Posted by: Northwest Eye in General on October 7, 2025
Overview
This article aims to help you understand corneal erosion, a condition that can be quite concerning. We recognize that experiencing corneal erosion can be sudden or a recurring issue, often linked to trauma, corneal dystrophies, and other risk factors. It’s common to feel anxious about the symptoms and what they mean for your health.
Understanding the causes and treatment options is crucial. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment can significantly improve your recovery outcomes. We want to reassure you that you are not alone in this journey; many have faced similar challenges and found effective solutions.
Remember, seeking care promptly can make a difference. We are here to help you through this process and ensure you receive the support you need.
Introduction
Understanding corneal erosion is vital for anyone concerned about eye health. This condition can lead to significant discomfort and complications if left untreated. We understand that it can be worrying to think about the health of your eyes. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for corneal erosion, offering you valuable insights into managing this common eye issue.
It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the various factors contributing to its onset and recurrence. So, how can you effectively recognize and respond to the signs of corneal erosion before it escalates into a more serious problem? We are here to help you through this process.
Define Corneal Erosion and Its Types
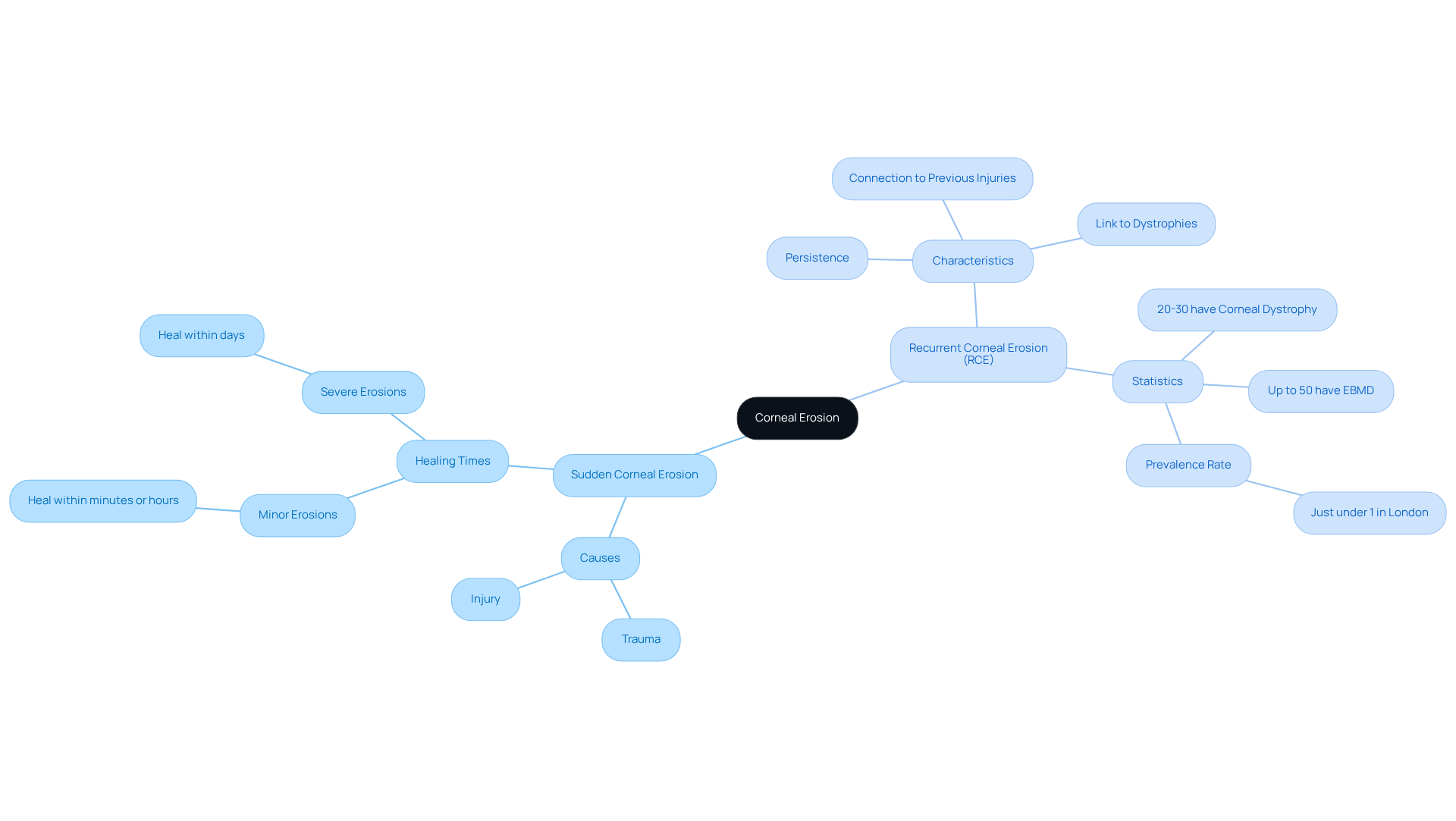
Corneal erosion refers to the damage that results in the loss of the outer layer of the cornea, known as the epithelium. We understand that this condition can be concerning, and it can manifest in two primary types:
- Corneal erosion occurs suddenly, often due to trauma or injury, such as scratches from fingernails or foreign objects. Minor eye surface erosions may heal within minutes or hours, while more severe cases may take days to recover. It’s common to feel anxious about sudden changes in your vision, but rest assured, help is available.
- Recurrent corneal erosion (RCE) is a persistent issue characterized by the epithelium’s failure to adhere properly to the underlying layers, resulting in repeated episodes of pain and discomfort. Corneal erosion (RCE) is frequently linked to prior injuries or underlying eye surface dystrophies, such as epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD). Research shows that approximately 20-30% of individuals with corneal erosion (RCE) experience some form of , and up to 50% of those with corneal erosion (RCE) have EBMD. This emphasizes the important connection between these conditions and the need for understanding.
Comprehending these categories is crucial for efficient diagnosis and treatment. Prompt intervention can greatly enhance outcomes and lessen the likelihood of complications. For example, surgical alternatives such as diamond burr superficial keratectomy are intended to tackle ongoing abrasions by improving adhesion of the eye’s outer layer, removing damaged tissue, or smoothing the surface of the eye. We want you to know that thorough management approaches can make a significant difference.
As noted by experts, “If you think you have an RCE, getting treatment early is the best plan of action.” Additionally, the prevalence of RCE is notable, affecting just under 1% of the population based on a five-year study of emergency patients at a London specialty eye hospital. Remember, we are here to help you through this process and ensure you receive the care you need.
Identify Causes and Risk Factors of Corneal Erosion
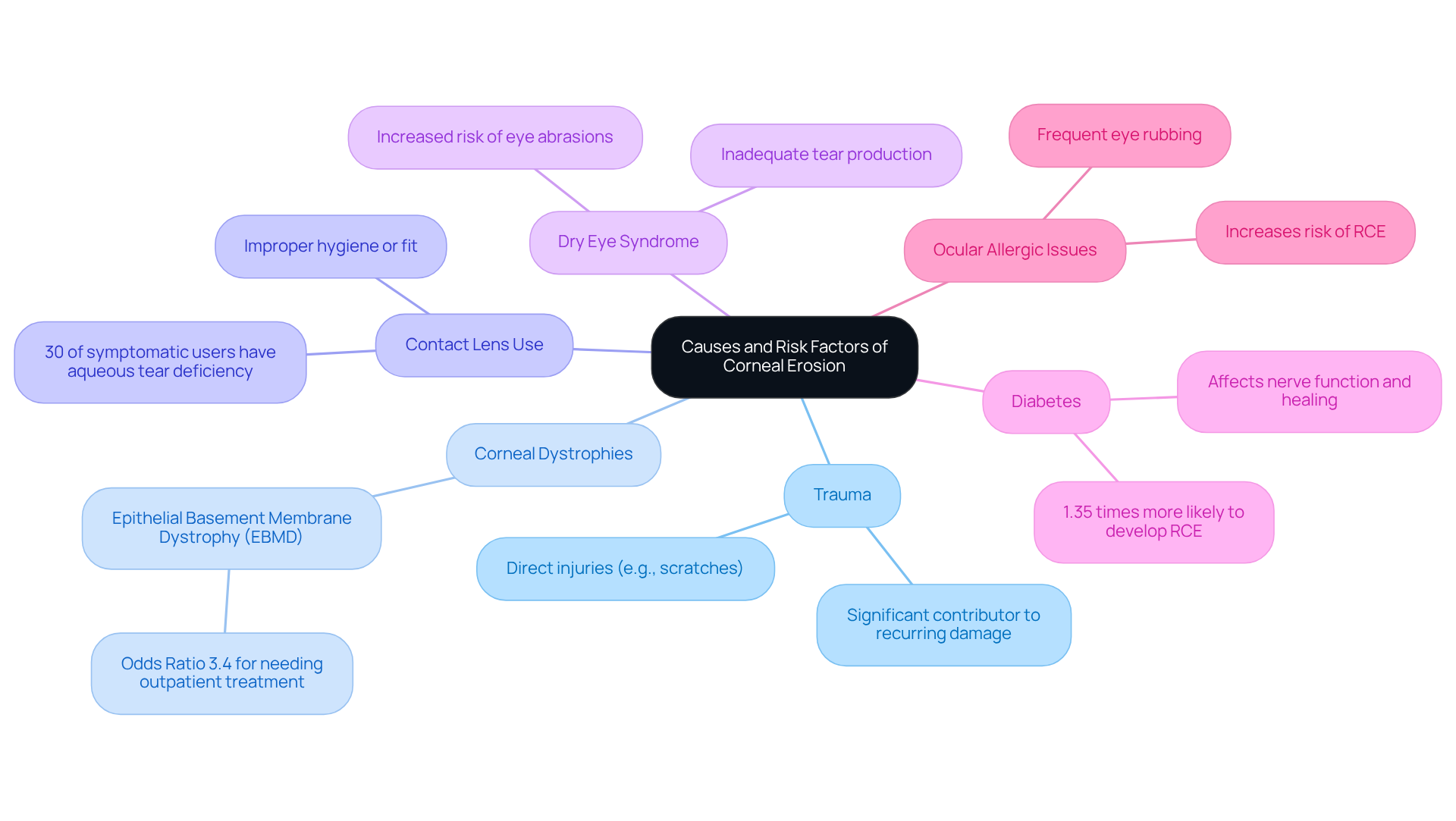
A variety of causes and risk factors can lead to corneal erosion, and we understand that this can be concerning. Here are some key contributors to keep in mind:
- Trauma: Direct injuries to the eye, such as scratches from fingernails or foreign bodies, are significant contributors to corneal erosion. Research shows that trauma contributes to a substantial portion of recurring eye surface damage cases, highlighting the necessity for protective measures.
- Corneal Dystrophies: Genetic conditions like epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) weaken the cornea’s structural integrity, resulting in poor epithelial adhesion and a heightened risk of damage. Studies indicate that individuals with EBMD have a greater chance of experiencing recurrent surface damage syndrome (RCES), with an odds ratio of 3.4 for needing outpatient treatment.
- Contact Lens Use: We recognize that improper hygiene or fit of contact lenses can lead to abrasions and damage. Recent findings indicate that 30% of symptomatic soft contact lens users suffer from aqueous tear deficiency, which can worsen surface damage to the eye.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: Inadequate tear production can significantly affect the surface of the eye, making it more vulnerable to damage. Individuals with dry eye issues frequently mention heightened discomfort and a greater occurrence of eye abrasions.
- Diabetes: Diabetes is a systemic issue that affects nerve function and healing processes, increasing the risk of corneal erosion. Studies have shown that diabetic patients are 1.35 times more likely to develop RCE compared to non-diabetic individuals, underscoring the importance of managing diabetes to mitigate ocular complications.
- Ocular Allergic Issues: These issues can lead to frequent eye rubbing and associated ocular surface injuries, significantly increasing the risk of RCE.
Identifying these risk factors is essential for prevention and prompt treatment, enabling improved management of eye health. It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but understanding these factors can empower you. The estimated crude annual incidence of RCES is 25.4 per 100,000 people, with a prevalence rate of 0.96%, underscoring the commonality of this condition. We are here to .
Recognize Symptoms of Corneal Erosion
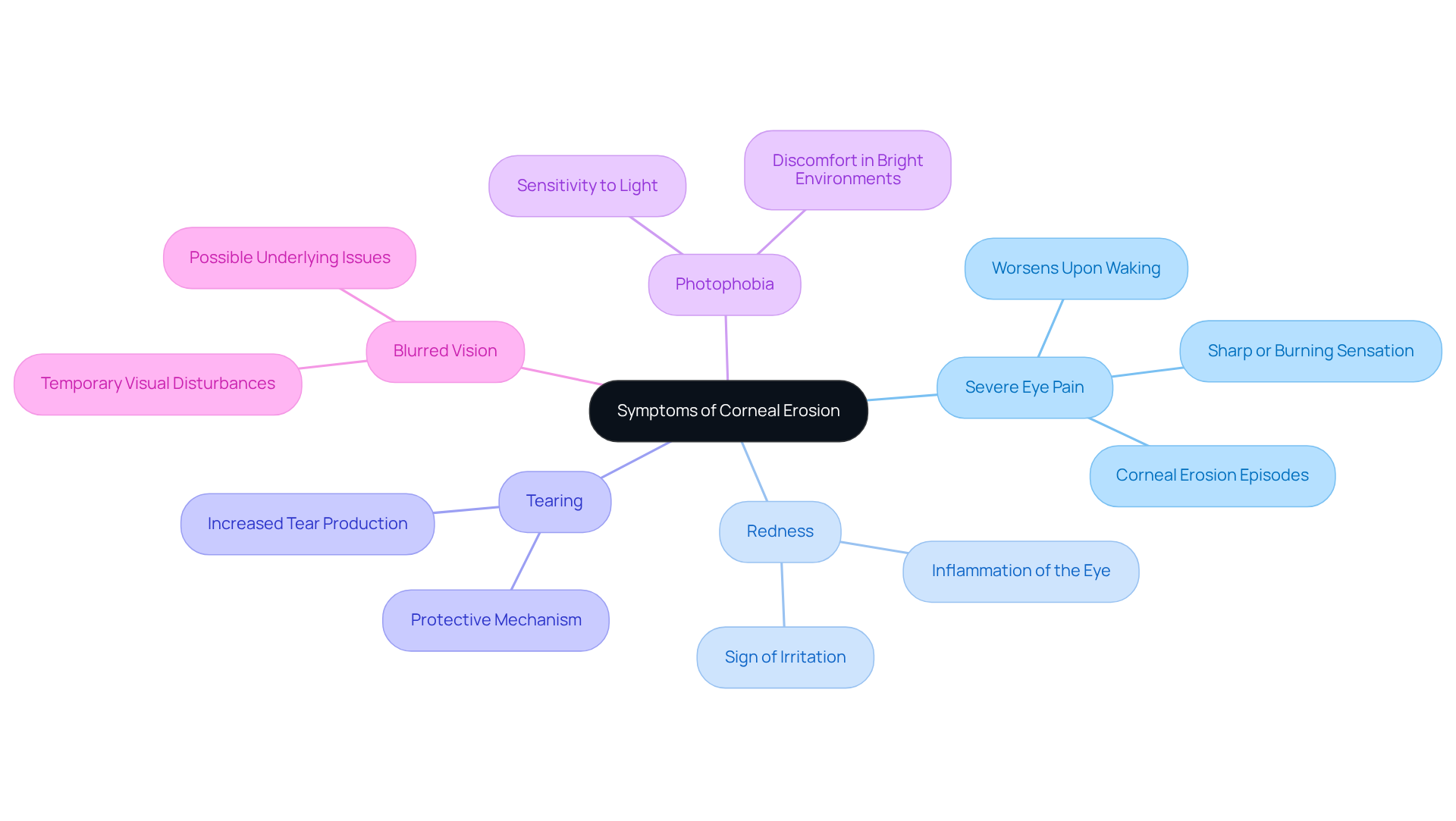
Indicators of eye surface damage can vary significantly in severity, and we understand that some individuals may experience intense symptoms. Key symptoms to be aware of include:
- Severe Eye Pain: This pain is often described as sharp or burning, particularly pronounced upon waking. Episodes of recurrent damage to the eye surface can lead to corneal erosion, which may cause sudden eye pain, tearing, and light sensitivity, especially in the morning.
- Redness: The affected eye may appear red and inflamed, signaling irritation and potential harm to the surface of the eye.
- Tearing: Increased tear production is common as the eye seeks to heal itself, serving as both a protective mechanism and a source of discomfort.
- Photophobia: Sensitivity to light is frequent among those with corneal erosion, making bright environments particularly uncomfortable.
- Blurred Vision: Temporary visual disturbances may occur during episodes of corneal erosion, complicating daily activities and possibly indicating underlying issues such as cataracts or diabetic retinopathy.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for facilitating . For instance, a study highlighted that 39.8% of individuals with a history of trauma reported recurrent corneal erosion (RCE), underscoring the importance of understanding the triggers of corneal erosion. Eye care professionals emphasize that early diagnosis and treatment of corneal erosion can significantly improve recovery outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. As one expert noted, ‘Early diagnosis and treatment will give you the best odds of a fast recovery and preventing future occurrences.’
We encourage you to be aware of these symptoms, as they can empower you to seek assistance promptly, ensuring better management of your eye health. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, we are here to help you through this process—please schedule an appointment with a Northwest Eye doctor for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment options.
Explain Diagnosis of Corneal Erosion
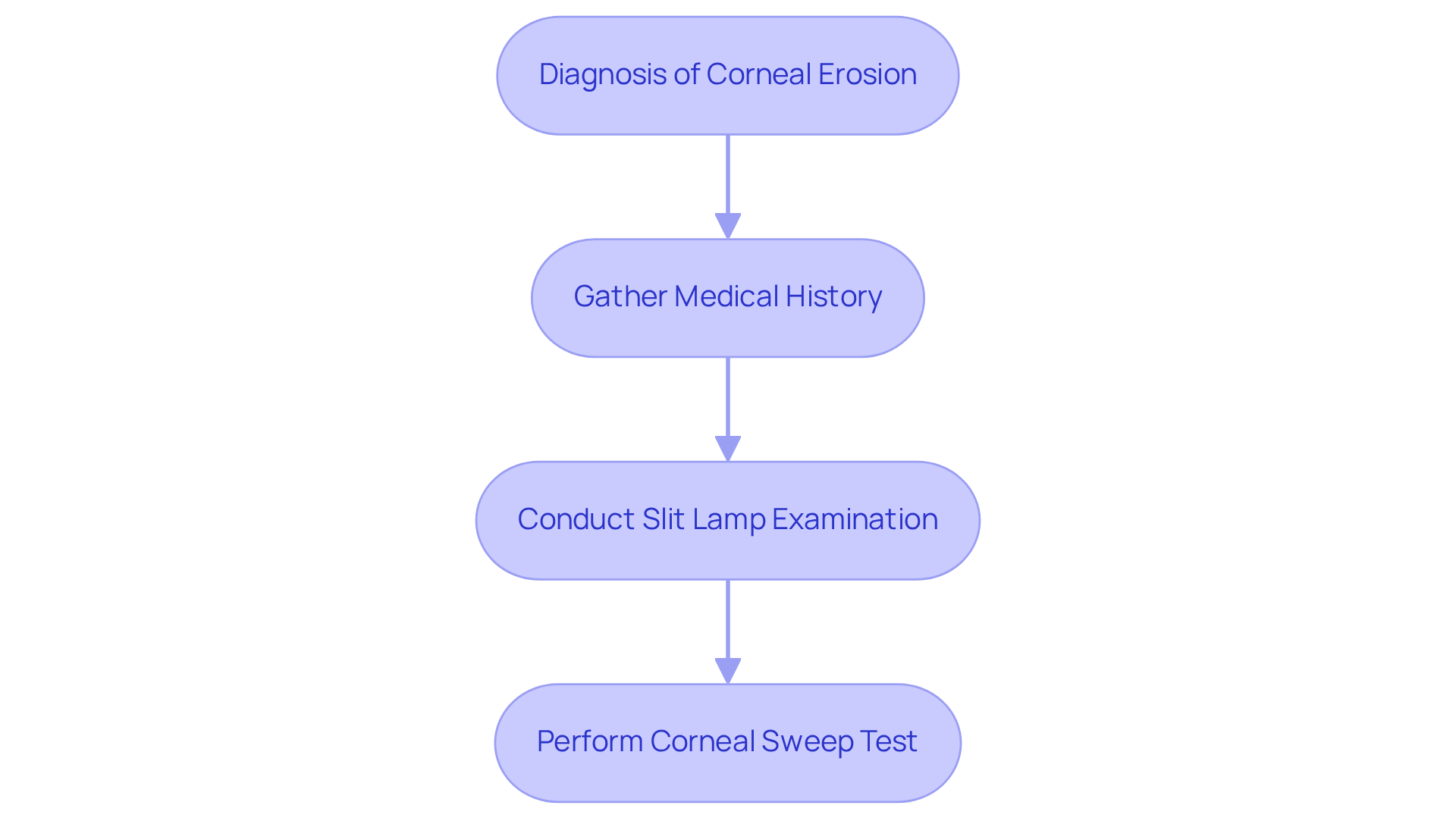
Diagnosing corneal erosion necessitates a thoughtful approach, and we want to ensure you feel supported throughout this process. Here are several key steps that can help guide your journey:
- Medical History: We begin by gathering comprehensive information about your symptoms, any past eye injuries, and underlying health conditions. This history is crucial, as many individuals report that their symptoms began after eye surgeries, particularly clear cataract operations. In fact, 71.4% of those who underwent clear corneal cataract surgery noticed their symptoms only after the procedure. This highlights the importance of a detailed patient history in diagnosing corneal erosion.
- Slit Lamp Examination: This essential diagnostic tool allows for a thorough examination of your cornea. During this process, fluorescein dye is often applied to make areas of degradation more visible. Recent advancements in slit lamp technology have improved the precision of these examinations, enabling ophthalmologists to identify even subtle damages that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Corneal Sweep Test (CST): As a newer diagnostic method, the CST is particularly beneficial for detecting damage that may not be apparent through conventional examination techniques. Studies indicate that this test can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy, especially when patients experience ongoing ocular discomfort without visible eye surface pathology. Remarkably, 58.6% of all eyes tested revealed hidden surface damage, underscoring the importance of the CST. D.B.K. noted that the CST is a safe and effective tool for identifying areas of loose epithelium, which can greatly assist in diagnosis.
These diagnostic steps are vital for confirming the presence of corneal erosion and guiding the selection of appropriate treatment options. By integrating patient history, advanced imaging techniques, and innovative tests like the CST, we are committed to improving patient outcomes. We understand that this process can feel overwhelming, but rest assured, we are here to .
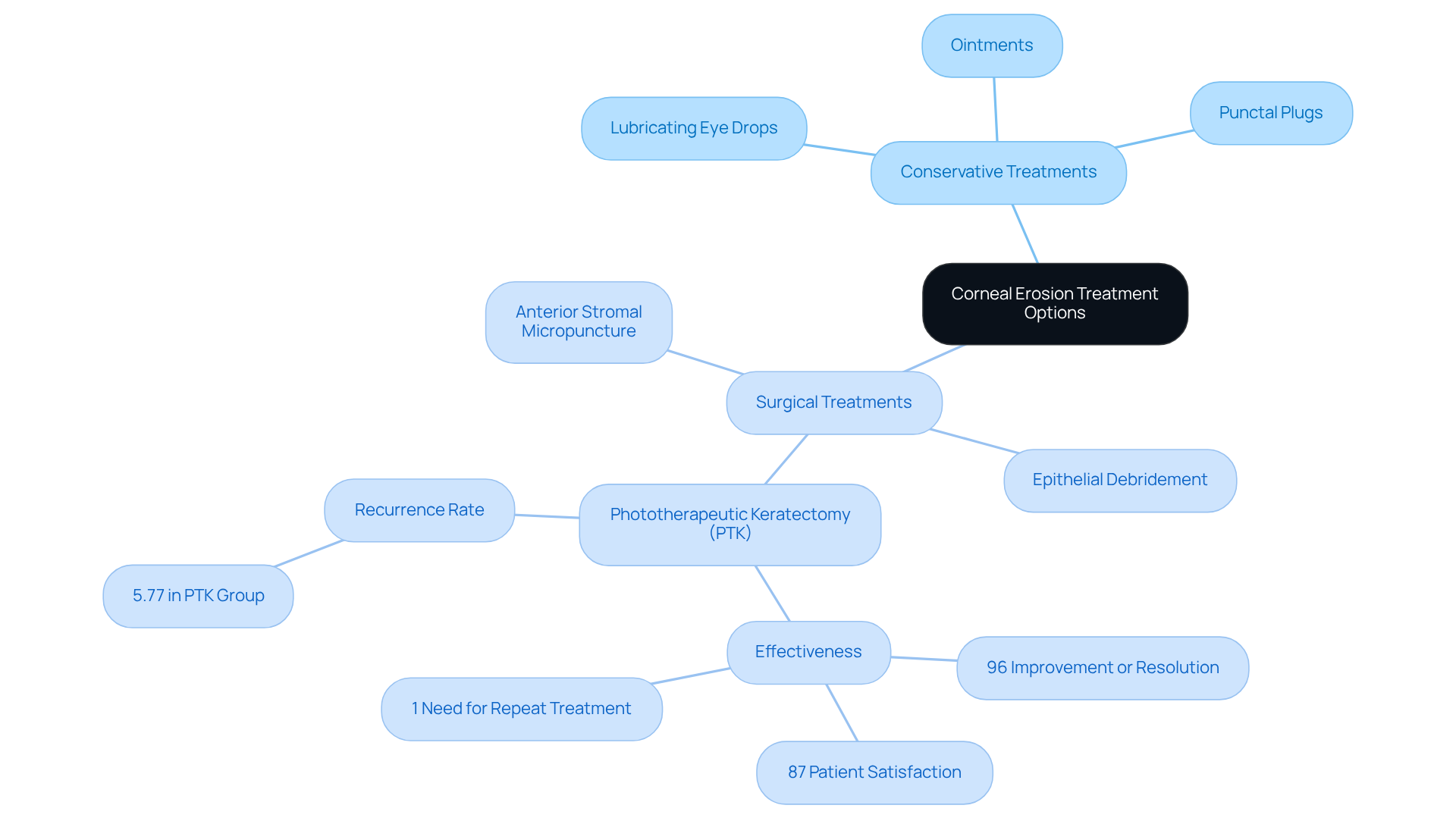
Explore Treatment Options for Corneal Erosion
The can differ depending on the severity and frequency of the episodes. We understand that navigating these choices can feel overwhelming, and we are here to help you through this process.
-
Conservative Treatments:
- Lubricating Eye Drops: Frequent use of artificial tears can help keep the cornea moist, providing comfort throughout the day.
- Ointments: Hypertonic ointments may be prescribed to promote healing overnight, offering relief while you sleep.
- Punctal Plugs: These can help retain tears and reduce dryness, ensuring your eyes feel more comfortable.
-
- Epithelial Debridement: This involves the removal of the damaged epithelium to promote healing, which can be a crucial step in your recovery.
- Phototherapeutic Keratectomy (PTK): A laser procedure that can smooth the corneal surface, helping to restore clarity and comfort.
- Anterior Stromal Micropuncture: This technique is designed to improve epithelial adhesion, supporting your healing journey.
Each treatment plan should be tailored to you, considering your specific symptoms and medical history. Remember, it’s common to feel uncertain about these options, but we are here to provide the support and guidance you need.
Conclusion
Corneal erosion is a significant eye condition that can lead to discomfort and vision issues if not properly understood and managed. We understand that experiencing this condition can be distressing, and it’s essential to recognize its different types, including sudden occurrences and recurrent cases. Seeking timely treatment is crucial, and understanding the causes and risk factors—such as trauma, corneal dystrophies, and underlying health conditions—can empower you in effective prevention and management.
Key insights include:
- The necessity of early diagnosis through a comprehensive medical history and advanced diagnostic tests like the corneal sweep test.
- Treatment options vary, ranging from gentle, conservative measures like lubricating eye drops and ointments to more invasive procedures such as epithelial debridement and laser treatments. Each approach should be personalized based on your unique symptoms and medical history, ensuring that you feel supported throughout the process.
Ultimately, being aware of corneal erosion and proactively managing it can significantly enhance your eye health and quality of life. If you are experiencing symptoms, we encourage you to seek professional evaluation and explore treatment options tailored to your specific needs. By addressing corneal erosion early, it is possible to mitigate discomfort and prevent future episodes, ensuring better long-term outcomes for your eye health. Remember, we are here to help you through this process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is corneal erosion?
Corneal erosion is the damage that results in the loss of the outer layer of the cornea, known as the epithelium. It can occur suddenly due to trauma or injury.
What are the two primary types of corneal erosion?
The two primary types are sudden corneal erosion, which occurs due to trauma or injury, and recurrent corneal erosion (RCE), which is characterized by repeated episodes of pain and discomfort due to the epithelium’s failure to adhere properly to the underlying layers.
How quickly can minor corneal erosions heal?
Minor eye surface erosions may heal within minutes or hours, while more severe cases may take days to recover.
What is recurrent corneal erosion (RCE)?
RCE is a persistent condition where the epithelium fails to adhere properly to the underlying layers, leading to repeated episodes of pain and discomfort. It is often linked to prior injuries or underlying eye surface dystrophies, such as epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD).
What percentage of individuals with RCE have underlying eye surface dystrophies?
Approximately 20-30% of individuals with RCE experience some form of eye surface dystrophy, and up to 50% of those with RCE have EBMD.
What are some common causes of corneal erosion?
Common causes include trauma (such as scratches), corneal dystrophies (like EBMD), improper contact lens use, dry eye syndrome, diabetes, and ocular allergic issues.
How does diabetes affect the risk of corneal erosion?
Diabetes affects nerve function and healing processes, increasing the risk of corneal erosion. Diabetic patients are 1.35 times more likely to develop RCE compared to non-diabetic individuals.
What is the estimated incidence of recurrent corneal erosion syndrome (RCES)?
The estimated crude annual incidence of RCES is 25.4 per 100,000 people, with a prevalence rate of 0.96%.
What treatment options are available for corneal erosion?
Treatment options can include surgical alternatives like diamond burr superficial keratectomy, which aims to improve adhesion of the eye’s outer layer, remove damaged tissue, or smooth the surface of the eye.
Why is early treatment important for recurrent corneal erosion?
Early treatment is important because it can significantly enhance outcomes and reduce the likelihood of complications associated with RCE.






