision impairment if not addressed.
Tonometry is the standard method used to measure eye pressure, providing essential data for assessments of eye health. However, it’s common to feel anxious about the results, especially since the United States Preventive Service Task Force has identified significant harm in the potential overdiagnosis and overtreatment of individuals with elevated IOP. This highlights the importance of careful interpretation of IOP measurements, and we are here to help you navigate this process.
Experts emphasize that understanding eye pressure is fundamental to eye health, with normal ranges of eye pressure being a key indicator of ocular well-being. Ryan Machiele observes that “communication among these specialists, who collaborate as an interprofessional team, is essential so that may be suitably compared over time.” This collaborative approach is vital in effectively managing eye pressure, ensuring that you receive the best possible care.
Recent advancements in treatment options, such as laser treatments for glaucoma, provide minimally invasive solutions to manage elevated eye pressure. These procedures demonstrate the importance of timely intervention to prevent vision loss. Furthermore, while complementary therapies may provide advantages, they should not substitute prescribed medications. It’s common to have questions about treatment options, so individuals should always consult with their healthcare provider before making any modifications to their treatment plans.
For individuals with cataracts, comprehending eye pressure and its effects is especially crucial, as increased tension can complicate their condition. Continuous research into eye pressure measurement techniques and management strategies is essential for improving patient outcomes and preventing vision loss. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
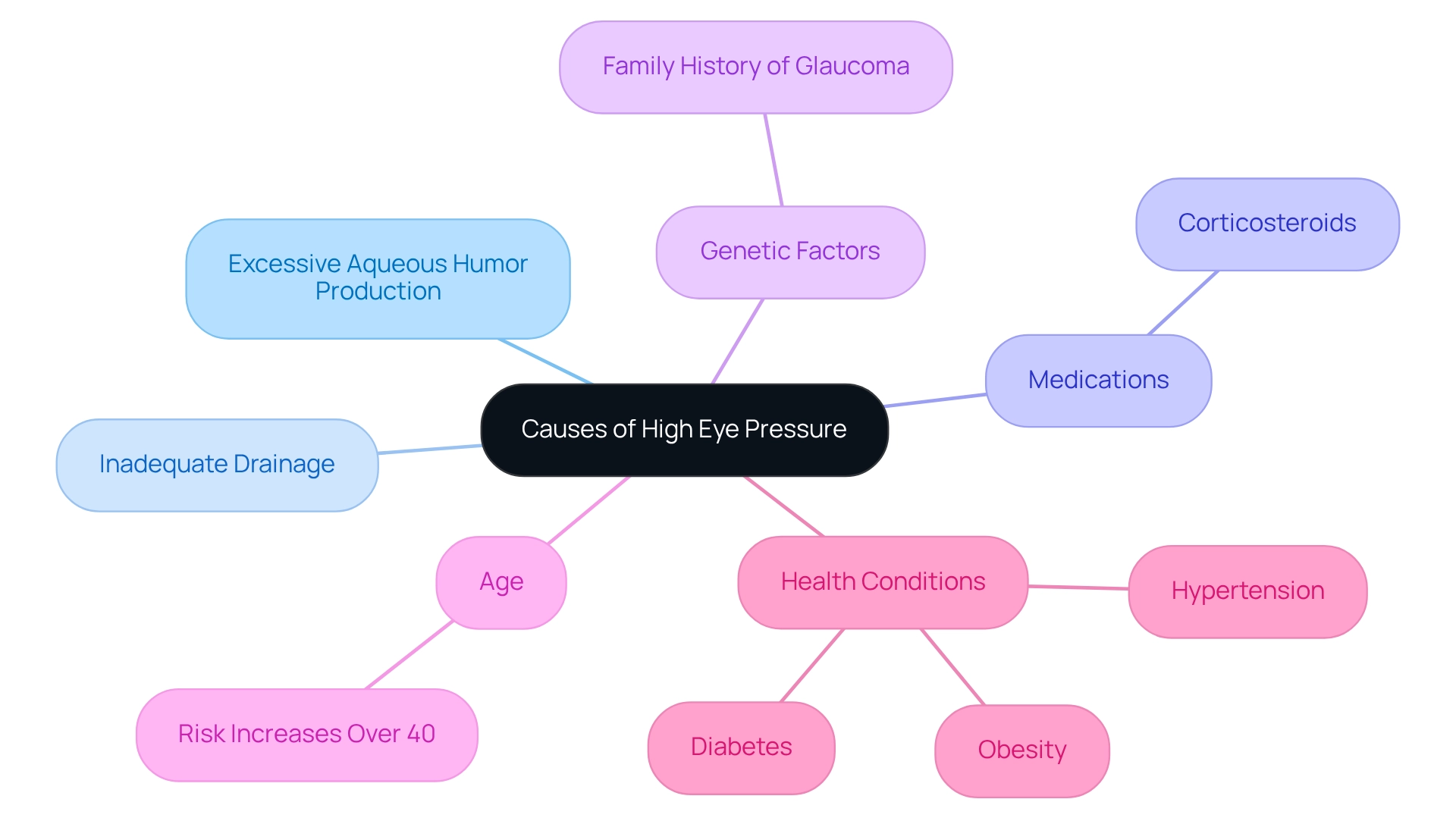
Identify Causes of High Eye Pressure: Risk Factors and Triggers
can result from several factors, and we recognize that this can be concerning. Here are some key contributors to elevated eye pressure:
- Excessive Aqueous Humor Production: Conditions that increase fluid production can elevate eye pressure, which may cause worry.
- Inadequate Drainage: Blockages in the eye’s drainage system can prevent proper fluid outflow, leading to heightened eye pressure.
- Medications: Certain medications, particularly corticosteroids, can raise eye pressure as a side effect, and it’s important to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of glaucoma or ocular hypertension raises the chances of developing elevated eye pressure. We know that this can feel overwhelming.
- Age: The risk of elevated eye pressure increases with age, particularly in individuals over 40, which is a common concern.
- Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity are associated with higher eye pressure. Understanding these risk factors is vital for monitoring your eye health and seeking timely medical advice. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we are here to help you through this process.
Recognize Symptoms of Elevated Eye Pressure: Signs to Watch For
Increased eye pressure often does not show noticeable symptoms in its early stages, making regular eye exams essential. We understand that it can be concerning to experience changes in your vision, so here are some signs to watch for:
- Blurred Vision: Difficulty focusing can indicate that eye pressure is affecting the optic nerve. In fact, studies indicate that approximately 30% of patients with increased eye pressure report experiencing blurred vision.
- Halos Around Lights: Seeing halos or rainbows around lights may signal elevated eye pressure. This symptom can be alarming, as it may suggest notable changes in tension.
- Vision Pain or Discomfort: Ongoing pain or discomfort in your vision can be a warning sign. According to ophthalmologists, this symptom should not be ignored, as it may indicate underlying issues related to eye pressure. Frequent headaches, especially around the eyes, may be linked to elevated eye pressure. Research indicates that nearly 25% of patients with elevated eye pressure report headaches as a symptom. This symptom frequently occurs alongside other indications of increased tension.
- Vision Loss: Gradual loss of peripheral vision is a serious symptom that requires immediate attention. Timely identification is essential, as untreated increased eye pressure can result in glaucoma and considerable vision impairment.
Recognizing these symptoms can lead to timely intervention and treatment. Statistics indicate that a significant percentage of individuals experience these symptoms, highlighting the importance of awareness and . Regular eye exams are essential for detecting high eye pressure, as emphasized by ophthalmologists who stress that early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes. We understand that risk factors for developing glaucoma can feel overwhelming, but being over 60, having a family history of glaucoma, and specific medical conditions such as diabetes or elevated blood levels are important to monitor. Incorporating these insights can assist you in grasping the essential importance of monitoring your eye health. We are here to help you through this process.
Explore Treatment Options for High Eye Pressure: From Medications to Surgery
Effective treatment for high eye pressure emphasizes lowering intraocular pressure (IOP) to prevent damage to the optic nerve. We understand that can be concerning, and we are here to help you through this process. The primary options include:
- Medications: Prescription eye drops are typically the first line of defense. These drops work by either reducing fluid production or enhancing drainage. Common classes include prostaglandin analogs, beta-blockers, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, each designed to target specific mechanisms of IOP regulation. Recent statistics indicate that these medications can lower eye pressure by an average of 25% in numerous individuals, significantly reducing the risk of optic nerve damage.
- Oral Medications: In certain situations, oral medications may be prescribed alongside eye drops to provide additional support in managing IOP. It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but know that your healthcare provider will tailor a plan that suits your needs.
- Laser Therapy: Procedures such as selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT) are effective in improving fluid drainage from the eye, thereby lowering eye pressure. Recent advancements in laser therapy have demonstrated encouraging success rates, with studies indicating that over 80% of individuals experience significant reductions in eye pressure post-treatment. An eye care specialist remarked, “Laser therapy has changed the approach we take in handling elevated eye tension, providing individuals a less invasive choice with outstanding results.”
- Surgery: For more severe cases, surgical interventions like trabeculectomy or the implantation of drainage devices may be necessary. These procedures establish new routes for fluid drainage, greatly minimizing eye pressure within the eye. The case study titled “Fighting Against The Silent Thief” illustrates how advancements in glaucoma surgery have empowered surgeons to effectively alter the trajectory of patients’ vision, providing interventions that help preserve eyesight and improve overall quality of life.
- Lifestyle Changes: Embracing a healthy way of living, which involves regular physical activity and a balanced diet, can also aid in controlling eye tension. Consistent follow-ups with an eye care professional are crucial for monitoring eye pressure and adjusting treatment plans as needed. Remember, small changes can make a significant difference.
Regular monitoring and proactive management are essential to maintaining eye health and preventing complications associated with elevated eye pressure. As individuals express a desire for more streamlined treatment options, the integration of innovative therapies and personalized care continues to evolve, ensuring better outcomes for those affected. Further investigation is needed to determine if patient preferences remain stable over time, highlighting the importance of ongoing dialogue between patients and their eye care providers. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy intraocular pressure (IOP) is vital for preserving your vision and overall eye health. We understand that navigating the intricacies of IOP, including its normal range and the potential consequences of elevated pressure, can be concerning. Regular monitoring through methods like tonometry allows for early detection of issues, especially for those at risk for glaucoma. Recognizing risk factors such as age, genetics, and certain health conditions empowers you to take proactive steps in managing your eye health.
It’s common to feel uncertain about symptoms associated with high eye pressure—such as blurred vision, eye pain, and headaches. This awareness serves as a critical reminder to prioritize regular eye examinations. Remember, timely intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of severe complications like vision loss.
Fortunately, various treatment options are available to effectively manage high IOP. From prescription medications to advanced laser therapies and surgical interventions, you have a range of strategies to consider. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can further enhance the effectiveness of these treatments and contribute to your overall well-being.
Ultimately, the journey to maintaining optimal eye health requires diligence and collaboration with healthcare professionals. By staying informed and vigilant about IOP, you can take meaningful steps toward preserving your vision and enjoying a healthier future. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring that you feel supported every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is eye pressure and why is it important?
Eye pressure, or intraocular tension (IOP), refers to the fluid force inside the eye, which is essential for maintaining its shape and function. It is crucial for eye health, as abnormal levels can indicate potential issues like glaucoma.
What is the normal range for eye pressure?
Normal eye pressure ranges from 10 to 21 mmHg. Measurements above this range may suggest potential problems.
How is eye pressure measured?
Eye pressure is typically measured using a method called tonometry, which provides important data for assessing eye health.
Why is monitoring eye pressure important for glaucoma patients?
Consistent observation of eye pressure is vital for those susceptible to glaucoma, as increased levels can lead to optic nerve damage and vision impairment if not addressed.
What are the potential risks associated with elevated IOP?
Elevated intraocular pressure can result in significant harm, including the risk of overdiagnosis and overtreatment, which is why careful interpretation of measurements is essential.
What advancements have been made in treating elevated eye pressure?
Recent advancements include laser treatments for glaucoma, which offer minimally invasive solutions to manage elevated eye pressure and prevent vision loss.
Should individuals consider complementary therapies for eye pressure?
While complementary therapies may provide some benefits, they should not replace prescribed medications. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to treatment plans.
How does eye pressure affect individuals with cataracts?
Understanding eye pressure is particularly crucial for individuals with cataracts, as increased tension can complicate their condition.
What role do specialists play in managing eye pressure?
Communication among eye care specialists is vital for effectively managing eye pressure and ensuring that ocular measurement data is accurately compared over time.
Why is ongoing research important in the context of eye pressure?
Continuous research into eye pressure measurement techniques and management strategies is essential for improving patient outcomes and preventing vision loss.






