Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on August 24, 2025
Overview
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is an important eye condition that can be concerning. It occurs when veins in the retina become blocked, which can lead to vision impairment. There are two main types of RVO:
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
- Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)
We understand that experiencing symptoms such as blurred vision and floaters can be alarming. It’s essential to recognize these signs and understand the risk factors associated with RVO, including hypertension and diabetes. Seeking timely medical intervention is crucial, as it can make a significant difference in your diagnosis and treatment.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Many people face similar challenges, and there is support available. By addressing these factors, we can work together to help preserve your vision and ensure you receive the care you need.
Introduction
Understanding the complexities of retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is essential for anyone concerned about their eye health. We understand that facing such a condition can be daunting. RVO, characterized by the blockage of veins in the retina, can lead to significant visual impairment if not addressed promptly.
This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for RVO, offering valuable insights that empower you to take proactive steps in managing your eye health. It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but with the right information, you can recognize the warning signs and navigate the available treatment pathways to safeguard your vision.
Define Retinal Vein Occlusion and Its Types
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is a serious condition that can significantly impact your vision. It occurs when a vein in the retina becomes blocked, leading to potential sight impairment. Understanding retinal vein occlusion is vital, as it can help you recognize symptoms and seek timely care.
There are two main types of RVO:
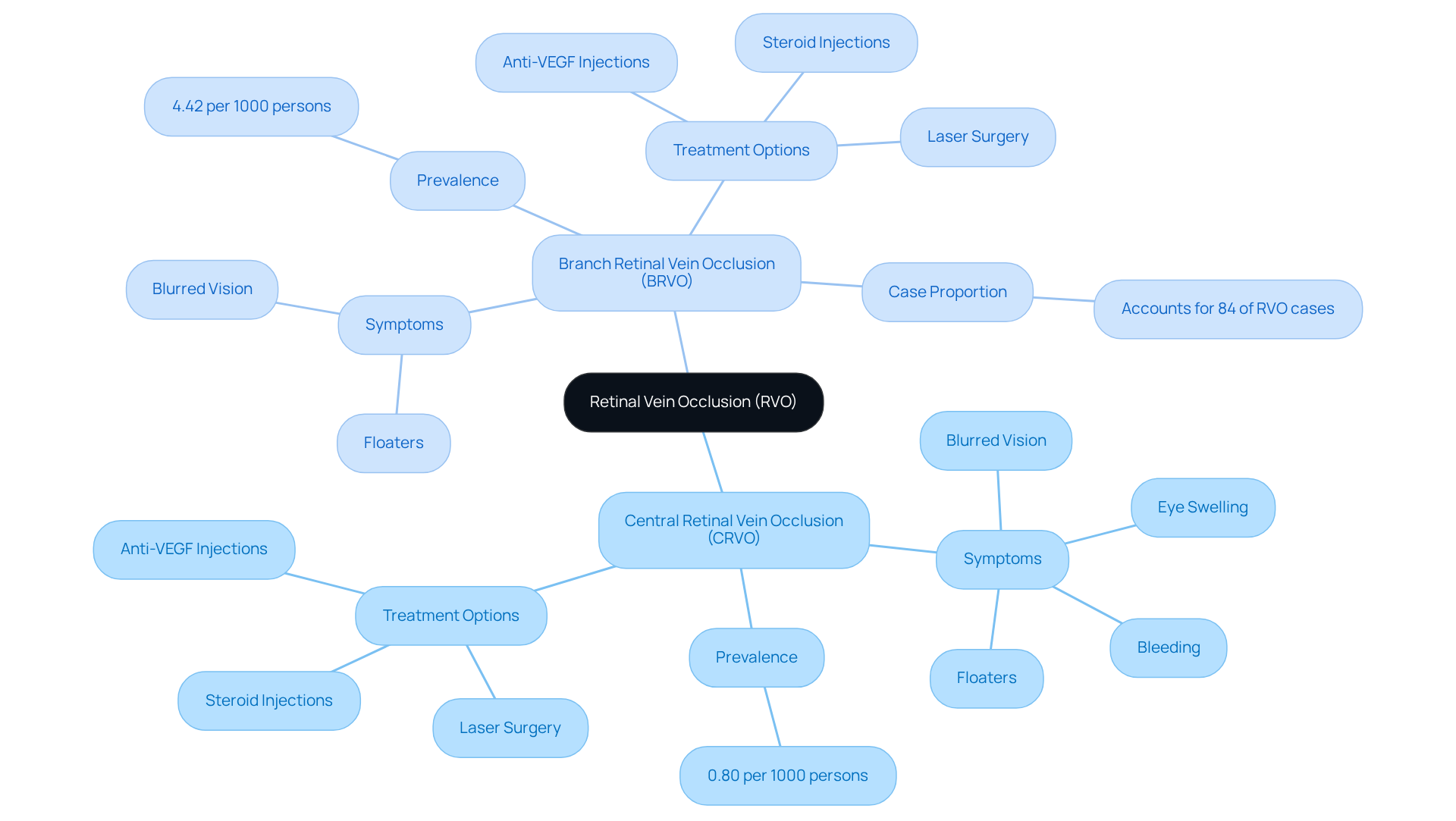
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO): This type occurs when the main vein in the eye is blocked. It can lead to significant vision loss and may present symptoms such as eye swelling, bleeding, and neovascularization, which can further threaten your sight. Common signs of CRVO include blurred vision, floaters, and discomfort in the eye. These symptoms often prompt individuals to seek medical help promptly. Recent studies show that the age- and sex-standardized prevalence of CRVO is about 0.80 per 1000 persons, particularly affecting older adults.
- Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO): This involves a blockage in one of the smaller branches of the retinal vein. While BRVO typically causes less severe vision loss than CRVO, retinal vein occlusion can still lead to if left untreated. The prevalence of retinal vein occlusion is around 4.42 per 1000 persons, with BRVO being the more common form, accounting for approximately 84% of all cases.
Recognizing these categories is crucial for identifying signs like blurred vision, which could indicate retinal vein occlusion or other conditions such as cataracts or diabetic retinopathy. For instance, individuals with CRVO may benefit from treatments like anti-VEGF injections, which have shown promising results in managing complications and preserving vision. Many patients who receive timely treatment for CRVO report improvements in their visual acuity, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis and intervention.
It’s important to note that about 1 in 4 individuals with retinal vein occlusion experience neovascularization of the eye, highlighting the seriousness of this condition. You can take preventive steps to lower your risk of developing RVO and its complications. Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco products can make a significant difference. Additionally, regular eye exams are essential for early detection and management of these conditions, as untreated symptoms can lead to serious health issues. If you’re experiencing unclear vision or any other concerning symptoms, we encourage you to seek professional medical assistance promptly.
Overall, being aware of retinal vein occlusion and its types, as well as their implications, can empower you to take charge of your eye health. Remember, “Maintaining your eye health can assist in safeguarding your sight, along with the well-being of your whole body,” as noted by the Cleveland Clinic. We are here to help you through this process and support you in managing your vision health effectively.
Explore Causes and Risk Factors of Retinal Vein Occlusion
Understanding the several interrelated factors that can lead to retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is important for taking proactive steps for your eye health. We recognize that navigating these health concerns can be overwhelming, so let’s break it down together:
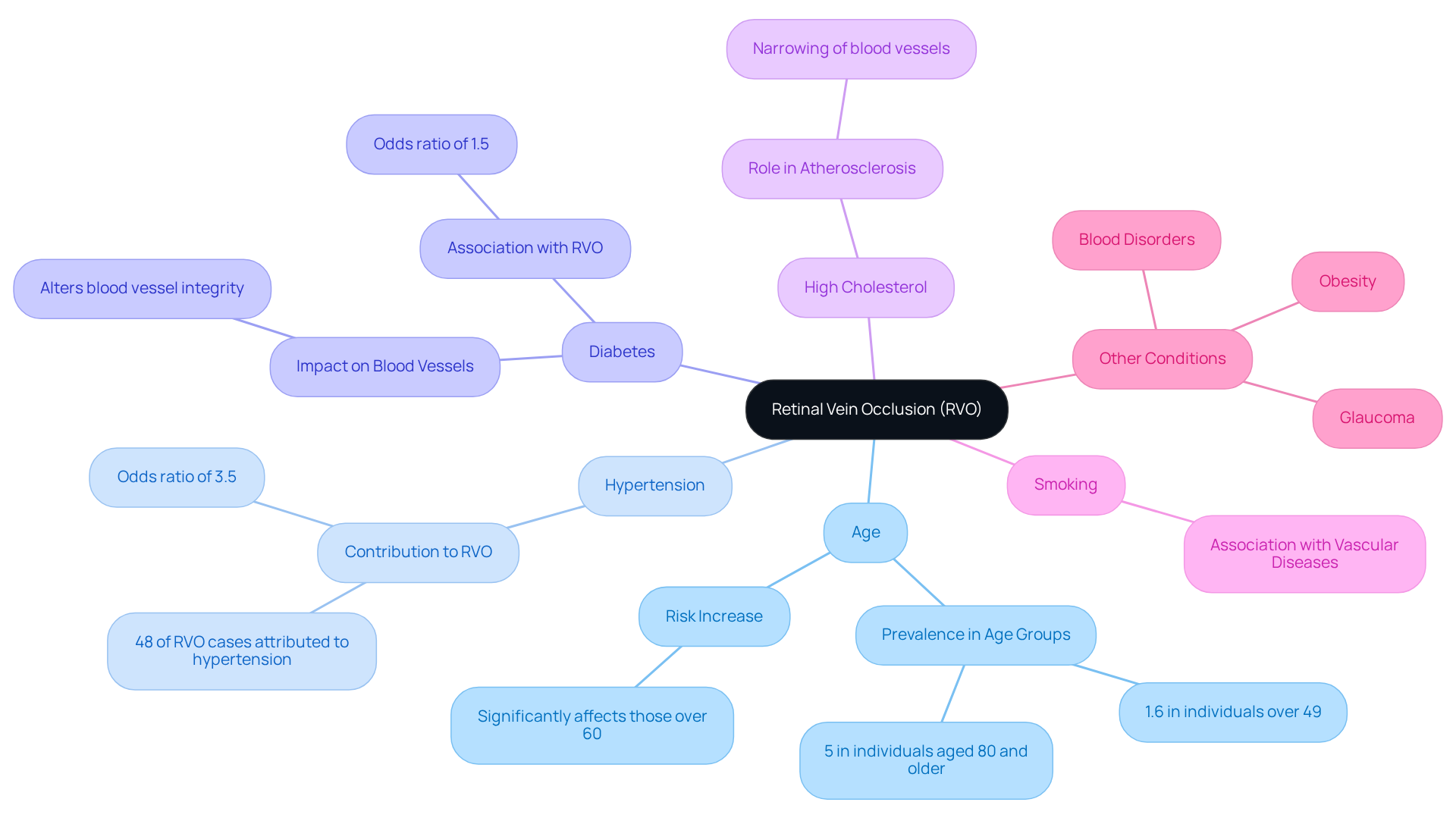
- Age: The risk of developing RVO increases with age, especially for those over 60. It affects approximately 1.6% of individuals over 49 years old, with prevalence reaching about 5% in those aged 80 and older.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure is a significant contributor, damaging blood vessels and increasing the risk of blockages. Studies indicate that retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is attributed to hypertension in about 48% of cases, with an odds ratio of 3.5, underscoring its critical role in vascular health.
- Diabetes: This condition alters blood vessel integrity, making them more prone to occlusion. While the association with retinal vein occlusion is less pronounced than with hypertension, diabetes still plays a notable role in vascular complications.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to atherosclerosis, which narrows blood vessels and increases the risk of retinal vein occlusion.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is associated with various vascular diseases, thereby increasing the likelihood of developing retinal vein occlusion.
- Other Conditions: Additional risk factors include glaucoma, obesity, and certain blood disorders, all of which can elevate the risk of RVO.
Recognizing these risk factors is essential for you, as it encourages regular eye examinations and proactive health management to prevent conditions like retinal vein occlusion. We understand that discussing these concerns can feel daunting, but about the risks associated with retinal vein occlusion can lead to better outcomes and potentially mitigate its impact. As observed by eye care experts, ‘Eye care specialists diagnose RVO through an eye exam and imaging tests of the retina.’ Regular eye exams are important for maintaining eye health and for the early identification of conditions such as retinal vein occlusion. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Identify Symptoms of Retinal Vein Occlusion
Signs of vein blockage in the eye (RVO) can significantly affect your sight, and they vary depending on the type and severity of the obstruction. RVO is the second most common disorder impacting the retina, and common symptoms include:
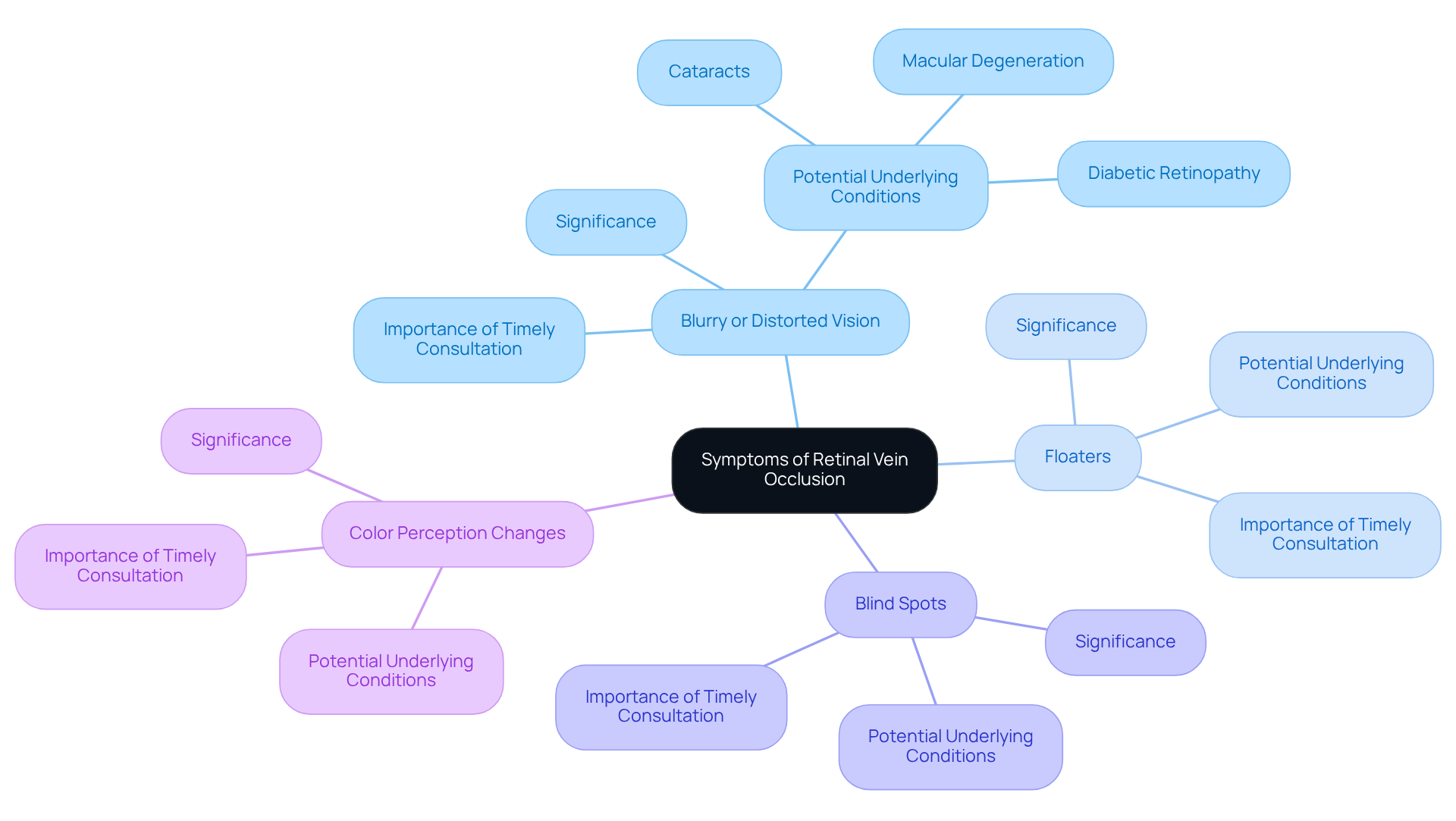
- Blurry or Distorted Vision: We understand that sudden changes in clarity, often affecting just one eye, can be alarming. Blurred vision may stem from various abnormalities linked with RVO and could indicate underlying eye diseases, such as cataracts, diabetic retinopathy, or macular degeneration. Research indicates that 5% to 15% of cases of retinal vein occlusion, specifically branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO), progress to secondary macular edema within a year, with half of these cases leading to loss of sight.
- Floaters: It’s common to notice dark spots or lines in your field of vision, which can be unsettling and may point to underlying issues.
- Blind Spots: The sudden appearance of areas with sight loss can occur, signaling the need for immediate medical attention.
- Color Perception Changes: You might find it challenging to distinguish colors or notice them appearing less vibrant, which can impact your daily activities.
If you are experiencing RVO, it’s essential to know that you also face a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke. This makes timely consultation with an eye care professional crucial. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital, as untreated symptoms can lead to serious health complications. Ophthalmologists emphasize that identifying RVO symptoms early can significantly reduce the risk of sight loss. This highlights the importance of routine eye examinations and being aware of changes in your eyesight. Treatment options, such as and steroid medications, may be discussed with your eye care specialist to manage the condition effectively. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you receive the care and support you need.
Understand Diagnostic Methods for Retinal Vein Occlusion
Diagnosing retinal vein occlusion can be a concerning process, but understanding the steps involved can help ease your mind. Here’s how eye care professionals ensure accurate identification and assessment of this condition:
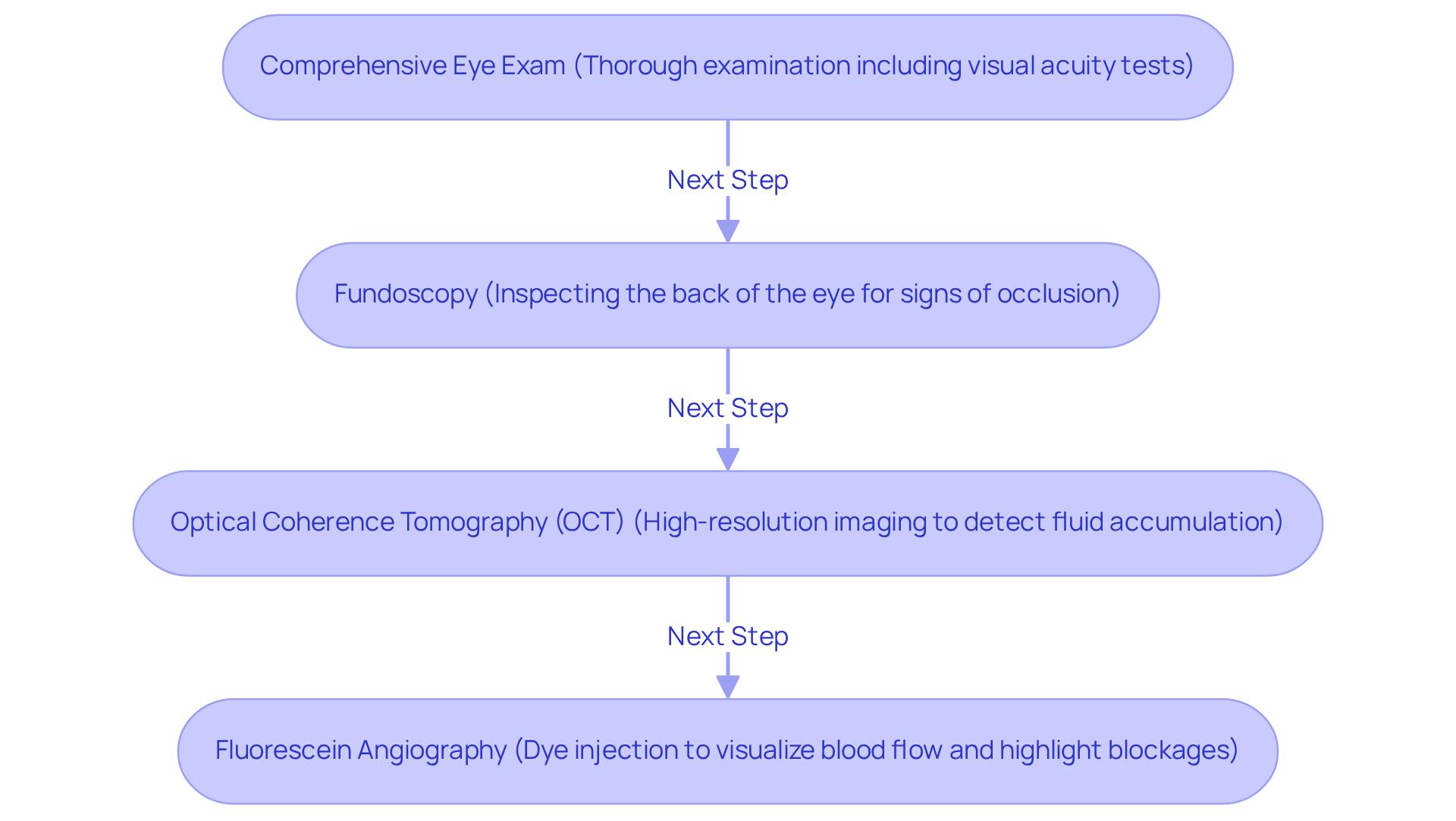
- Comprehensive Eye Exam: Your eye care professional will conduct a thorough examination, including visual acuity tests to evaluate the clarity of your vision. We understand that this may feel overwhelming, but it’s a crucial first step.
- Fundoscopy: During this procedure, the doctor inspects the back of your eye for signs of occlusion, such as eye hemorrhages or swelling. These indicators are critical in , and knowing they’re being checked can provide reassurance.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): This advanced imaging technique offers high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina. It allows for the detection of fluid accumulation and other structural changes. Studies show that OCT has an accuracy rate exceeding 90% in diagnosing retinal vein occlusion, making it a cornerstone in modern ophthalmic practice. Given that RVO affects over 16 million people globally, accurate diagnosis is crucial. The incidence of RVO is notably higher in older populations, with rates of 136.09 per 0.1 million person-years for those aged 50 and older.
- Fluorescein Angiography: In this procedure, a dye is injected into your bloodstream, and photographs are taken to visualize blood flow in the retina, effectively highlighting areas of blockage. Knowing this helps you understand the thoroughness of the diagnostic process.
These diagnostic tools are essential for confirming retinal vein occlusion and tailoring the appropriate treatment plan. As Dr. Li observes, “The incorporation of OCT in standard practice has greatly enhanced our capacity to diagnose and manage eye conditions effectively.” It’s important to recognize that retinal vein occlusion ranks as the fifth leading cause of blindness globally, highlighting the critical nature of timely and accurate diagnosis.
The combination of these methods not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also aids in monitoring disease progression and treatment response. Complications related to retinal vein occlusion, such as cystoid macular edema, neovascularization, vitreous hemorrhage, neovascular glaucoma, and detachment of the retina, further emphasize the need for precise diagnosis and prompt intervention. We are here to help you through this process, ensuring you receive the care and support you need.
Review Treatment Options for Retinal Vein Occlusion
Treatment for retinal vein occlusion focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. We understand that navigating these options can feel overwhelming, but several effective treatments are available to support you:
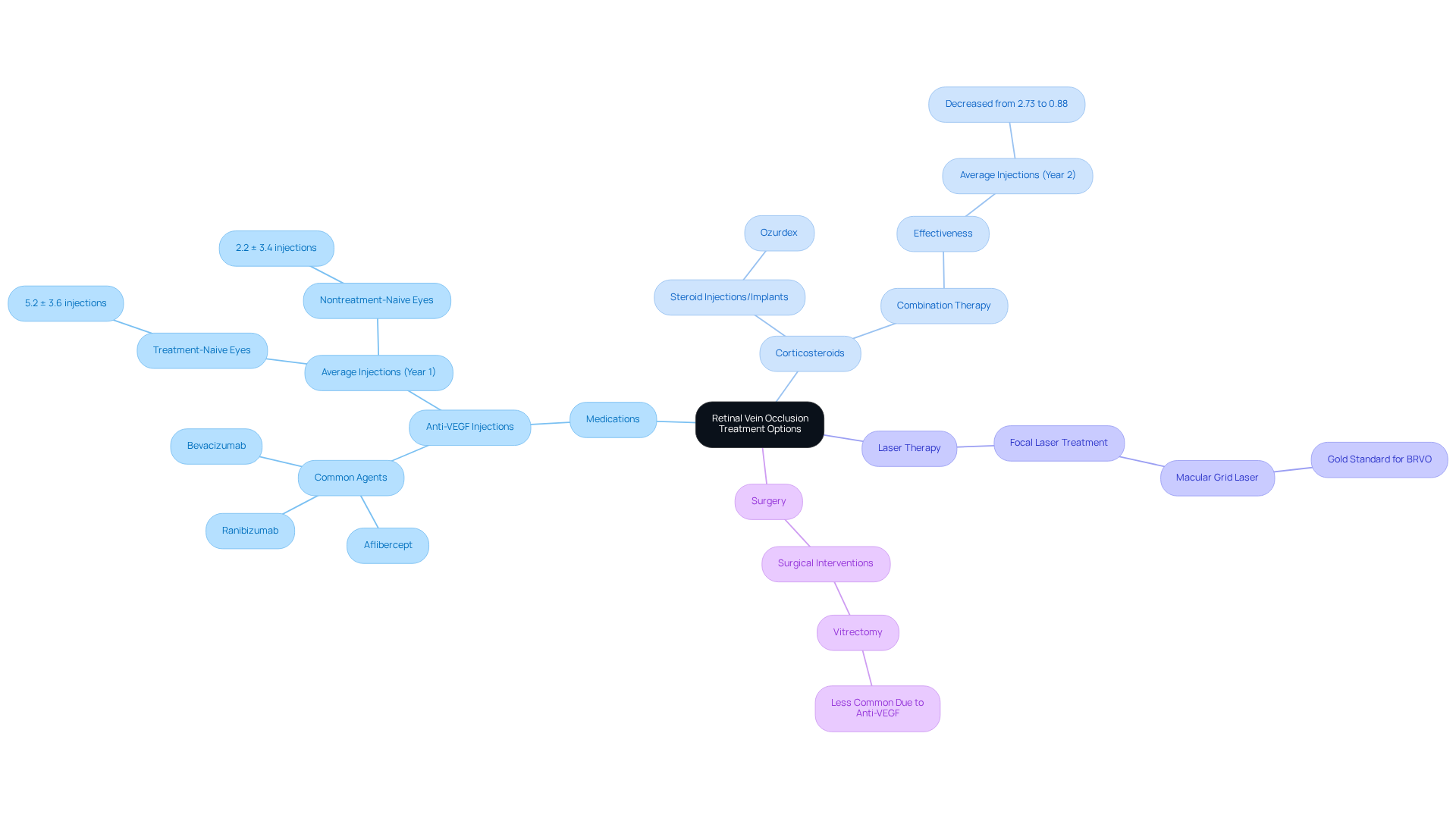
- Medications: Anti-VEGF injections, such as aflibercept and ranibizumab, are commonly employed to reduce retinal swelling and enhance visual acuity. In real-world settings, the average number of anti-VEGF injections for treatment-naive eyes is approximately 5.2 ± 3.6 in the first year. This demonstrates their critical role in managing retinal vein occlusion, and we want you to know that these treatments can make a significant difference in your vision.
- Corticosteroids: Steroid injections or implants, like Ozurdex, help mitigate inflammation and swelling in the retina. Recent studies indicate that combination therapy, involving both anti-VEGF agents and corticosteroids, can be particularly effective for patients experiencing persistent macular edema after multiple anti-VEGF treatments. The average number of intravitreal injections per person decreased from 2.73 to 0.88 in the second year, reflecting improved patient outcomes. We are here to support you in finding the best approach for your needs.
- Laser Therapy: Focal laser treatment remains a viable option for addressing complications such as macular edema, especially in cases where anti-VEGF injections alone are insufficient. The Branch Vein Occlusion Study established macular grid laser as a gold standard for treating macular edema due to branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO). It’s common to feel uncertain about these options, but we’re here to guide you.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to restore blood flow or address significant complications. While surgical options like vitrectomy have become less common due to the effectiveness of , they may still be considered in specific scenarios where initial treatments are inadequate. Remember, we are here to help you through this process and discuss all available options.
The selection of treatment is tailored to the type of retinal vein occlusion, the severity of symptoms, and your overall health. Regular follow-up with an eye care professional is crucial for monitoring progress and adjusting treatment strategies as needed. As noted by specialists, “Our results are in line with other real-world studies…” indicating that the treatment intensity often decreases significantly in the second year. This reflects improved patient outcomes and the effectiveness of initial therapies, reassuring you that progress is possible.
Conclusion
Understanding retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is essential for anyone concerned about their eye health. We recognize that this condition, characterized by the blockage of veins in the retina, can lead to significant vision impairment if not addressed promptly. By recognizing the types of RVO—namely Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) and Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)—along with their symptoms and treatment options, you can take proactive steps in managing your eye health.
This article outlines the critical aspects of RVO, including its causes such as:
- Age
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Other risk factors
It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but recognizing symptoms like:
- Blurred vision
- Floaters
- Blind spots
can empower you to seek help. Furthermore, the diagnostic methods, including comprehensive eye exams and advanced imaging techniques, clarify how eye care professionals assess the condition. Treatment options, ranging from anti-VEGF injections to laser therapy, illustrate the advancements in managing RVO effectively.
Ultimately, awareness and education play a crucial role in combating retinal vein occlusion. Regular eye exams and a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. We encourage you to seek professional medical advice if you experience any concerning symptoms. By prioritizing your eye health and staying informed about RVO, you can safeguard your vision and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is retinal vein occlusion (RVO)?
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is a serious condition that occurs when a vein in the retina becomes blocked, potentially leading to significant vision impairment.
What are the two main types of retinal vein occlusion?
The two main types of RVO are Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO), which involves blockage of the main vein in the eye, and Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO), which involves blockage in one of the smaller branches of the retinal vein.
What are the symptoms of Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)?
Symptoms of CRVO may include blurred vision, floaters, discomfort in the eye, swelling, and bleeding. These symptoms often prompt individuals to seek medical help.
How common is Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)?
The age- and sex-standardized prevalence of CRVO is about 0.80 per 1000 persons, particularly affecting older adults.
What are the symptoms and prevalence of Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)?
BRVO typically causes less severe vision loss than CRVO but can still lead to significant complications if untreated. It accounts for approximately 84% of retinal vein occlusion cases, with a prevalence of around 4.42 per 1000 persons.
What treatments are available for CRVO?
Treatments for CRVO may include anti-VEGF injections, which have shown promising results in managing complications and preserving vision.
What are the common risk factors for developing retinal vein occlusion?
Common risk factors include age (especially over 60), hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, glaucoma, obesity, and certain blood disorders.
How does hypertension contribute to retinal vein occlusion?
Hypertension is a significant contributor to RVO, attributed to approximately 48% of cases. It damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blockages.
Why is it important to recognize the symptoms and risk factors of retinal vein occlusion?
Recognizing symptoms like blurred vision and understanding risk factors encourages timely medical attention and regular eye examinations, which are crucial for early detection and management of RVO.
What steps can individuals take to lower their risk of developing RVO?
Individuals can lower their risk by maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, avoiding tobacco products, and scheduling regular eye exams for early detection and management of eye health issues.






